What is a smart sensor and how does it work?
A smart sensor is a device that takes input from the physical environment and uses built-in compute resources to perform predefined functions when it detects specific input. It can also process data before passing it on.
Smart sensors enable more accurate and automated collection of environmental data with less erroneous noise among the accurately recorded information. These devices are used for monitoring and control mechanisms in a variety of environments, including smart grids, battlefield reconnaissance, exploration and science applications.
The smart sensor is also a crucial and integral element in the internet of things. IoT technology makes it possible to provide a unique identifier for almost anything and transmit data from or about those things over the internet or a similar sensor network. One implementation of smart sensors is as components of a wireless sensor and actuator network. These networks can have thousands of nodes, where each is connected to one or more other sensors and sensor hubs as well as to individual actuators.
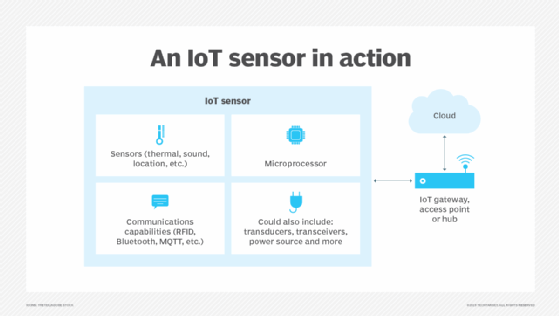
Low-power mobile microprocessors typically provide compute resources in IoT environments. At a minimum, a smart sensor is made of a sensor, a microprocessor and some kind of wireless communication technology. The compute resources are an integral part of the physical design. A sensor that just sends its data along for remote processing isn't considered a smart sensor.
A smart sensor might also include several other components besides the primary sensor. These components can include transducers, amplifiers, excitation control, analog filters, analog-to-digital converters and compensation that provides a built-in correction of less-than-ideal measurements or output. A smart sensor also incorporates software-defined elements that provide functions such as data conversion, digital processing and communication to external devices.
How do smart sensors work?
A smart sensor connects a raw base sensor to integrated computing resources that enable the sensor's input to be processed. The base sensor is the component that provides the sensing capability. It might be designed to sense heat, light or pressure. Often, the base sensor will produce an analog signal from an application algorithm that must be processed before it can be used. This process is also called signal processing.
With signal processing, an intelligent sensor's integrated technology comes into play. An onboard microprocessor uses a technique called filtering to remove signal noise and convert the sensor's signal into a usable, digital format.
Smart sensor technology also contains integrated communications capabilities that let it connect to a private cloud computing environment or the internet. This lets sensors communicate with external devices.
What are smart sensors used for?
Smart sensors have many uses. They're commonly found in industrial environments and are the driving force behind Industry 4.0 and industrial automation, robotics and other advanced instrumentation.
Factories use smart sensors for diagnostic purposes. Smart temperature sensors ensure machines aren't overheating, and vibration sensors monitor machines at risk of vibrating loose. Smart sensors also enable process control, such as monitoring a manufacturing process and making necessary adjustments so it can meet quality and production goals. Smart sensors automate these tasks that were once manual processes.
Smart sensors also play a key role in the advancement of modern security systems. Thermal imaging sensors detect an intruder's body heat. Similarly, devices such as smart locks, motion sensors, and window and door sensors are commonly connected to a common network. This lets the security sensors work together to create a comprehensive security status picture. They're frequently used in homes and industrial applications to detect various leaks.
The following are some other uses for smart sensors:
- Infrastructure. Utility and energy companies use smart sensors to manage power grids, identify potential infrastructure problems, such as water and waste pipe leaks, and gather data on energy and utility use.
- Agriculture. Smart sensors analyze climate, track soil moisture, ambient temperature and humidity, as well as track livestock.
- Logistics. These applications include the use of RFID devices to track motor vehicles and improve the efficiency of inventory management.
- Public sector. Government agencies, especially those managing smart cities, use smart sensors to monitor traffic flow, respond quickly to emergencies, and monitor air quality.
- Smart homes. Consumers with smart homes use sensors to track and run thermostats, appliance performance, interior and exterior lighting, and security systems.
- Healthcare. Smart sensors gather patient health data, such as heart rates and blood oxygen levels; monitor the performance of smart healthcare systems in hospitals and provide environmental data.
What are the different types of smart sensors?
There are many types of special-purpose sensors in use. Five main types of smart sensors are commonly used in industrial IoT environments:
- Level sensors. These measure the volume of space taken up in a container. A vehicle's fuel gauge might be connected to a level sensor that monitors the level of fuel in the tank.
- Temperature sensors. These monitor a component's temperature so a corrective action can be taken if the temperature gets too high or low. For example, a temperature sensor can ensure machinery doesn't overheat.
- Pressure sensors. These are used to monitor the pressure of gases or fluids in a pipeline. A sudden drop in pressure might indicate a leak or a flow control system issue.
