What is mobile hotspot?
A mobile hotspot is a portable hardware device or software that serves as a wireless access point for connecting devices to the internet. It provides Wi-Fi routing capabilities similar to a home wireless router, except on a smaller scale.
A mobile hotspot is the transportable version of a stationary hotspot, which also facilitates Wi-Fi access to the internet but within a fixed location. Alternatively, a mobile hotspot can be established -- and relocated to -- virtually anywhere with a power supply and data connection.
Mobile hotspots can take the form of standalone devices, or other devices like smartphones, or laptops can use software to activate hotspot capabilities. Creating a mobile hotspot with a smartphone effectively turns the device into a router. Nearby devices such as laptops or tablets can interface with the mobile hotspot much as they do with other wireless routers. The mobile hotspot connects to the internet via a wireless cellular signal, rather than relying on a standard data signal.
Mobile hotspots are also known by various other names, such as portable hotspots, Wi-Fi hotspots, portable Wi-Fi hotspots and pocket routers. In some cases, mobile hotspots are referred to as travel routers. However, travel routers are a different type of device that usually rely on public Wi-Fi or Ethernet connections to enable internet access, rather than cellular signals.
How does a mobile hotspot work?
A mobile hotspot works by converting a 3G, 4G or 5G signal to a Wi-Fi signal and vice versa. It creates a Wi-Fi network that can be shared by multiple devices within a certain range of physical distance -- usually about 10 meters (32 feet) -- of the hotspot. This functionality is called tethering. The device is meant to be portable so that it can be used in locations such as cars, trains, coffee shops or hotel rooms, rather than be restricted to a specific location, as is the case with a home or business router. A mobile hotspot requires only a viable cellular signal to facilitate other devices' connections to the internet.
All modern smartphones include hotspot functionality, so the user can turn on a hotspot in just one or two steps.
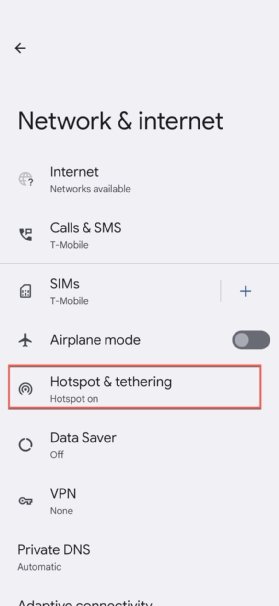
For example, the settings menu on Android devices includes a "mobile hotspot" icon that only needs to be turned on. When the hotspot is on, the hotspot name will be visible in the device's settings under Wi-Fi options.
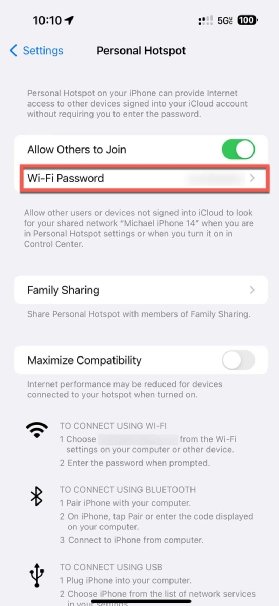
It's equally easy to set up a hotspot on iOS devices. The user needs to open the Settings menu, go to the Cellular section, and turn on Personal Hotspot. Finally, to allow other devices to connect, the Allow Others to Join setting should be turned on.
Types of mobile hotspot devices
There are two types of mobile hotspot devices: smartphones with built-in tethering capabilities and dedicated hardware devices built specifically to act as mobile hotspots.
When smartphones are used as mobile hotspots, they are sometimes referred to as cellphone hotspots or phone hotspots. Most modern smartphones support tethering, which means that they can share their internet connection with other devices. To use this feature, the phone must be connected to a cellular network, with the phone's tethering feature enabled. Also, the phone's cellular service plan must support tethering. This feature has become increasingly common in recent years, so it's rare to encounter a smartphone that doesn't have built-in tethering capabilities.
When a smartphone hotspot is activated, the phone cannot be connected to a Wi-Fi network at the same time. This is because its Wi-Fi capabilities are used to create the hotspot. However, a user can continue to use the device as they normally would when tethering is enabled. For example, they can exchange email or text messages, browse the internet, watch online videos or use mobile apps.
Smartphone tethering can be convenient, but it does come with limitations. Most service plans limit the amount of data that can be used for tethering, and multimedia-heavy services can use up data quickly. In addition, tethering can drain the phone's battery, especially if multiple devices are connected. For these reasons, smartphone tethering tends to be better suited for occasional use and if alternate options are unavailable.
