Patch Tuesday
What is Patch Tuesday?
Patch Tuesday is the commonly known name of Microsoft's monthly release of security fixes for the Windows operating system and other Microsoft software. It is also referred to as Update Tuesday.
The Microsoft Security Response Center publishes bulletins using the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) identification numbers for each vulnerability on the Security Update Guide website. Each bulletin gives remediation information and a link to a Microsoft Knowledge Base article with more details on the update.
Most Patch Tuesday updates correct vulnerabilities in the Windows desktop and server OS. They also fix issues in Microsoft Office applications, Azure hybrid cloud applications and the Visual Studio Code editor. The updates cover supported Windows systems, including Windows OSes that have reached end of life but have protection through Microsoft's Extended Security Update program.
Microsoft releases most of its security patches on Patch Tuesdays. Fixes for more serious vulnerabilities, called out-of-band patches, are the exception.
When is Patch Tuesday?
Patch Tuesday occurs on the second Tuesday of each month at about 10 a.m. Pacific Time (5 p.m. Coordinated Universal Time). This is when Microsoft releases its monthly software updates. The company selected the Tuesday schedule to give administrators a dedicated day to prepare to deploy updates.
Until Microsoft introduced the cumulative update servicing model in 2016, administrators could choose to deploy individual patches. They could also decide to not install a security update and to roll back patches.
With Windows 10, Microsoft launched the Windows as a service cumulative update model. This approach compiles all security and nonsecurity updates for a month and all previous updates in a single package. With it, customers could no longer pick which updates they wanted to apply.
Microsoft extended this Windows 10 servicing model to other supported versions of Windows OSes in late 2016. With this approach, Windows administrators can only decide the order of patch deployment, rather than select which patches to apply. If a system encounters an issue that cannot be remediated, the administrator must roll back the entire cumulative update until Microsoft issues a fix.
For Windows OS, Microsoft releases a monthly rollup on Patch Tuesday. It consists of that month's security and reliability updates and includes all previously released updates. Microsoft calls this its B release. Microsoft offers cumulative, nonsecurity previews it calls the C release. The C release is typically published in the third or fourth week of the month. Administrators can test it on Windows systems before the official release on the following Patch Tuesday.
Other companies, such as Oracle and Adobe, also have adopted patch deployment schedules that coincide with Patch Tuesday.
Why is patching important?
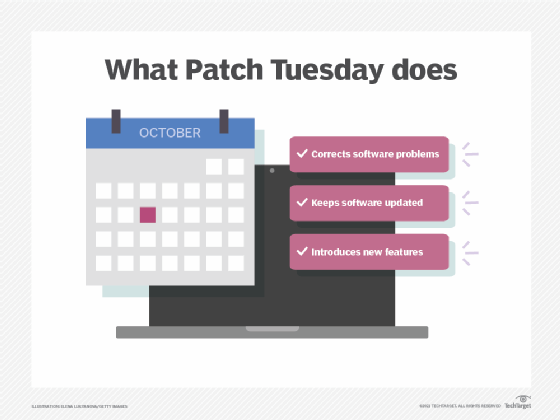
Regular patching provides the following advantages:
- Corrects software problems, including vulnerabilities, bugs and compatibility issues.
- Keeps software updated and functioning properly.
- Introduces features.
Patches provide protection from a range of security vulnerabilities including the following:
- Denial of service.
- Elevation of privilege.
- Remote code execution.
- Spoofing.
Microsoft urges its customers to patch as soon as it releases these security updates. Malicious actors constantly scrutinize the code in Microsoft's patches to gather clues to develop malware variants.
IT pros must practice sound patch management to ensure the patches do not cause issues with other enterprise products or disrupt users. Best practices dictate that administrators use a testing phase, such as a pilot group, to check for problems before applying patches to systems in a production environment.
Patches can also introduce problems. Some IT pros have given the Wednesday following Patch Tuesday the nickname "Crash Wednesday" because that is when they must correct problems from the Tuesday patches.
How does Microsoft distribute patches?
Microsoft describes its monthly fixes for Windows as a quality update that includes security fixes, bug corrections and feature refinements. The company combines security and nonsecurity releases in a monthly rollup, which it distributes in the following four ways:
- Windows Update.
- Windows Server Update Services.
- System Center Configuration Manager.
- Microsoft Update Catalog.
For a time, Microsoft also distributed security updates for third-party applications. The most notable application in this category was the Adobe Flash Player when it was still under Adobe support.
What updates are released on Patch Tuesday?
The security updates Microsoft releases on Patch Tuesday are primarily for Microsoft software products, features and roles but also include apps that run on Apple and Android mobile devices.