- Infrared sensors. These sensors are used in thermal imaging cameras and for temperature monitoring in noncontact infrared thermometers. Other infrared sensors are optical sensors tuned to a frequency that helps them see light in the infrared spectrum. These sensors are used in medical equipment, such as pulse oximetry devices, and in electronic devices designed for remote control operation.
- Proximity sensors. These are used to detect the location of a person or object in relation to the sensor. In retail environments, proximity sensors can track customer movements throughout a store.
- Motion sensors. Similar to proximity sensors, these sensors detect movement; they're often part of building and home security systems.
- Flow sensors. These monitor in-home water systems for leaks and send alerts if one is detected.
Other smart sensors monitor electrical power consumption, vibration in factory equipment, humidity, moisture and light.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of smart sensors?
Smart sensors come with a range of benefits, but they also have challenges and drawbacks.
Smart sensor advantages
The advantages of smart sensors are most prominent when they're used for data collection in austere or remote locations. The following advantages depend on deploying the right type of sensor where they're most needed:
- Energy efficiency and sustainability. A smart sensor can be programmed to be highly sensitive or receptive to even slight changes in surrounding conditions, such as temperature, humidity, moisture or acoustics. These highly accurate and reliable measurements provide a level of monitoring and data collection that can contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability efforts.
- Access to data in difficult environments. Smart sensors can collect data in remote places where it would be difficult or dangerous for people to go. Remotely operated, wireless smart sensors are particularly helpful in challenging environments.
- Real time, high performance. Smart sensors can collect data with consistency and speed when real-time data is needed.
- Built-in analytics and processing. Unlike traditional sensors, smart sensors feature certain built-in analytics and processing capabilities of the signals and data they receive, leading to increased efficiency because they require fewer outside analytics tools or resources.
Smart sensor disadvantages
Smart sensor developers have consistently upgraded their offerings to address drawbacks. Some of these disadvantages include the following:
- Susceptibility to tempering and hacking. Malicious actors, especially those looking to access collected data meant for private use, can do so if a device's cybersecurity measures are insufficient.
- Costs. Many devices are expensive, and the cost of the upkeep required over time can also be cost prohibitive.
- Maintenance. Sensors at some point require recalibration or upgrades because of data latency or other issues. Ones located in remote settings or challenging environments can be difficult and costly to reach.
- Expertise. Smart sensor systems often require levels of IT expertise that not all organizations have. New hires or training could be needed.
- IoT deployment requirements. Whether in a smart home or an industrial setting, other factors must be taken into consideration before deploying IoT devices, like the power consumption required, the need for stable online connectivity and the ability to handle higher volumes of data.
How are smart sensors different from base sensors?
Smart sensors include an embedded digital motion processor (DMP), whereas base sensors don't. A DMP is a microprocessor that's integrated into the sensor. It lets the sensor perform onboard processing of the sensor data. This might mean normalizing the data, filtering noise from electrical signals or performing other types of signal conditioning. In any case, a smart sensor performs data conversion digital processing prior to any communication to external devices.
A base sensor is simply a sensor that isn't equipped with a DMP or other compute resources that would let it process data. Whereas a smart sensor produces output that's ready to use, a base sensor's output is raw and must typically be converted into a usable format.
Smart sensors are generally preferred over base sensors because they include native processing capabilities. Even so, there are situations where it might be more advantageous to use a base sensor. If an engineer is designing a device and needs complete control over sensor input, then a base sensor would be preferable. Base sensors also cost less than smart sensors because they contain fewer components.
Standards, regulations and frameworks for smart sensors
Owing to their growing importance and use, several standards, regulations, frameworks and groups have emerged in support of smart sensor technology for IoT applications:
- IEEE 1451. The IEEE developed these standards for smart transducers. 1451.0 describes core functions and connectivity requirements, Among the additional standards in the series are details on transducer electronic data sheets and several various communications protocols.
- ISO/IEC 21813:2019. This International Organization for Standardization and International Electrotechnical Commission framework lets IoT devices, including smart sensors, exchange information with each other.
- ISO/IEC 27400:2022. This standard provides guidance on IoT security and privacy.
- IoXt Alliance Certification. This is an industry organization that supports the development of guidelines for security management in IoT devices.
- U.K. Product Security and Telecommunications Infrastructure Act of 2024. This provides security requirements for IoT devices.
- General Data Protection Regulation. This European Union regulation has requirements for smart sensors that collect personal data.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. This agency has requirements for health-related smart sensor devices, such as implants and diagnostic equipment.
- National Institute for Standards and Technology. NIST's SP 800-213 (2021) standard establishes guidance and requirements for cybersecurity of IoT devices in the U.S.
Future of smart sensors
Key drivers in the growth of smart sensor use are expected to be smart cities, next-generation infrastructure management and industrial production management. Other areas where heavy use is expected include healthcare, especially wearable devices; edge-based integration of AI technology; and driverless motor vehicles, which will depend on information provided by smart sensors. AI is also expected to be a major driver for smart sensors in many markets.
Smart sensors are most often associated with industrial equipment. Learn more about how they're used to collect data in manufacturing settings.






