What is virtual memory?
Virtual memory is a memory management technique where secondary memory can be used as if it were a part of the main memory. Virtual memory is a common technique used in a computer's operating system (OS) as it is effective at optimizing memory usage.
Virtual memory uses both hardware and software to enable a computer to compensate for physical memory shortages, temporarily transferring data from random access memory (RAM) to disk storage. Mapping chunks of memory to disk files enables a computer to treat secondary memory as though it were main memory.
Today, most PCs come with at least 8 gigabytes (GB) of RAM. But, sometimes, that is not enough to run several programs at the same time. Virtual memory frees up RAM by swapping data that has not been used recently over to a storage device, such as a hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD).
Virtual memory is important for improving system performance, multitasking and using large programs. However, users should not overly rely on virtual memory, since it is considerably slower than RAM. If the OS has to swap data between virtual memory and RAM too often, the computer begins to slow down, resulting in a condition called thrashing.
Virtual memory was developed at a time when physical RAM-based memory was expensive. Computers have a finite amount of RAM, so memory eventually runs out when multiple programs run simultaneously. A system using virtual memory uses a section of a hard drive or SSD to emulate RAM. With virtual memory, a system can load larger or multiple programs running at the same time, enabling each one to operate as if it has more disk allocation space, without having to purchase more RAM.
How virtual memory works
Virtual memory uses both hardware and software to operate. When an application is in use, data from that program is stored in a physical address using RAM. A memory management unit (MMU) maps the address to RAM and automatically translates addresses. The MMU can, for example, map a logical address space to a corresponding physical memory address.
If, at any point, the RAM space is needed for something more urgent, data can be swapped out of RAM and into virtual memory. The computer's memory manager is in charge of keeping track of the shifts between physical and virtual memory. If that data is needed again, the computer's MMU uses a context switch to resume execution.
While copying virtual memory into physical memory, the OS divides memory with a fixed number of addresses into either pagefiles or swap files. Each page is stored on a disk, and when the page is needed, the OS copies it from the disk to main memory and translates the virtual addresses into real addresses.
However, the process of swapping virtual memory to physical is rather slow. This means using virtual memory generally causes a noticeable reduction in performance. Because of swapping, computers with more RAM are considered to have better performance.
Types of virtual memory
A computer's MMU manages virtual memory operations. In most computers, the MMU hardware is integrated into the central processing unit. The CPU also generates the virtual address space. In general, virtual memory is either paged or segmented.
Paging divides memory into sections or paging files. When a computer uses up its available RAM, pages not in use are transferred to the hard drive or SSD using a swap file. A swap file is a space set aside on the hard drive to be used as the virtual memory extension for the computer's RAM. When the swap file is needed, it is sent back to RAM using a process called page swapping. This system ensures the computer's OS and applications do not run out of real memory. The maximum size of the pagefile can be one and a half to four times the physical memory of the computer.
The virtual memory paging process uses page tables, which translate the virtual addresses that the OS and applications use into the physical addresses that the MMU uses. Entries in the page table indicate whether the page is in RAM. If the OS or a program does not find what it needs in RAM, then the MMU responds to the missing memory reference with a page fault exception to get the OS to move the page back to memory when it is needed. Once the page is in RAM, its virtual address appears in the page table.
Segmentation is also used to manage virtual memory. This approach divides virtual memory into segments of different lengths. Segments not in use in memory can be moved to virtual memory space on the drive. Segmented information or processes are tracked in a segment table, which shows if a segment is present in memory, whether it has been modified and its physical address. In addition, file systems in segmentation are only made up of segments that are mapped into a potential address space of a process.
Segmentation and paging differ as an amount of memory model in terms of how memory is divided; however, the processes can also be combined. When combined, memory gets divided into frames or pages. The segments take up multiple pages, and the virtual address includes both the segment number and the page number.
Other page replacement methods include first in, first out (FIFO), optimal algorithm and least recently used (LRU) page replacement:
- The FIFO method has memory select the replacement for a page that has been in the virtual address for the longest time.
- The optimal algorithm method selects page replacements based on which page is unlikely to be replaced after the longest amount of time; although difficult to implement, this leads to fewer page faults.
- The LRU page replacement method replaces the page that has not been used for the longest time in the main memory.
How to manage virtual memory
Managing virtual memory within an OS can be straightforward, as there are default settings that determine the amount of drive space to allocate for virtual memory. Those settings work for most applications and processes, but there may be times when it is necessary to manually reset the amount of drive space allocated to virtual memory -- for example, with applications that depend on fast response times or when the computer has multiple hard disk drives or SSDs.
When manually resetting virtual memory, the minimum and maximum amount of drive space to be used for virtual memory must be specified. Allocating too little space for virtual memory can result in a computer running out of RAM. If a system continually needs more virtual memory space, it may be wise to consider adding RAM. Common OSes may generally recommend users not increase virtual memory beyond one and a half times the amount of RAM.
Managing virtual memory differs by OS. IT professionals should understand the basics when it comes to managing physical memory, virtual memory and virtual addresses.
What are the benefits of using virtual memory?
The advantages to using virtual memory include the following:
- It can handle twice as many addresses as main memory.
- It enables more applications to be used at once.
- It frees applications from managing shared memory and saves users from having to add memory modules when RAM space runs out.
- It can increase speed when only a segment of a program is needed for execution.
- It increases security because of memory isolation.
