
What is a mobile operating system?
A mobile operating system (OS) is software that enables smartphones, tablets and other devices to run applications and programs. It provides an interface between the device's hardware components and software functions.
A mobile OS typically starts when a device powers on, presenting a screen with icons or tiles that show information and provide application access. Mobile OSes also manage cellular and wireless network connectivity and phone access.
Millions of people use mobile OSes worldwide, powering a wide range of devices, from smartphones to tablets and wearable technology. These systems offer users a wide selection of features, including calling and messaging, internet and cellular data connectivity, multitasking capabilities, interactive user interfaces (UIs) and access to a wide range of third-party applications and services to further enhance the user experience (UX).
Types of mobile operating systems
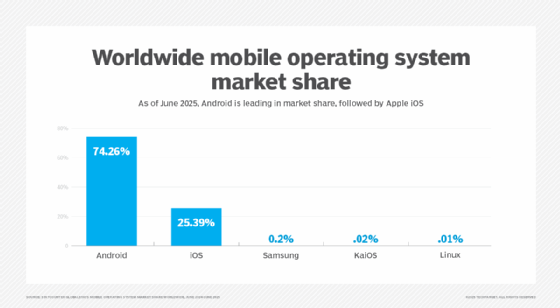
There are several mobile OSes on the market today, but two of the most widely adopted are iPhone's OS, Apple iOS, and Google's open source platform, Android OS. These two mobile OSes take different approaches to the mobile OS and end-user experience.
Apple distributes the only devices that natively support iOS and takes a walled garden approach, regulating all mobile apps and services that can run on iOS devices. Apple developed iOS to run on its own XNU kernel. The company has also released several device-specific mobile OSes, such as watchOS for the Apple Watch and iPadOS for iPad tablets.
Google takes an open source approach with Android, enabling original mobile device manufacturers to customize the Android source code to fit their devices. Android runs on the Linux kernel. Additionally, because it is open source and globally popular, Android has become a staple in developing various equipment such as kiosk, machinery and TV OSes.
Other mobile OSes are available, but their adoption rates are well below those of iOS and Android and are mostly found outside of the U.S. These include KaiOS, Sailfish OS and Huawei's HarmonyOS.
Several mobile OSes are no longer commonly supported, including BlackBerry 10, Nokia's Symbian, LG webOS -- formerly Palm webOS and HP webOS -- and Microsoft's Windows Phone OS.
Features of mobile operating systems
Mobile OSes deliver various features to users. The distinguishing feature is the ability to connect to the internet using the smartphone's built-in modem and a wireless service provider such as Verizon or AT&T. This is a major difference between mobile OSes and most desktop OSes, which rely on a Wi-Fi network or Ethernet connection to access the internet, giving end users the ability to work remotely.
Mobile OSes offer a native web browser application that lets users search the internet and visit webpages. They also provide application stores that enable users to download and interface with mobile applications. Mobile OSes running on devices equipped with GPS receivers and location sensors also have native global positioning system (GPS) applications that enable users to search for locations, follow step-by-step directions and, in some cases, share locations with different devices. iPhone and Android, for example, have GPS applications; KaiOS does not.
Other standard mobile OS features include native email applications that can link work and personal email accounts, a calendar application to keep track of tasks, meetings and events and a contacts library to organize and search for contact information.
Mobile OSes also include important enterprise management controls. With devices now housing both user and corporate data, it is important that these mobile OSes are secure, and that data can be remotely managed and accessed if needed. Apple and Google have developed standard application programming interfaces that enable mobile device management vendors to create platforms for securing devices that include features under the following categories:
UI
- Customizable home screens and app stores.
- Features and capabilities that can be enabled or disabled.
Multitasking
- Support for multiple accounts.
- Multimedia capabilities such as music and video players.
Networking and connectivity
- Access to cloud storage.
- Provisioning Wi-Fi and certificates.
- Messaging and collaboration features.
Security
- Pin code generation and encryption.
- Advanced enterprise and corporate management security options.
- Remote wipe and factory reset if a device is lost or stolen.
- Safeguards to ensure end-user privacy and security for bring your own device programs.
Settings
- Battery settings.
- Security and system updates.
- Hide sensitive apps in a different location.
- Central location to customize various device settings.
Notifications
- App notifications to turn notifications for apps on or off.
- Ability to control which notifications and content are visible on the lock screen.
Applications
- The Google Play Store contains a larger number of apps than the App Store.
- Google Play Protect scans Android apps from malicious software.

History and timeline of mobile operating systems
The history of mobile OSes dates to the early and mid-1990s, when manufacturers evolved beyond embedded systems to new OSes for their personal digital assistants, or PDAs, such as PenPoint OS from GO Corp., which ran on Intel x86-powered tablet PCs and Apple's Newton.
