What is Microsoft Windows 10?
Windows 10 is a Microsoft operating system (OS) for PCs, tablets and some internet of things devices. Microsoft released Windows 10 in July 2015 and plans to end support in October 2025. After this date, devices running Windows 10 will still function, but they will become increasingly vulnerable to security risks and may eventually lose compatibility with newer hardware and software.
When Windows 10 was released in 2015, Microsoft stated its intention to shift to a Windows-as-a-service delivery model that would provide the OS with continuous updates instead of infrequent version releases. To convert as many users as possible for the as-a-service model and ensure a consistent platform for developers, Microsoft allowed Windows 7 and 8.1 users to upgrade to Windows 10 for free. By 2019, Windows 10 was installed on over 800 million active devices.
Today, it's estimated that almost half of all Windows devices are still using the Windows 10 OS. Microsoft is encouraging users to transition to Windows 11 before support for Windows 10 ends in October. But Windows 11 has stricter minimum hardware requirements than Windows 10, and many older and entry-level PCs can't meet these requirements.
For those who cannot upgrade to Windows 11, Microsoft is offering a paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program for Windows 10. This enables users to continue receiving security updates for up to three years after the October 2025 end-of-support date. Devices must be running Windows 10, version 22H2 to be eligible to install updates from the ESU program.
Windows 10 features
Windows 10 includes numerous features and capabilities that were not available with Windows 8, the previous version of the Windows OS. The company never publicly released a product called Windows 9 -- and it never explained why.
Core features
- Microsoft replaced the full-screen Start screen introduced in Windows 8 with a redesigned, left-aligned Start menu that combines the traditional layout with customizable Live Tiles.
- Microsoft's original digital assistant, Cortana, was integrated into the taskbar for voice commands, reminders and search. Cortana was later deprecated in later Windows 10 builds.
- A feature called Task View helps users manage multiple open windows and organize their work more efficiently by using virtual desktops.
- A new web browser called Microsoft Edge replaced Internet Explorer.
- A feature called Action Center gives users a centralized place to view alerts and access frequently used system controls. In Windows 11, Action Center was redesigned and split into separate interfaces for notifications and quick settings.
- Windows 10 introduced Continuum, a feature designed for 2-in-1 devices, like Microsoft Surface, that can function as both a laptop and a tablet. Continuum automatically switches the interface between desktop mode and tablet mode depending on how the device is being used.
- The Snap Assist feature makes it easier for users to compare documents, multitask or keep multiple apps visible at once without manually resizing each window.
- Windows Hello is a security feature in Windows 10 that enables users to sign in to their devices using biometric authentication or a PIN, rather than a traditional password.
- DirectX 12 is a low-level graphics application programming interface included in Windows 10 that is designed to improve performance and visual quality in games and multimedia applications.
Productivity and integration features
- Universal Windows Platform (UWP) enables Windows apps to run across a wide range of Microsoft devices.
- OneDrive integration enables seamless file synchronization and cloud access across all devices connected to a Microsoft account.
- Windows Ink supports stylus input for tasks like note-taking, drawing and annotating, enhancing productivity on touch-enabled and pen-capable devices.
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) lets users run Linux distributions natively within Windows, making it easier for developers and system administrators to work across platforms. WSL capabilities expanded significantly in later Windows 10 updates.
- A feature called Timeline enables users to view and resume previously opened files and activities for up to 30 days.
- Nearby Sharing is a Windows 10 feature that lets users share files, links and content wirelessly with nearby Windows 10 devices using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.

Windows 10 history and reception
Microsoft announced Windows 10 on Sept. 30, 2014, and released a technical preview the following day through a new initiative called Windows Insider Program. This marked a shift in how Microsoft developed and delivered OSes because it included Windows users in the development process. Essentially, Windows Insiders Program enabled volunteers to try out prerelease versions of Windows 10 and provide Microsoft with feedback. Microsoft development teams used the feedback to make improvements before the official Windows 10 release.
One of the primary goals of Windows 10 was to unify the Windows platform across a wide range of devices. To facilitate the unification effort, Microsoft introduced UWP, a platform that enables developers to build apps that can be run on all types of Windows 10 devices. The unification effort also included a common app store, shared security and update models, and a responsive interface that could adapt to different screen sizes and input methods.