Microsoft uses a severity rating system that designates a patch as critical, important, moderate or low. Critical patches are for exploits that need no user action, such as the presence of a malicious network worm. Important patches need user interaction to trigger the exploit, such as opening a specially crafted file from an email.
A vulnerability that is under attack without a patch is a zero-day exploit. That means researchers have found evidence of active exploitation before a patch is available. In these situations, Microsoft will often provide mitigation instructions to prevent exploitation until a security update is available. For example, the company might recommend changing certain values in a Windows registry key.
Microsoft security updates apply to many types of software, including the following:
- Components in Windows OS.
- Applications on smartphones and tablets.
- Open source software projects.
Some of the products, features and roles that have security updates on a typical Patch Tuesday could include the following:
- Azure Open Management Infrastructure.
- Microsoft Business Central.
- Microsoft Accessibility Insights for Android.
- Microsoft Defender for IoT.
- Microsoft Edge for Android.
- Microsoft Office.
- Microsoft Windows Codecs Library.
- Microsoft Windows Domain Name System.
- Visual Studio.
- Windows BitLocker.
- Windows Common Log File System Driver.
- Event Tracing for Windows.
- Windows Installer.
- Windows Kernel.
- Windows Print Spooler Components.
- Windows Scripting.
Microsoft typically stops publishing security fixes for products after the end-of-life date in the product's support lifecycle. However, Microsoft deviated from its normal practices in 2017 and released patches for unsupported OSes to protect them from the WannaCry and EternalBlue ransomware attacks and variants based on that malware. Those unsupported OSes included Windows XP, Windows 8 and Windows Server 2003.
What are out-of-band patches?
An out-of-band patch is a software fix released outside of the Patch Tuesday schedule. These patches are released to stop the spread of critical vulnerabilities.
For example, Microsoft would release such a patch for a zero-day exploit that was considered a threat to many systems. It would release an out-of-band patch and an advisory to prompt users to take immediate action. If the patch applied to Windows OS, Microsoft would include it in the next Patch Tuesday as part of its cumulative update servicing model.
Patch Tuesday changes and Windows 10
In March 2017, Microsoft transitioned to the Security Update Guide, which focuses on the CVEs being targeted, regardless of the product. The update guide also introduced new application programming interfaces (APIs) for customers who want to automate some of the Patch Tuesday work.
Microsoft also developed a PowerShell module called MsrcSecurityUpdates that works with an API to access security update data for jobs, such as building reports.
Windows 10 users can pause quality updates one time for up to 35 days.
Where can you find Patch Tuesday update details?
Users can find an overview of that month's Patch Tuesday security updates in Microsoft Security Update Guide release notes.
The Security Update Guide lists all security updates within a specified date range. It also lists the release date, the affected product, the vulnerability's impact and its severity level. It includes a download link for the update and a link to corresponding Microsoft Knowledge Base articles and the CVE details of each patch.
A good place to get information about Patch Tuesday is Microsoft's Security Update Guide Frequently Asked Questions page. The support policies for security updates are available in Microsoft's Lifecycle Product Database.
Microsoft releases security notifications whenever there are updates that affect customer security. Users with a Microsoft account can subscribe to email alerts. Microsoft also issues security advisories for security information that might not classify as a vulnerability but is still important.
Patch Tuesday history
Microsoft introduced Patch Tuesday in October 2003 to make patch deployment easier.
Until the introduction of the Security Update Guide in November 2017, Microsoft would publish security bulletins on its Security Advisories and Bulletins website for the vulnerabilities corrected in a month. The site broke down information for the month's security updates by section: security bulletins, security bulletin summaries, security advisories and acknowledgments.
Microsoft followed a regular monthly security update schedule until February 2017 when it cancelled the Patch Tuesday release because of a last-minute issue. It was the first time Microsoft had cancelled a Patch Tuesday release.
Microsoft did not disclose what the issue was, but experts believe it was related to the U.S. National Security Agency's (NSA) Windows exploits. Unknown threat actors had stolen information on those exploits and, later, the Shadow Brokers hacking group published it. According to reports, the NSA disclosed the exploits to Microsoft before their publication. Microsoft patched several critical vulnerabilities in the March 2017 Patch Tuesday, including the NSA's Windows exploits.
Later in 2017, Microsoft changed the name, layout and the functionality of its security bulletins site and unveiled a new site with the Security Update Guide. Instead of the verbose bulletin-style format used to describe the vulnerabilities, customers can run searches and use date ranges to limit the vulnerabilities returned.
Users can search, filter and sort data to produce reports and export them to Excel. They can also find information more readily, such as whether a vulnerability is being actively exploited or has been publicly disclosed.
Ben Lutkevich is a site editor for Software Quality. Previously, he was a technical features writer for WhatIs.com, as part of the Learning Content team.