memory management unit (MMU)
What is a memory management unit (MMU)?
A memory management unit (MMU) is a computer hardware component that handles all memory and caching operations associated with the processor. In other words, the MMU is responsible for all aspects of memory management. It's usually integrated into the processor, although, in some systems, it occupies a separate integrated circuit (IC).
Effective memory management requires systems administrators to consistently monitor memory use and performance. Tools to help with this process are included in a computer OS and are available for third-party vendors.
What does an MMU do?
The work of the MMU falls into three major categories:
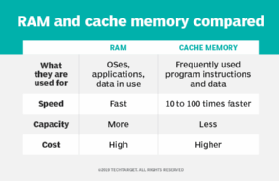
- Hardware memory management oversees and regulates the processor's use of random access memory and cache memory.
- OS memory management ensures adequate memory resources are available for the objects and data structures of each running program.
- Application memory management allocates each individual program's required memory, then recycles freed-up memory space when the operation concludes.
How does the MMU work?
Next to the central processing unit (CPU), memory is the most important part of a computer. It's where the work gets done and where instructions and other computing functions are performed. Memory ensures a computer's utilities work correctly and applications and input/output functions are performed.
An MMU is an essential part of memory subsystems, keeping all memory-related functions operating efficiently. Memory management helps with the following functions:
- Memory distribution. The MMU moves memory resources to where they can best meet system requirements, typically before and after systems processes are executed.
- Monitoring. It tracks all memory resources.
- Efficiency. It conserves main memory and other memory resources.
- System integrity. It reduces the likelihood of memory fragmentation and poor memory allocation.
- Data integrity. It ensures data integrity is maintained.
- Data risk. It minimizes the risk of data corruption.
- Cost control. It keeps memory-related costs down.
Physical vs. logical memory management
The main differences between logical and physical memory are the following:
- Logical memory. Logical memory addresses -- also called virtual address space-- are created by the CPU and execute many different functions. Logical memory is also called virtual memory because its size can be dynamically changed based on user processing requirements.
- Physical memory. In contrast, the MMU computes physical addresses. They're then loaded into the memory address register of the memory subsystem, which is also called physical memory. When physical addresses contain logical addresses, they're called the physical address space. In contrast to logical addresses, physical addresses don't change.
Best practices for memory management
System administrators must regularly monitor memory system performance metrics, such as the following:
- available memory,
- memory use,
- paging activity and
- fragmentation.
The key to effective memory management and memory protection is having the right tools, such as those provided by the OS and third-party memory management applications. It's also important to respond to alarms based on problems with memory functions and blocks of memory, and to perform proactive maintenance activities to ensure memory resources are optimized.
Learn about memory management techniques that will improve system performance.
