decision-making process
What is a decision-making process?
A decision-making process is a series of steps one or more individuals take to determine the best option or course of action to address a specific problem or situation. Often, managers and executives use the process to plan how to carry out business initiatives or set specific actions in motion. Ideally, a business decision is based on the analysis of objective facts, aided by the use of artificial intelligence (AI) or other advanced technologies and tools.
7 steps of the decision-making process
When planning a strategy or initiative or when responding to an issue or threat, decision-makers must frequently choose from multiple options. There are a variety of alternatives to weigh and a large volume of decisions that must be made on an ongoing basis. This makes the implementation of an effective decision-making process a crucial element of managing business operations successfully.
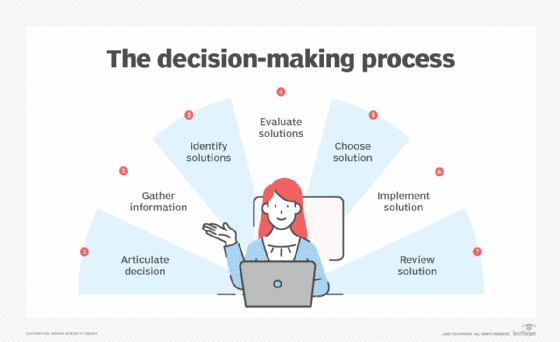
Decision-making processes vary in terms of the number of steps they include and what each step accomplishes. The process usually involves these seven steps or similar steps:
1. Articulate the decision to be made. The decision-making team should clearly identify the decision it's attempting to make. Everyone on the team should fully understand the circumstances surrounding the decision and what they're trying to achieve by making this decision. There should be no ambiguity about the problem or situation involved. The more precisely the team can articulate the decision and why it should be made, the easier it will be to proceed with the rest of the decision-making process and the better the outcome.
2. Gather relevant information. Once the decision has been defined, the team should gather all pertinent information. It might seek historical data related to the issue or track down information about similar efforts in the organization that have either succeeded or failed. It should gather relevant information from outside the organization, such as studies or market research. The team might also benefit from talking to external colleagues in similar circumstances or perhaps hiring a consultant.
3. Identify possible solutions. Armed with the necessary information, the team can start identifying potential options for addressing its situation. The team might need to determine how it's going to expand storage capacity for the coming year, for example. Possible solutions could include purchasing new storage systems, expanding into the cloud, repurposing existing systems, leasing equipment, or other options. This is a good time for creative thinking and brainstorming, although the final list of solutions should include only the most viable ones.
4. Evaluate the possible solutions. The team should carefully evaluate each possible solution, identifying both its strengths and weaknesses. It should also look within and without the organization for examples of how similar solutions have fared. In certain cases, the team might eliminate some alternatives here because of obvious problems or overriding challenges. The team's evaluation should also include an assessment of how a particular solution might impact key stakeholders and implementation requirements.
5. Choose the best solution. After evaluating the potential solutions, the team should decide on which one would best suit its needs. Sometimes, the choice will be straightforward and one solution will have percolated up to the top of the list. In other cases, the choice will not be so clear-cut and the team will need to weigh the tradeoffs between several promising solutions. That said, the team might find that the best decision is to combine several of the alternatives into one overarching solution.
6. Implement the selected solution. Once the decision is made, it's time to act. The team should develop a detailed implementation plan, designating responsibilities specifically. Every decision has consequences; the planning should account for possible challenges and identify a process for handling unexpected setbacks. Open communication is essential, along with clearly defined roles and expectations.
7. Review the implemented solution. Once the solution is implemented, the team should evaluate its implementation and the decision to select that solution. The team should ensure the solution addresses the original issue. If it does not, the team might need to repeat at least part of the decision-making process. The team should evaluate whether another alternative might have proven better. This is also a good time to review the entire decision-making process to determine what worked and where the process could be improved so future decision-making can be more streamlined and effective.
What is a decision-making model?
A decision-making model is a system or process that individuals can follow or imitate to ensure they make the best choice among various options. A model makes the decision-making process easier by providing guidelines to help businesses reach a beneficial conclusion.
Decision models also make the decision-making process visible and easily communicable for everyone involved, including managers, employees and other stakeholders. Models can support a wide variety of purposes across departments, businesses and industries, but they are especially useful when selecting software vendors or new tools, choosing new courses of action, or when implementing changes that affect many people.
Types of decision-making models
Decision-making models often incorporate, consolidate or expand on the seven decision-making steps described previously. The exact approach will depend on the model and individuals implementing those models. Common types of decision-making models include the following:
Rational model. Rational decision-making is the most popular model. Logical and sequential, it focuses on listing as many alternative courses of action as possible. Once all options are laid out, they can be evaluated to determine which is best. This model often includes pros and cons for each choice, with the options listed in order of their importance.
A rational decision-making model typically includes these steps:
- Identify the problem or opportunity.
- Establish and weigh decision criteria.
