Wi-Fi (802.11x standard)
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is a term for certain types of wireless local area networks (WLAN) that use specifications in the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. For example, Wi-Fi Direct is a peer-to-peer specification that allows devices certified for Wi-Fi Direct to exchange data without an internet connection or a wireless router. Products that pass Wi-Fi Alliance tests for interoperability, security and application-specific protocols are labeled "Wi-Fi CERTIFIED," a registered trademark of the Alliance.
Advances in wireless technology over the past several decades have made the convenience and portability of mobile devices nearly ubiquitous. Users are no longer tethered by a landline, whether on a home network or in a business office. Advances in wireless technology standards make it a convenient, efficient and secure way to provide significant broadband bandwidth.
The term Wi-Fi was coined by the Wi-Fi Alliance as a play on Hi-Fi, an abbreviation for high fidelity, which referred to high-quality audio reproduction. Wi-Fi is often thought to be short for wireless fidelity. However, according to the group, Wi-Fi isn't an abbreviation. The confusion might stem from the fact that the Alliance briefly used, "The standard for wireless fidelity," as a slogan for Wi-Fi.
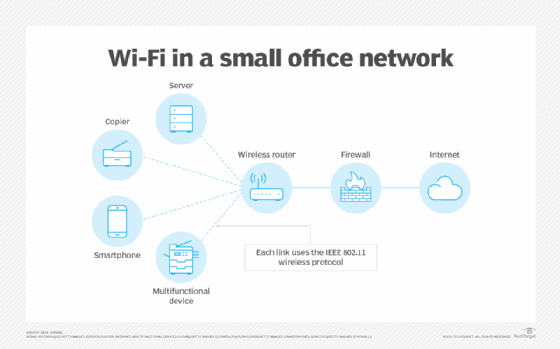
How does Wi-Fi work?
A Wi-Fi network uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit information across a LAN. A Wi-Fi range extender can be used to extend the network's reach. Computers use wireless adapters to translate data transmitted by radio waves. These waves differ from those FM or AM radios emit where the frequency is measured in megahertz (MHz). Wi-Fi signals are transmitted in frequencies between 2.5 and 5 gigahertz (GHz). This signal is transmitted from the adapter through a router and is then sent to the internet.
Each device on the network connects wirelessly to the Wi-Fi router. The router, in turn, connects to the internet. The connected devices can communicate with one another as well. A firewall provides security from unauthorized external access. However, the internal wireless links can be breached if the technology used doesn't have sufficient security built into the router and each device.
Who uses Wi-Fi and why?
Wi-Fi technology is predominantly used in homes, offices and any area that can benefit from wireless communications and portability. It's usually available in schools, libraries, airports, hotels and other venues where public Wi-Fi is available.
Wi-Fi offers users the convenience of wireless internet access, which eliminates the need for cables. It provides flexibility in device placement and makes it easier to share a single internet connection across multiple devices. It can also be more cost-effective compared to wiring an infrastructure.
Wi-Fi is useful for a range of activities, including browsing the web, checking emails, streaming video and audio content, online gaming and remote working. It's an essential technology that offers convenience, accessibility and increased productivity for users worldwide.
What are hotspots?
A Wi-Fi connection is used as an alternative to a wired LAN. Many airports, hotels and fast-food facilities offer free Wi-Fi connections to public access networks, but they may require registration to access the network. These wireless connection locations are known as hotspots. Businesses offer mobile hotspots as a convenience to customers and consider them a competitive advantage. Some businesses may charge a daily or hourly fee for access. An interconnected area of hotspots and network access points is known as a hot zone.
Modern smartphones and tablets are also able to turn into Wi-Fi hotspots. They use cellular network connections to provide wireless internet connectivity to computers and other wireless devices.
To access Wi-Fi hotspots, computers must include wireless adapters. These can be found on laptops and mobile devices, such as tablets or cellphones. If a computer doesn't include an adapter, one can be purchased and inserted into a PCI slot or USB port. Then the device should be able to locate Wi-Fi networks in the area. These can be open or protected networks; users must have a Wi-Fi password to join a protected network.
A Wi-Fi network that isn't adequately protected is susceptible to access by unauthorized users looking for a free internet connection. The activity of locating and exploiting a vulnerable wireless LAN is called war driving. An identifying iconography, called warchalking, has evolved to identify public places with open Wi-Fi networks.
Any entity that has a wireless LAN should use security safeguards. These include the following:
- The Wired Equivalent Privacy encryption standard.
- The more recent Wi-Fi Protected Access.
- Internet Protocol Security.
- A virtual private network, or VPN.
IEEE 802.11 standards
Originally, Wi-Fi certification applied only to products using the 802.11b standard. Today, Wi-Fi refers to products that use any 802.11 standard. The 802.11 specifications are part of an evolving set of wireless network standards known as the 802.11 family. The specification under which a Wi-Fi network operates is called the flavor of the network.
Following is a list of legacy 802.11 Wi-Fi standards and their capabilities. The IEEE considers these to be superseded standards. Their fundamental properties have been retained -- with updates and refinements -- in the current active Wi-Fi standards, which follow this list.
| Legacy standard | Description and capabilities |
| 802.11 | The original 1999 WLAN media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications. |
| 802.11a | |
| 802.11b |
|
| 802.11d |
|
| 802.11e |
|
| 802.11g |
|
| 802.11h |
|
| 802.11i |
|
| 802.11j |
|
| 802.11k | Radio resource measurements for networks using 802.11. |
| 802.11m | Maintenance of 802.11 specifications, and corrections and amendments to existing documentation. |
| 802.11n |
|
Source: IEEE 802.11 Standards Association
The following are active IEEE standards in the 802.11 family of standards. These standards retain the original capabilities of 802.11 but define more recent modifications and revisions to 802.11.
| Active standards | Description and capabilities |
| 802.11-2020 | Corrects an error in the position of the Protected Announce Support field in the Extended RSN Capabilities field in the RSN Extension element. |
| 802.11ax-2021 | Updates 802.11-2020 by modifying 802.11 PHY and MAC sublayer for high-efficiency operation in frequency bands between 1 GHz and 7.125 GHz. |
| 802.11ay-2021 | Modifies the 802.11 PHY and MAC sublayer to provide at least one mode of operation that can support a maximum throughput of at least 20 Gbps. |
| 802.11az-2022 |
|
| 802.11ba-2021 | Modifies the 802.11 PHY and MAC sublayer to support wake-up radio operation. |
| 802.11bd-2022 | Modifies the 802.11 PHY and MAC sublayer to support next-generation vehicle-to-everything communications in the 5.9 GHz and 60 GHz frequency bands. |
| 8802-11-2022 | Provides technical corrections and clarifications to 802.11 plus updates to MAC and PHY functions. |
| 8802-11-2018; Amd 3-2020 | This amendment updates MAC address and PHY functions to support operation in the Chinese millimeter frequency bands at 45 GHz and 60 GHz. |
| 8802-11-2018; Amd 4-2020 | Enhances the ability of 802.11 media to provide transit links internal to IEEE 802.1Q bridged networks. |
| 8802-11-2012; Amd 1-2014 | Specifies how management frames are prioritized and provides a protocol for achieving this activity. |
| 8802-11-2012; Amd 3-2014 | Modifies the rules for the MAC and PHY layers to support operation in frequencies around 60 GHz and the ability to support very high transmission speeds. |
Source: IEEE 802.11 Standards Association
Wi-Fi is one part of the full wireless infrastructure picture. Learn everything you need to know about wireless communication in our guide.







