Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
What is Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)?
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) is a security protocol commonly used to protect wireless networks. PEAP extends the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) by encapsulating the EAP connection within a Transport Layer Security (TLS) tunnel. PEAP was designed to provide authentication for 802.11 wireless local area networks (WLANs) to achieve greater security than what could be realized with EAP alone.
EAP is an authentication protocol developed for wired networks that supported point-to-point connections, where physical security was usually assumed. EAP was later adopted for IEEE 802.1X port-based authentication, but it soon became apparent that there were a number of security concerns related to the protocol. For example, it included no per-packet integrity protection or standardized mechanism for key exchange, and it provided no support for fast reconnects, fragmentation and reassembly, or success and failure acknowledgments.
PEAP addresses EAP deficiencies by wrapping an EAP session within a TLS channel. According to the original PEAP draft, the encapsulation makes it possible to protect the following features:
- User identity and negotiation.
- EAP headers, methods and method sequencing.
- Notifications, acknowledgments and result exchanges.
- Client-server parameter exchanges.
PEAP also provides server authentication, a standardized mechanism for key exchange, key derivation and key management. In addition, PEAP supports session resumption, fragmentation and reassembly, and quick reauthentication when roaming between wireless access points.
PEAP protects client credentials by encrypting the identity exchange within the TLS session. Encapsulating the exchange in this way helps to resist dictionary attacks by protecting the EAP method used for the authentication process.
These protections also extend to EAP conversation terminations, which can help to reduce the risk of denial-of-service attacks. In addition, PEAP leverages the TLS key derivation method, which provides the keying material needed by the EAP methods running in the TLS tunnel. This eliminates the need to develop the type of secure key hierarchy that EAP requires on its own.
How does PEAP work?
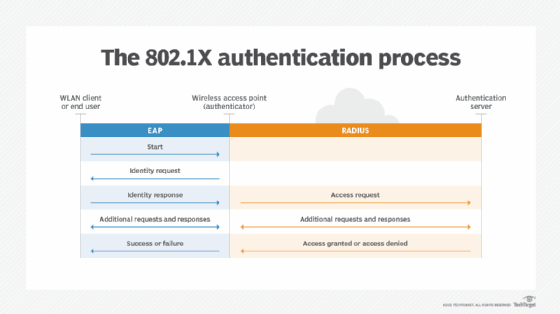
When a PEAP conversation begins, the EAP server and EAP peer (client) initiate communication and agree to use PEAP to carry out their conversation. At that point, the EAP server takes on the role of PEAP server, and the EAP client takes on the role of PEAP peer. The server and peer then begin their conversation, which consists of two phases:
- Phase 1. During this phase, the PEAP server is authenticated and a TLS session is established between the server and PEAP peer. The conversation typically begins with an identity exchange in which the authenticator sends a request/identity packet to the client and the client responds with a response/identity packet. The server and peer exchange TLS messages by placing the TLS records into the message payload.
- Phase 2. This phase operates within the TLS session, where a complete EAP conversation is carried out. The conversation can occur only if the TLS session was successfully established in the first phase. The PEAP server authenticates the PEAP peer within the TLS session, which provides the security necessary to protect the authentication data. As part of this process, the server and client agree on which inner EAP method to use for the authentication process. When the authentication is complete, the second phase ends, concluding the PEAP conversation.
During the second phase, the PEAP server initiates the agreed-upon inner EAP method. The inner method carries out the actual authentication process within the TLS session. PEAP supports multiple inner methods, but the one most commonly used is the EAP Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 2 (EAP-MSCHAPv2).
EAP-MSCHAPv2 is a Microsoft-defined EAP method that encapsulates MSCHAPv2, an authentication protocol that relies on usernames and passwords to authenticate access accounts. Windows OSes provide native support for EAP-MSCHAPv2, along with other EAP methods. When MSCHAPv2 is used as an inner method in PEAP communication, it is sometimes referred to as PEAP-MSCHAPv2.
PEAP is often compared to EAP-TLS, an EAP variation that relies on certificate-based authentication rather than password-based authentication like PEAP. Certificate-based authorization is typically considered more secure than password-based. Passwords can be lost, stolen, shared or intercepted, putting corporate networks at risk. That said, certificate-based security also comes with its own challenges. It can be difficult and expensive to implement, especially when supporting a large number of clients. Deploying such an infrastructure might be too difficult or expensive to implement for some companies, which is why many organizations have stuck with PEAP.
Learn more by checking out our overview of 802.1X authentication methods and EAP. Explore the differences between WEP, WPA, WPA2 and WPA3 wireless security.