Dedicated hotspot devices are another form of mobile hotspot. Favored by frequent travelers, dedicated hotspots are pocket-sized devices that contain a SIM card for connecting to a cellular network. Most wireless carriers sell dedicated mobile hotspot devices, along with wireless data plans that support the devices.
Dedicated mobile hotspot devices typically run on rechargeable batteries like smartphones, but some can also be plugged into a power source. Given they do not support any other applications or services, they often have a longer battery life. Dedicated mobile hotspots can also support a greater number of connecting devices than a smartphone.
Dedicated mobile hotspots are also known as dedicated hotspots, mobile hotspot devices or simply mobile hotspots. Many companies offer dedicated portable routers known as MiFis (short for mobile Wi-Fi). These devices connect wirelessly to a cell tower to create a portable Wi-Fi network that internet-enabled devices can then use to connect to the internet.
Newer 5G hotspots enable high-speed, low-latency internet access than prior generations of the technology. 5G hotspots also support more devices and typically have a longer battery life than 3G or 4G devices. They work over 5G cellular networks, so the device (smartphone or dedicated device) must support 5G speeds.
Mobile hotspots and Bring Your Own Network (BYON)
Most organizations provide Wi-Fi services to enable their employees to connect to the internet for work purposes. However, employees might also use their own mobile hotspots at work or home, a process sometimes referred to as bring your own network (BYON).
BYON means that employees use their own cellular or Wi-Fi service to set up a mobile hotspot that then allows them to access work resources like files, systems and data, even if they are away from the corporate network. They might have good reasons for doing this. For example, they might be working remotely and cannot physically access the corporate WAN or LAN. Or they might be traveling and want to save money by using a local cellular service provider instead of an expensive roaming cellular service. A third reason for adopting BYON might be that remote or traveling employees might not want to rely on insecure public Wi-Fi networks to do their work.
Safety concerns with mobile hotspots and BYON
BYON helps to extend corporate networks across disparate geographic locations, allowing growing organizations to connect employees in more locations than traditional IT resources can support. BYON also offers a convenient and cost-effective way for employees to access the internet. With proper protections in place, mobile hotspots are also safer than public Wi-Fi. However, they can also introduce cybersecurity risks into the corporate network.
For example, an employee who uses a smartphone to create a mobile hotspot at work might be simultaneously connected to three networks: the carrier's cellular network, the employee's mobile hotspot and the corporate network via a virtual private network (VPN) connection. If the endpoint, cellular network or personal hotspot were compromised in any way, sensitive corporate data could be at risk. If the device is not included in the company's security perimeter, enterprise security infrastructure and services might not be able to safeguard the device -- ultimately exposing the organization and its data. A third risk is that the connection between the device and any websites its user visits might not be encrypted, allowing criminals to eavesdrop and steal data like login credentials.

Strategies to address the security risks of mobile hotspots
Businesses can minimize the risks of BYON and mobile devices by adopting a BYON solution that can protect employee devices, secure traffic between the devices and the corporate network, and safeguard the corporate network from external threats. The most effective solutions extend corporate-level security to remote networks, ensuring that sensitive data never gets exposed. These tools prevent breaches while also respecting employees' privacy.
It's also important to implement a BYON policy that defines the acceptable use of personal devices, disallows unauthorized devices from accessing the corporate network, and addresses both the organization's security requirements and employees' privacy concerns. The policy should clearly state which corporate resources employees can access from their personal devices and mobile hotspots. It should also specify the minimum security controls required for each personal device, the methods used by the company for authenticating the devices (e.g., SSL certificates) and the company's rights to modify the devices for security purposes (e.g., remote wiping if a device is lost or stolen).
Employee education is also vital to minimize BYON risks. Organizations must teach remote employees about the risks of using their device as a mobile hotspot and strategies to mitigate these risks, including by improving their cyber hygiene and following the organization's standard cybersecurity best practices.
Individuals can also take steps to protect themselves by doing the following:
- Using a strong password for their private (e.g., home) Wi-Fi network.
- Filtering out unnecessary ports by using the device's port filtering feature.
- Randomizing and lengthening the display name of the hotspot's Wi-Fi network.
- Using a VPN for all the devices connecting to the hotspot to encrypt the connection between the devices and the internet.
Learn how to troubleshoot when a hotspot is not working on Android and fix an iPhone Personal Hotspot. Find out if a hotspot works when a mobile device has no service. See how to improve mobile hotspot security in a few steps and explore the differences between a wireless access point and a router.