Apple iOS
In 2007, Apple launched its first mobile OS with the release of its first iPhone device. At release, however, Apple marketing stated the iPhone ran a mobile version of OS X. The iPhone marked a significant UX and functionality shift from earlier platforms. With an easy-to-use interface, intuitive design and a full-screen device with a software-based keyboard, it quickly became one of the market's most popular mobile options.
In 2008, Apple released iPhone OS 2, which included the App Store for iPhone users. This enabled third-party developers to create apps for iPhones and other iOS devices, giving users access to a vast library of apps and games, further enhancing their UX. In 2010, Apple launched iOS 4, the first version called iOS. The first iPad was also released in 2010. In 2015, Apple introduced a new OS, watchOS, as part of its comprehensive iOS platforms.
Since 2015, Apple has released new versions of iOS and watchOS each September, from iOS 9/watchOS 2 through the most recent, iOS 18/watchOS 11 in 2024. Prominent new features include Apple Intelligence, which adds a large language model (LLM) integration to Siri, and Rich Communications Services (RCS), which supports read receipts and high-quality multimedia sharing across platforms. The latter boosts Android compatibility, which potentially could boost iOS's market share.
Apple will release iOS 26 in 2025, a departure from its regular OS naming convention. The company is now naming its releases based on the year. This applies to iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS and visionOS. This new iOS version, which is expected in the fall, offers a streamlined system with improvements to the Control Center, security upgrades and new features in the Camera app.
iOS remains one of the leading mobile OSes on the market, with hundreds of millions of daily users. With frequent updates and improvements made to the platform each year, enhancing security, privacy and management controls, iOS will likely remain at the forefront of mobile technology for some time.
Blackberry
BlackBerry OS 1.0 was released in 2002 and was followed by numerous iterations as the company worked to improve and expand the platform. In 2008, BlackBerry launched version 4.6, which featured a new browser and support for Wi-Fi-enabled devices. Version 5.0 introduced an improved interface that made navigation easier, as well as other features like voice dialing and HTML email support. Version 6 offered Flash Player compatibility and integration with third-party social networks like Twitter and Facebook.
In 2016, Blackberry stopped designing its own phones and started licensing its brand to other companies for manufacturing and marketing. The last Blackberry phone, the Key2LE, was released in 2018. In 2022, Blackberry decommissioned its OS, software and services.
Google Android
In 2008, Google released Android as a competitor to iOS and other platforms. In the early days of Android, devices were mainly made by HTC and Motorola, with other companies joining later. Android has since become one of the most popular mobile OSes available. It is a fully customizable OS that enables end users and corporations to build custom experiences.
The first version of Android came out in 2008 as Android 1.0. It had a basic UI and did not include standard features such as Google Play Store. Over the next few years, the platform continued to evolve, with Android 2 Eclair released in 2009, followed by Android 3 Honeycomb in 2011, and Android 4 Ice Cream Sandwich in 2012. Android 5 Lollipop was released in 2014 and introduced a new design language called Material Design and WearOS. Google released eight new versions in the next eight years, leading up to Android 14, which included an enhanced UX, stronger end-user privacy settings and enterprise management controls.
Android 15 was released in September 2024. This Android version included several new features, including a Privacy Sandbox which facilitated online advertising without the use of third-party cookies, support for app archiving and improved satellite network compatibility.
Android 16 was released on June 10, 2025, for Google Pixel devices. It will be available in the coming months for other phone brands.
Microsoft Windows Mobile
Microsoft Windows Mobile was first released in 2000 as Pocket PC, also labeled Windows Mobile Classic and Windows Mobile Professional. It enabled users to access many of the same features of their desktop computers, such as Office Outlook and Internet Explorer. The platform received updates until 2010, when it was replaced by Windows Phone 7. Microsoft designed Windows Phone 7's user interface from scratch to make it more touch-friendly. The platform eventually evolved into Windows 10 Mobile, with its last release in 2017.
Mobile operating system trends
As the smartphone market continues to expand and smartphone OSes continue to evolve, new trends have begun as consumer expectations have shifted. These trends include the following:
- Integrated AI. Smartphone OSes, notably the Android phone and iPhone, are increasingly using AI, continuously improving photos, predictive text and in-phone digital assistants.
- Fifth-generation wireless network facility. As 5G networks have proliferated globally, smartphone OSes are exploiting the enhanced connectivity they offer, making the IoT more accessible and enabling greater data-heavy applications.
- Greater cross-platform integration. Apple's reversal on RCS -- it resisted implementing it for years -- is a concession to user demand for greater brand integration as users mix and match smartphones, tablets and smart watches. This trend will certainly continue.
- Augmented reality and virtual reality. AR and VR apps will continue to proliferate, and mobile OSes will need to accommodate them.
Before trading in your mobile device for a newer model, check out this Assurant mobile trade-in and upgrade data trends review.