The public's response to the changes introduced in Windows 10 was primarily positive. Critics and end users considered Windows 10 to be significantly more user-friendly than its predecessor, Windows 8. The integration of Cortana, Microsoft's digital assistant, also created positive interest in Windows 10. While the assistant's role was diminished in later versions of the OS, it's inclusion in Windows 10 is still considered to be important because it highlighted Microsoft's commitment to making AI an important aspect of the Windows user experience (UX).
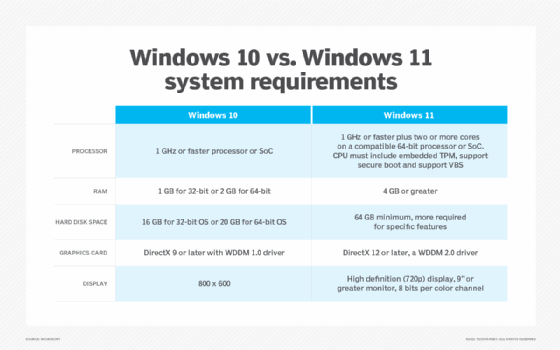
Windows 10 system requirements
As with all other Windows OSes, Windows 10 has certain system requirements that must be met for successful installation and use. Devices that do not meet these minimum requirements may be incompatible with Windows 10.
According to Microsoft, the minimum system requirements for Windows 10 are the following:
- Processor: 1 gigahertz or faster processor, or system on a chip.
- RAM: 1 gigabyte for 32-bit systems, 2 GB for 64-bit systems.
- Hard disk space: 16 GB for 32-bit OS, 20 GB for 64-bit OS.
- Graphics card: DirectX 9 or later with Windows Display Driver Model 1.0.
- Display: Minimum resolution of 800x600 pixels.
Windows 10 versions
Windows 10 was released under Microsoft's Windows-as-a-service delivery model and initially received feature updates twice a year. Before 2020, Windows 10 version names were based on the year and month the update was intended to be released. For example, version 1803 was meant to launch in March 2018.
The problem was that Microsoft sometimes released Windows 10 updates later than planned, and this made the naming convention confusing. To reduce ambiguity, Microsoft began using an "H" system for identifying different versions of the OS. The letter "H" refers to which half of a year the update was made available.
Here is a list of the major versions of Windows 10:
- Version 1507. Also known as the initial release, this version of Windows 10 introduced Microsoft Edge and Cortana, brought back the classic Start menu and debuted Action Center.
- Version 1511. Also known as the November Update, this release enhanced system performance, added colored title bars and improved Cortana functionality.
- Version 1607. Also known as the Anniversary Update, this release introduced Windows Ink, Windows Hello support for apps and websites, and WSL.
- Version 1703. Also known as the Creators Update, this release brought new creative tools, such as Paint 3D, Night Light, Game Mode and enhanced privacy settings.
- Version 1709. Also known as the Fall Creators Update, this release introduced the Timeline feature and OneDrive Files On-Demand.
- Version 1803. Also known as the April 2018 Update, this release added Nearby Sharing and dictation features.
- Version 1809. Also known as the October 2018 Update, this release introduced Snip & Sketch, clipboard history and a dark theme for File Explorer.
- Version 1903. Also known as the May 2019 Update, this release introduced a troubleshooting feature called Windows Sandbox and separated Cortana from Windows Search.
- Version 1909. Also known as the November 2019 Update, this release was a minor update focused on performance and quality improvements. It was delivered to 1903 users as an enablement package.
- Version 2004. Also known as the May 2020 Update, this release improved Cortana's user interface (UI), enhanced tablet usability and introduced WSL 2 with a full Linux kernel.
- Version 20H2. Also known as the October 2020 Update, this release made subtle improvements to the Start menu and enhanced notifications.
- Version 21H1. Also known as the May 2021 Update, this release delivered minor performance enhancements for Windows Hello multicamera support.
- Version 21H2. Also known as the November 2021 Update, this release was the last feature update that made significant changes. It simplified passwordless authentication, provided support for Wi-Fi 6E and added graphics processing unit compute support for WSL.
- Version 22H2. Also known as the 2022 Update, this was the final feature update for Windows 10. It was delivered through an enablement package that activated dormant features already present in the OS when the computing device was restarted.
