What is hacktivism?
Hacktivism is the act of misusing a computer system or network for a socially or politically motivated reason. Individuals who perform hacktivism are known as hacktivists.
Hacktivism is meant to call the public's attention to something the hacktivist believes is an important issue or cause, such as freedom of information, human rights or a religious point of view. Hacktivists express their support of a social cause or opposition to an organization by displaying messages or images on the website of the organization they believe is doing something wrong or whose message or activities they oppose.
Hacktivists are typically individuals, but there are hacktivist groups as well that operate in coordinated efforts. Anonymous and Lulz Security, also known as LulzSec, are examples. Most hacktivists work anonymously.
What motivates hacktivists?
Hacktivists usually have altruistic or ideological motives, such as social justice or free speech. Their goal is to disrupt services and bring attention to a political or social cause. Modern motivations also include climate activism, opposition to authoritarian regimes and combatting disinformation campaigns.
For example, hacktivists might leave a visible message on the homepage of a website that gets a lot of traffic or embodies a point of view that the individual or group opposes. Hacktivists often use denial-of-service or distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks where they overwhelm a website and disrupt traffic.
Hacktivists want others to notice their work to inspire action or change. They often focus on social change but also target government, business and other groups that they don't agree with for their attacks. Sending a message and eliciting change trump profit motives for hacktivists.
The rise of hacktivism in the digital era
The internet and advancements in technology have created a fertile ground for hacktivism. With the growth of social media, encrypted communication tools and decentralized networks, hacktivists now have more tools than ever to organize and execute their campaigns.
- Social media amplification. Social platforms have become a battleground for hacktivists, allowing them to share their messages with millions in real time. Campaigns like the Arab Spring benefited significantly from online activism supported by hacktivist groups.
- Cryptocurrency and anonymous funding. The advent of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies like bitcoin has provided hacktivists with a way to fund their activities anonymously, bypassing traditional financial systems.
- Targeting misinformation. Hacktivist campaigns increasingly focus on exposing misinformation and propaganda, with efforts targeting media outlets, political campaigns and even social media platforms.
- Hacktivism and AI. AI-powered tools now enable hacktivists to automate their activities, such as using phishing campaigns or identifying vulnerabilities in systems faster than ever before.
What is the difference between a hacker and a hacktivist?
Hackers and hacktivists generally use the same tools and techniques to achieve their goals. Unlike hacktivists, hackers are not defined solely by social causes. The answer to the question, "Is hacktivism good or bad?" is a point of debate. The legality of hacktivist acts is less contentious.
DoS and DDoS attacks are federal crimes in the United States under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act. Those types of attacks are illegal in many other places as well, including the European Union, United Kingdom and Australia. Website defacement, where attackers access a website and change its contents, is considered cyber vandalism and is a crime. Corporate data theft is also illegal.
Opponents of hacktivism argue that these acts cause damage in a forum where there is already ample opportunity for non-disruptive free speech. Others insist that such acts are the equivalent of peaceful protest and, therefore, are protected as a form of free speech. Hacktivists often consider their activities a form of civil disobedience, meaning they willfully break a law to further their protest.
Types of hacktivism
Hacktivists use a variety of techniques to get their message across. Their tactics include the following:
- Anonymous blogging. Activists, whistleblowers and journalists use this tactic. It protects the blogger, while providing a platform for them to speak out about an issue, such as human rights violations or oppressive government regimes.
- DoS and DDoS attacks. Hacktivists use these attacks to prevent users from accessing targeted computer systems, devices or networks. DoS and DDoS attacks flood systems with traffic, overwhelm resources and make them difficult to access.
- Doxing. This involves the gathering of information -- through hacking or social engineering -- about a person or organization and making it public. The information is typically sensitive and is sometimes used in extortion schemes.
- Geobombing. This technique enables internet users to add a geotag to YouTube videos to display the location of the video on Google Earth and Google Maps. Hacktivists use geobombing to display the location of videos posted by political prisoners and human rights activists.
- Leaking information. This is a popular activist tactic. Typically, an insider source will access sensitive or classified information -- which implicates an individual, organization or government agency in an activity that reflects negatively on them -- and make it public. WikiLeaks is known for publishing leaked data.
Recently, whistleblowers have exposed financial corruption, environmental violations and political scandals through strategically leaked documents.
- RECAP. This software lets users search for free copies of documents that are otherwise only accessible by paying a fee to the United States federal court database known as Public Access to Court Electronic Records (PACER). RECAP is PACER spelled backward.
- Website defacement. Hacktivists change website code or software so visitors see errors or messages expressing the attacker's point of view. The message may be threatening or embarrassing, or the attack may disable a key function of the site or software to get the hacktivist's message across.
- Website mirroring. Here, hacktivists replicate a legitimate website's content but with a slightly different URL. This technique is often used to get around censorship that blocks a site. If a website has been censored, the hacktivist will duplicate the content and attach it to a different URL on a mirror site so the content is still accessible.
Distributed denial-of-service attacks around the world
DDoS attacks have become a common tool of hacktivists and hackers to send a message, garner attention or affect public affairs in some way. For example, China's Great Cannon DDoS operation was used in 2019 against pro-democracy organizers in Hong Kong.
Another example is the DDoS attack that targeted the U.K.'s Labour Party in the lead-up to the Dec. 12, 2020, election. Notorious hacking group Lizard Squad claimed responsibility for the attack. The group is known for initiating large-scale, public DDoS attacks.
Attacks of this type and other cybersecurity threats continued to spike with the increase of remote workers after the COVID-19 pandemic. Whether the attacks are motivated by morality, profit, political power or reasons that are unclear, the cybersecurity industry is preparing for all manner of attack.