- It enables multiple larger applications to run simultaneously.
- Allocating memory is relatively inexpensive.
- It does not need external fragmentation.
- CPU use is effective for managing logical partition workloads.
- Data can be moved automatically.
- Pages in the original process can be shared during a fork system call operation that creates a copy of itself.
In addition to these benefits, in a virtualized computing environment, administrators can use virtual memory management techniques to allocate additional memory to a virtual machine (VM) that has run out of resources. Such virtualization management tactics can improve VM performance and management flexibility.
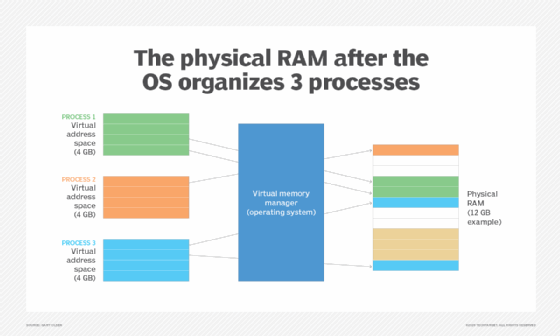
What are the limitations of using virtual memory?
Although the use of virtual memory has its benefits, it also comes with some tradeoffs worth considering, such as the following:
- Applications run slower if they are running from virtual memory.
- Data must be mapped between virtual and physical memory, which requires extra hardware support for address translations and may also affect performance.
- The size of virtual storage is limited by the amount of secondary storage, as well as the addressing scheme with the computer system.
- Thrashing can occur if there is not enough RAM, which makes the computer perform slower.
- It may take time to switch between applications using virtual memory.
- Virtual memory reduces the amount of available drive space.
Virtual memory vs. physical memory
When comparing virtual and physical memory, the biggest distinction commonly made is related to speed. RAM is considerably faster than virtual memory, but it tends to be more expensive.
When a computer requires storage, RAM is the first resource used. Virtual memory, which is slower, is used only when the RAM is filled.
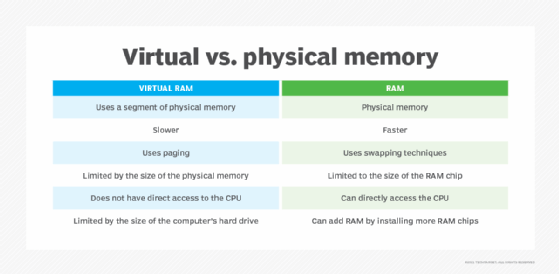
Users can actively add RAM to a computer by buying and installing more RAM chips, such as dual in-line memory modules (DIMMs). Adding RAM is useful if the system's slowdowns are due to memory swaps happening too often. The amount of RAM depends on what is installed on a computer. Virtual memory, on the other hand, is limited by the size of the computer's hard drive or SSD. Virtual memory settings can often be controlled through the OS.
In addition, RAM uses swapping techniques, while virtual memory uses paging. While physical memory is limited to the size of the RAM chip, virtual memory is limited by the size of the hard disk or SSD. RAM also has direct access to the CPU, while virtual RAM does not.
The history of virtual memory
Before virtual memory was developed, computers had RAM and secondary memory. Early computers used magnetic core memory for main memory and magnetic drums for their secondary memory. Computer memory was expensive and was usually in short supply back in the 1940s and 1950s. As computer programs grew in size and complexity, developers had to worry that their programs would use up all of a computer's main memory and run out of memory.
In those early days, programmers used a process called overlaying to run programs that were larger than available memory. Parts of a program that were not continually in use were set up as overlays that, when needed, would overwrite the existing overlay in memory. It required extensive programming to make overlaying work, and that was a key impetus for the development of automated virtual memory.
German physicist Fritz-Rudolf Güntsch has been credited with developing the concept of virtual memory in 1956, although this point has been contested. Güntsch did, however, end up describing a form of cache memory.
The first apparent real instance of a virtual memory system came from the University of Manchester in Manchester, England, in its attempt to develop a one-level storage system for the Atlas computer. The system used paging to map virtual addresses to a programmer onto the primary memory. Atlas was developed in 1959 and later commissioned in 1962.
In 1961, the first commercial computer with virtual memory was released by Burroughs Corp. This version of virtual memory used segmentation, as opposed to paging.
In 1969, IBM researchers demonstrated that virtual memory overlay systems worked better than the earlier manual systems. Mainframes and minicomputers in the 1970s generally used virtual memory. Virtual memory technology was not included in early PCs because developers thought running out of memory would not be a problem with those machines. That assumption proved incorrect. Intel introduced virtual memory in the protected mode of the 80286 processor in 1982 and paging support when the 80386 came out in 1985. Virtual memory is an important part of Microsoft's Windows family of OSes.
The future of virtual memory
Considering the ways computing systems are being used today, such as for data analytics and AI, there is likely to be an ongoing need to have memory resources that can adapt and scale to address computing requirements.
Among the important developments of virtual memory that portend a strong future are the use of cloud computing technology to increase virtual memory capacities, faster non-volatile memory technologies, increased use of AI to enhance memory functionality and security, and advances in quantum computing technology to further increase virtual memory performance.
Physical memory alone was insufficient for storage systems. To alleviate the performance burden and complement the physical form, computer architects developed virtual memory. Further explore how physical vs. virtual memory compare.