- Collect and organize all related information.
- Analyze the situation.
- Develop a variety of options.
- Assess all options and assign a value to each one.
- Decide which option is best.
- Implement the decision.
- Evaluate the decision.
Intuitive model. This type of decision-making relies more on experience and accumulated knowledge than on formalized decision-making steps like those in the rational model. The intuitive model depends heavily on an inner knowing -- or intuition -- about what the right option is. However, this approach is not based solely on gut feelings. It also incorporates unconscious behavior such as pattern recognition or similarity recognition, while considering the importance or prominence of an option.
Recognition primed decision (RPD) model. This model is a combination of rational and intuitive decision-making. Its defining element is that the decision-maker considers only one option instead of weighing all. This model is often used in situations that call for an immediate decision.
The RPD process involves these steps:
- Identify the problem, including all its characteristics, problem cues, expectations and business goals.
- Think through the plan and perform a mental simulation to see if it works and what modifications might be needed.
- If the plan seems satisfactory, make the final decision and implement the plan.
In the RPD model, alternative courses of action are considered only if the original plan does not produce the intended results. The success rate of this model correlates to the decision-maker's experience and expertise.
Creative model. In this model, decision-makers collect information and insights about the problem and develop initial possible solutions. Then, they enter an incubation period where they do not actively think about the options. Instead, they allow their unconscious to take over the process in hopes that it will eventually lead them to a realization and answer, which they can then test and finalize.
When to use decision-making models
Even when rules and procedures are set up for more systematic decision-making, intuition can still play a role for decision-makers. For example, after gathering data about possible solutions, they might find that several offer similar advantages or that they lack the information needed to make a decision with sufficient confidence. This is a good use case for incorporating an intuitive decision-making model.
Decisions that occur frequently and have clear optimal outcomes often benefit from structured, rational decision-making models. A rational approach uses clearly prescribed steps -- often with the help of data analytics software -- to evaluate the options and arrive at a decision.
An organization can sometimes benefit by involving more people in the decision-making process, an approach known as participatory decision-making. For example, managers might seek input and feedback on decisions from the workers they oversee. This approach could potentially offer new and innovate ideas for solving a problem, while helping to engage employees.
Data-driven decision-making
Traditionally, business managers or corporate executives made decisions using their intuitive understanding of the situation. However, intuitive decision-making has several drawbacks. For example, a gut-feeling approach makes it hard to justify decisions after the fact. It also bases enterprise decision-making on the experience and accumulated knowledge of individuals, who can be vulnerable to cognitive biases that lead to bad decisions.

Today, businesses typically take more systematic, data-driven approaches to the decision-making process. In this way, managers and executives can use techniques such as cost-benefit analysis and predictive modeling to justify their decisions. It also enables lines of business to build process automation protocols that can be applied to new situations as they arise, removing the need for each decision to be handled as a unique event.
If designed properly, a data-driven, systematic decision-making process reduces the possibility that the biases and blind spots of individuals will yield poor decisions. On the other hand, data isn't infallible. Observing a decision's business impact is a crucial step in case things go wrong. The potential for humans to choose the wrong data also highlights the need for monitoring the analytics and decision-making stages rather than blindly going where the data is pointing.
Challenges in the decision-making process
Balancing data-driven and intuitive approaches to decision-making is not easy. Managers and executives might be skeptical about making decisions that rely on data if that data goes against their intuition. They might also feel that their experience and knowledge are being discounted or ignored. As a result, they might push back against the findings of business intelligence (BI) and analytics tools during the decision-making process.

Getting everyone on board with business decisions can also be a challenge, particularly if the decision-making process isn't transparent and decisions aren't explained well to the affected parties. An organization should implement a policy for how decisions should be communicated internally and put into place a change management strategy to deal with the effects of decisions on business operations when warranted.
Decision-making models can also be used to avoid these challenges by creating a structured, transparent process.
Decision management
Decision management -- also known as enterprise decision management or business decision management -- aims to improve the decision-making process by using all available information to increase the precision, consistency and agility of decisions. Decision management also focuses on making good choices by taking known risks and time constraints into consideration.
Decision models and decision support systems are key elements of decision management. Decision management processes also use business rules, business intelligence, continuous improvement, artificial intelligence and predictive analytics to access the capabilities of big data and support demanding operational requirements as well as user expectations.
Decision management systems treat decisions as reusable assets and introduce technology at decision points to automate the decision-making process. Decisions might be fully automated, or they might be presented as possible choices for someone to select.
Increasingly, organizations that deal with financial services, banking and insurance are integrating decision-making software into their business process systems and customer-facing applications. This approach is especially useful for high-volume decision-making because automating such decisions can enable more efficient, information-based and consistent responses to events such as potential security threats.
Using the right strategies is a crucial key to unlocking the benefits of real-time analytics and empowering organizations with agile data-driven decision-making. See how to empower decision-making with real-time insights.