Emerging threats in hacktivism
In addition to the aforementioned forms of hacktivism, several new forms have emerged in recent years. These include the following:
- AI-powered hacking. Hacktivists increasingly use artificial intelligence to identify vulnerabilities and automate attacks, making their campaigns faster and harder to counteract.
- State-sponsored hacktivism. Governments are suspected of covertly supporting hacktivist groups to target political adversaries or spread disinformation, blurring the lines between hacktivism and cyberwarfare.
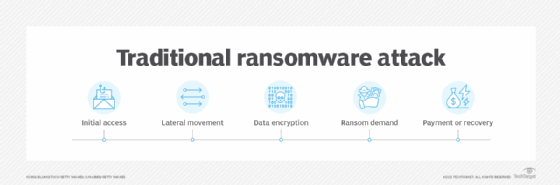
- Ransom hacktivism. This involves hacktivists encrypting data and demanding concessions instead of money, using ransomware for political or social goals.
Examples of hacktivist groups
Many hacktivist groups keep a low profile. The following are among the more well-known organizations.
Cult of the Dead Cow
This group, also known as cDc Communications, was founded in 1984 as a hacking collective and media organization. Its original stated goal was "global domination through media saturation," but it eventually evolved into a more political focus on human rights and the free flow of information. In the mid to late 1990s, the group focused on combating human rights abuses in China. During this initiative, a member of the group who went by the name Omega coined the term hacktivism when communicating with Chinese hacktivists via a group email.
CDc spun off two other hacktivist groups: Ninja Strike Force, founded in 1996, and Hacktivismo, formed in 1999. Hacktivismo focused on creating anti-censorship technology. It took a unique stand against using DoS attacks, saying it viewed disabling websites as counter to the principle of free speech online. Hacktivismo also published a code of conduct for civil disobedience online, entitled the "Hacktivismo Declaration," in which it said it would challenge state-sponsored censorship of the internet. CDc and Hacktivismo are credited with putting a positive spin on the term hacker.

Anonymous
This decentralized, international group has become one of the most well-known hacktivist groups because of several high-profile attacks. Anonymous first appeared in 2003 on the 4chan forums and came into the spotlight in 2008 when it attacked the Church of Scientology. The group has adopted the Guy Fawkes mask from the graphic novel by Alan Moore and film V for Vendetta as its symbol. The group often uses the tagline "We are Anonymous. We are Legion. We do not forgive. We do not forget. Expect us."
Anonymous' members do not identify themselves. Nevertheless, several individuals associated with the group have been arrested for illegal activities. The group is known to use controversial techniques, such as doxing, and it has declared war on politicians, including Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton, and supported the Occupy Wall Street movement.
In 2022, Anonymous declared cyberwar against Russian government entities following the invasion of Ukraine, claiming responsibility for attacks on state media and leaking sensitive data.
WikiLeaks
Julian Assange launched the WikiLeaks website in 2006 to host leaked documents, describing itself as an independent, nonprofit online media organization. The first notable documents published on the site were the nearly 80,000 documents about the U.S. war in Afghanistan leaked in 2010, followed by nearly 400,000 documents about the war in Iraq. WikiLeaks is also known for revealing over 20,000 emails and 8,000 email attachments from the Democratic National Committee that were sent during the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign.
LulzSec
Five members of Anonymous started LulzSec in 2011 and use handles but no other identifying information. The most significant LulzSec attack was when it took down the Federal Bureau of Investigation's website in 2011. The attack precipitated the arrest of several members.
Syrian Electronic Army
This group of Syrian hacktivists also surfaced in 2011 and claims to support Syrian president Bashar al-Assad. The group was hosted on Syria's national public networks and aims to defend the Syrian government's reputation and to attack computer systems deemed a threat to Syria. The group gained attention in April 2013 when it performed several DDoS and defacement attacks against U.S. government agencies and companies, including a fake tweet about an explosion at the White House that injured the president.
Longstanding, influential hacktivist groups, like Anonymous and WikiLeaks, continue to make themselves heard. Investigative journalist Nicky Hager described the impact of WikiLeaks publishing the Iraq War Logs and a video of a U.S. helicopter firing on civilians.
Ethical debate: Is hacktivism good or bad?
The answer to whether hacktivism is good or bad depends on one's perspective. Supporters liken hacktivism to digital civil disobedience, arguing that it exposes corruption and advocates for justice.
Critics counter that hacktivist activities often violate laws, disrupt essential services and risk harming innocent individuals. Furthermore, the potential for misuse of stolen data raises ethical and privacy concerns.
Legal repercussions for hacktivists can be severe. Acts such as DDoS attacks, website defacement and corporate data theft are federal crimes in many countries, punishable by hefty fines and imprisonment.
How to protect against hacktivism
Organizations can take the following steps to protect themselves:
- Implement advanced firewalls. Use firewalls that can detect and mitigate DDoS attacks.
- Encrypt sensitive data. Strong encryption can prevent leaked data from being easily exploited.
- Regular security audits. Identify and patch vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
- Educate employees. Ensure employees recognize phishing attempts and suspicious activity.
- Use threat intelligence. Stay updated on hacktivist campaigns and threats targeting your sector through threat intelligence.
Hacktivism sits at the intersection of technology and activism, offering a digital platform for individuals and groups to advocate for change. While its methods and impacts remain controversial, its influence on modern social and political landscapes is undeniable.
Does your organization's threat intelligence program need updating? Most do. Find out the best approach to automating and modernizing a threat intelligence strategy. Also, learn about the different types of firewalls, explore top seven enterprise cybersecurity challenges, see how to fix the top five cybersecurity vulnerabilities and read about the types of security incidents and how to prevent them.





