virtual address
What is a virtual address?
A virtual address is a binary number in virtual memory that lets a process use a location in primary storage (main memory) or, in some cases, secondary storage. Virtual memory abstracts the physical memory by providing each process with a set of virtual addresses that enables it to use a block of physical memory independently of other processes.
The simplest way to think of a virtual address is as a pointer to a physical address, which is a specific location in primary or secondary storage. The physical address is typically in a primary storage device such as dynamic random access memory, but might be a secondary storage device such as a solid-state drive or hard disk drive. Because a virtual address can point to a secondary storage device, data can be temporarily relegated to that device when a process requires more space than what is available in main memory.
Memory management and virtual addresses
When a process is launched on a computer, the operating system (OS) assigns a set of virtual addresses to the process, providing it with the memory it needs to carry out its operations. This set of addresses is referred to as the process's virtual address space. The address space is private and cannot be accessed by other processes unless it has been specifically shared.
To support memory allocation, the OS divides the computer's memory into regular-sized pages -- usually 4 kilobytes (KB) -- and assigns a physical address to each one. The OS also maintains a page table for each process that maps the virtual addresses to the physical addresses. All operations that read or write data to memory use the virtual addresses exclusively; they have no knowledge of the physical addresses.
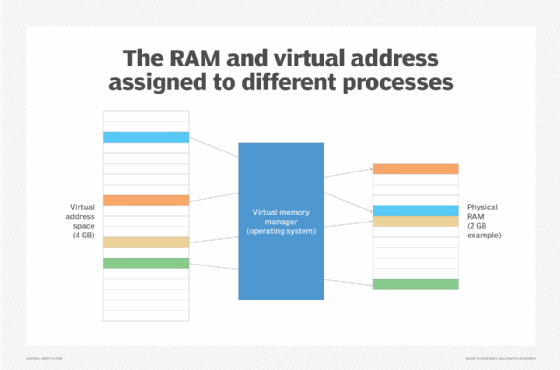
The processor's memory management unit (MMU) maintains the page table and handles all the translation operations between the virtual and physical addresses. The MMU is a hardware component in the central processing unit that manages all the processor's memory and caching operations. The MMU might be integrated directly into the processor or set up as a separate integrated circuit.
The MMU allocates memory to the individual process, translates the addresses for that process and deallocates memory when it is no longer needed. The translation operations are invisible to the running process, allowing it to "think" that it has all the primary storage to itself. In addition, the MMU includes the translation lookaside buffer, which caches recent translations, helping to accelerate access times to memory.
Translating virtual addresses
A virtual address is made up of two parts: a virtual page number and the page offset. The OS assigns the page numbers to virtual memory, creating virtual pages. The virtual page numbers point to the physical page numbers in the page table, as shown in the figure below. The page offset is not included in the page table because it is the same in the virtual address and physical address, so no translation is needed. The offset provides a pointer for locating a specific byte within the referenced page.
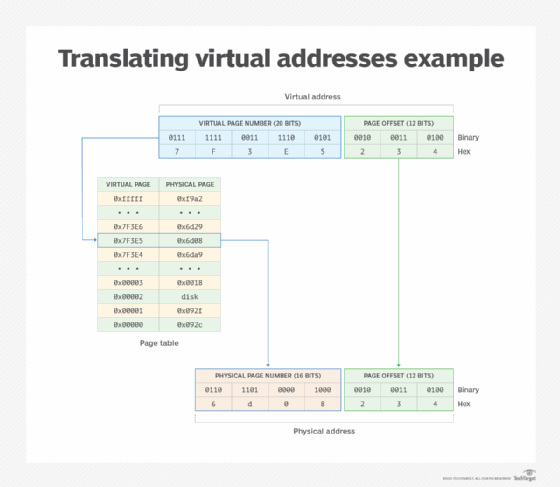
The figure shows a simplified overview of what a virtual address and its translation might look like on a 32-bit system. In this case, the virtual address has a hexadecimal value of 0x7F3E5234, which is equivalent to the following binary value: 0111 1111 0011 1110 0101 0010 0011 0100.
Moving from right to left, the first 12 bits (0010 0011 0100) are the page offset, and the last 20 bits (0111 1111 0011 1110 0101) represent the virtual page number. A 12-bit offset is used because that's what's needed to support all the possible locations in a 4 KB page, which requires 12 bits to address all the positions within the page.
Together, these two portions add up to 32 bits. This size address can support up to 1,048,576 virtual page numbers ranging from 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 to 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 in binary or 0x00000 to 0xfffff in hexadecimal.
The MMU uses the page table to map the virtual page number to the physical page number. In this example, the physical page number has a binary value of 0110 1101 0000 1000 or hexadecimal value of 6d08. The hexadecimal value for the entire physical address is 6d08234, which is equivalent to the following binary value: 0110 1101 0000 1000 0010 0011 0100.
Each physical page number on this system is 16 bits, so the physical address is only 28 bits total, when counting the 12-bit page offset. This is the same page offset as the one in the virtual address, so no translation is necessary.
The 16-bit page number can support only 65,536 physical addresses, a number significantly less than the number of virtual addresses supported by the 20-bit virtual address number. Virtual memory and its addresses make it possible to assign more memory resources to a process than what is available in primary storage. The OS manages these differences in the background. For example, the OS might delay loading parts of an application or swap out files to secondary storage, which is why the page table can also point to physical addresses in secondary storage.
Learn about memory management techniques that will improve system performance.
