laptop
What is a laptop?
A laptop, sometimes called a notebook computer by manufacturers, is a battery- or AC-powered personal computer (PC) smaller than a briefcase. A laptop can be easily transported and used in temporary spaces such as on airplanes, in libraries, temporary offices and at meetings.
A laptop can be turned into a desktop computer with a docking station, which is a hardware frame that supplies connections for peripheral input/output devices such as a monitor, keyboard and printer.

Types of laptops
Differences in these core components are what distinguish laptop computers. Some core characteristics of laptops are the following:
- Size. One of the key points of a laptop is portability. Smaller laptops are lightweight and easier to carry. A bigger laptop offers a bigger screen size.
- Screen resolution. Higher resolution liquid crystal display or LCD screens display sharper graphics and increase the usable viewing area. High pixel density displays are becoming increasingly popular.
- Processing power. Laptop processors have two, four or eight cores and, because of that, vary in performance.
- Memory. Typically, laptop random access memory (RAM) is 4, 8 or 16 GB. The most common RAM is 8 GB, and memory is often soldered to the motherboard.
- Input. Laptops often have a built-in microphone, video camera and various input ports, such as Lightning, HDMI and USB ports. Some companies have gradually reduced the number of ports on the laptop body. Laptops use several different approaches for integrating a mouse into the keyboard, including touch pads, trackballs and pointing sticks.
- Durability. Laptops vary in durability; some are designed for use in rugged conditions.
- Design. Laptop designs and accompanying marketing terms vary. Notebooks, netbooks and subnotebook types denote different laptop sizes. New laptops, such as hybrid and convertible ones, feature displays that detach from the computer and function as touchscreen tablets.
- Accessories. Various laptop accessories -- such as a detachable keyboard or a second touchpad -- can influence purchasing decisions.
- Battery life. Laptops are battery-powered, as well as having power adapters to plug into a power source. Batteries vary among laptops, and battery life can also influence buyers.
Users buy different types of laptops for different purposes. A gaming laptop might require higher resolution and processing power, whereas a good laptop for business might be lightweight for traveling and have more memory. A laptop for use in field service might need to be more durable.

Laptop features and characteristics
Laptops come with the following components:
- Power supply. The laptop's internal power supply recharges the computer's rechargeable battery.
- Central processing unit (CPU). The CPU handles the main processing tasks for the computer and dictates the computer's performance.
- Graphics processing unit (GPU). The GPU is a special type of processor that accelerates graphics processing.
- RAM. The RAM is the computer's short-term memory. It only holds data when the computer is powered on.
- Storage. Storage is the laptop's long-term memory and holds data when the computer does not have electricity.
- I/O ports. These serial ports let users plug in external devices such as displays, optical mouses and external storage.
- Display. The display provides a screen where users can see the graphical user interface (GUI). Laptop displays usually are connected by hinges to the bottom half of the computer.
- Keyboard and touchpad. These parts of the laptop let the user communicate with the computer and are usually embedded in the body of the laptop.
- Operating system. The OS provides a GUI that enables the user to interact with computer.
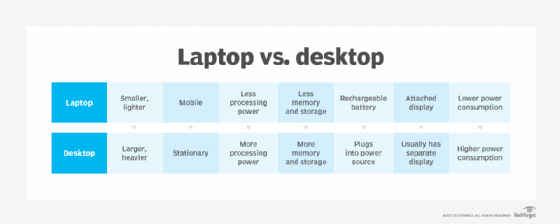
The difference between laptops and desktops
Desktops and laptops are two different types of PCs. They are used for the same basic functions but have significant differences in design.
Laptops are designed to be portable computers. They are smaller and lighter than desktops. The name connotes the user's ability to put the computer in their lap while they use it.
Laptops have rechargeable batteries that can be used for a set period away from a power source. The display screen hinges up from the body of computer to open. Laptops are generally lower in energy consumption than desktop computers.
Desktops are designed to be stationary and often reside on a desk. Desktops must be plugged in to a power source to be used. Unlike laptops, the display screen is usually separate from the computer, although this is not always the case.
Because desktops are generally bulky, stationary items, they may come with features that laptops don't. An example is a compact disc drive: Many laptops no longer include a disk drive, whereas desktops do.
History of laptops
Some landmark events in the development of laptops include the following:
- 1981. The first mobile computer, the Osborne I, was introduced. It had a 5-inch screen and opened on a hinge just like modern laptops. It was considered a luggable, or a computer that had to be lugged around. It was the size of a portable sewing machine and weighed 24 pounds.
- 1983. The first laptop marketed using the term laptop was the Gavilan SC. The first laptop with a color display was the Commodore SX-64.
- 1991-1992. The Apple PowerBook in 1991 and IBM ThinkPad in 1992 helped establish de facto laptop standards, such as the palm rest and trackpoint device.
- 2007. Asus' Eee PC 701 was the first netbook largely resembling modern laptops.
Today, laptops are ubiquitous in the work environment. Some companies use a bring-your-own-device framework, which can pose difficulties for mobile device management and mobile device security in the workplace.