Quality updates vs. feature updates
In Windows 10, quality updates and feature updates are two distinct types of system updates that serve different purposes in Microsoft's Windows-as-a-service model.
Quality updates are regular, incremental updates that focus on improving the reliability, security and stability of Windows 10. They are delivered monthly, typically on the second Tuesday of each month, known as Patch Tuesday. Quality updates are cumulative, which means that each new update contains all the changes from previous updates. Installing the latest quality update brings a system fully up to date.
Feature updates are major upgrades to Windows 10 that introduce new features, significant UI or UX changes, and architectural enhancements. Sometimes, feature updates also deprecate or remove older components.
Windows 10 servicing channels
Servicing channels, in the context of Windows 10, refers to three different release tracks for Windows 10. Devices can be assigned to a particular channel by using Microsoft Configuration Manager, Windows Server Update Services or Group Policy settings. The following are the channels:
- The General Availability Channel (GAC) is the default servicing channel for most users and organizations. Feature updates for the GAC are released annually -- initially twice a year. Once released, devices configured for this channel automatically receive the update through Windows Update, unless update deferrals or management policies have been put in place to delay deployment.
- The Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) is designed for devices that perform a single, critical function and require a stable, unchanging OS environment. LTSC releases typically occur every two to three years and are bundled with volume licensing agreements.
- Windows Insider Program is a voluntary program for IT professionals, developers and enthusiasts who want to test upcoming Windows features and provide feedback to Microsoft. Devices that use this channel receive previews of Windows builds, not the final release. To acquire the final release of a build, Insider Program participants can opt out of the testing program and join the GAC.
Windows 10 security
Microsoft Windows 10 includes numerous security features and capabilities to address the security concerns of previous versions of Windows.
One key feature is the Windows Security app, which is available in Windows 10 version 1703 and later. Through the Security app's interface, users can view and manage settings related to the following:
- Virus and threat protection.
- Account protection.
- Firewall and network protection.
- App and browser control.
- Device security.
- Device performance and health.
Users cannot uninstall the Windows Security app, and attempting to disable it is inadvisable because it provides real-time threat protection. This protection is delivered through features such as Microsoft Defender Antivirus, Windows Firewall and Microsoft Defender SmartScreen, which help block malicious websites, downloads and applications. Many security-related tasks, including manual malware scans, can be performed directly within the app.
Windows 10 also introduced an extensive security feature called Virtual Secure Mode. VSM uses hardware-based virtualization to create isolated environments known as Virtual Trust Levels. VTLs prevent processes in one isolated environment from accessing memory in another. Additionally, Isolated User Mode helps secure sensitive data and credentials by ensuring that critical processes run in a protected space, even if the main OS is compromised.
To protect stored data, Windows 10 offers BitLocker Drive Encryption. BitLocker enables users to encrypt built-in OS drives. For removable storage, such as USB flash drives, external hard drives or Secure Digital cards, users can extend encryption protection by using BitLocker To Go.
Windows 10 also includes built-in support for two-factor authentication (2FA) through Windows Hello and integration with Microsoft accounts and Microsoft Entra ID, formerly Azure Active Directory. To use 2FA with Windows 10, users must first enable 2FA on their Microsoft account, or their organization must enforce it through Entra ID.
Windows 10 and data privacy
Microsoft collects diagnostic, usage and interaction data from Windows 10 devices to improve UX, deliver personalized recommendations and display targeted advertisements. Users can adjust the OS' privacy settings to retain control over how much personal information they share with Microsoft.
Windows 10 users can take further steps to manage how their data is collected and used by doing the following:
- Visiting Microsoft's opt-out page to disable personalized advertising.
- Using the Microsoft privacy dashboard to view, download and/or delete data associated with their Microsoft account.
- Contacting Microsoft directly to request assistance or exercise data rights under applicable privacy laws.
Organizations can also control how data is collected from managed devices by using Group Policy, Windows Configuration Designer or Microsoft Intune. These tools enable IT administrators to enforce data privacy and compliance policies across multiple users and devices in enterprise environments.
Understanding the end of support for Windows 10 is crucial for administrators. While upgrading to Windows 11 is the easiest option, organizations also have the choice to extend support for Windows 10.