electronically stored information (ESI)
What is electronically stored information (ESI)?
Electronically stored information (ESI) is data that is created, altered, communicated and stored in digital form. The term itself was legally defined in 2006 following revisions made to the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (FRCP) to help with electronic discovery (e-discovery) and litigation pertaining to electronic records.
Types of electronically stored information
Any document or information stored in electronic form constitutes ESI. The information may be structured or unstructured. It may also be written (textual), visual or aural. Thus, all the following can be considered ESI:
- Documents.
- Graphs.
- Charts.
- Drawings.
- Photographs.
- Videos.
- Images.
- Recordings.
- Spreadsheets.
- Emails and attachments.
- Voicemails and communication logs, including call logs and social media activity logs.
- Information stored in databases and the cloud.
ESI can be stored in or retrieved from many electronic sources, including computer hard disk or solid state drives; network servers; removable drives, such as USB drives; social media websites; devices connected to Wi-Fi, such as smartphones and tablet PCs; and IoT devices, such as smart watches and smart appliances.
United States Federal Rules of Civil Procedure and ESI
In December 2006, the United States FRCP were amended to include a new legal definition of ESI. Specifically, Rule 34(a)(1) -- a new and expansive rule -- defined ESI as "any type of information that is stored electronically," including documents and email, and "stored in any medium." Rule 34 was deliberately left broad enough to cover all computer-based information types that were available at the time as well as flexible enough to encompass future technological developments that may result in the emergence of new ESI types and media.
By defining ESI and how it should be managed, Rule 34 functions as a starting point for changes in the FRCP's e-discovery rules. Under this rule, one party (Party A) may present another party (Party B) with a legal request for Party A to "inspect, copy, test or sample" any designated documents or ESI stored by Party B in any medium. On receiving a discovery request from Party A for information pertaining to a lawsuit (that is subject to the FRCP e-discovery rules), Party B must take action to develop and produce a response to the request.
Since the 2006 amendments, courts in the United States are now legally allowed to oversee routine e-discovery processes during litigation cases. The amendments also do the following:
- Specify the early disclosure and discussion requirements for all counsel representing the parties involved in e-discovery and litigation.
- Define how inadvertent waivers of privilege should be addressed.
- Provide some protection for parties worried about information spoliation sanctions.
Allowable ESI formats under FRCS Rule 34
Rule 34 of the FRCS allows Party A to specify the form in which Party B must produce ESI, depending on which form has more utility for Party A. Thus, Party A may ask for some ESI to be produced as a paper printout and for others to be produced as an electronic document, such as a PDF file or TIFF image.
Per FRCS Rule 34, Party A is allowed to obtain the required information from Party B from the stored medium either directly or by requesting Party B to translate it into a "reasonably usable form." The purpose of translation is to ensure that it doesn't become difficult or burdensome for Party A to use the ESI efficiently in the litigation.
In general, Party B must produce ESI "either in a form or forms in which it is ordinarily maintained or in a form or forms that are reasonably usable." Also, if Party B objects to the form request or if Party A does not specify a particular form of production, Party B must state the form(s) it intends to use to produce the requested ESI.
ESI and e-discovery
The main purpose of ESI is to help parties involved in litigation with e-discovery processes. E-discovery is a crucial component of many legal cases and FRCS specifies the ways in which parties may request and provide information during e-discovery.
To ensure that they don't run afoul of FRCS rules if they are ever involved in a legal case, organizations must properly manage ESI, especially privileged information. Proper information management can ensure ESI is correctly identified during e-discovery and also protected from unauthorized or malicious users.
Proper ESI management includes the following:
- Knowing what kind of ESI is being produced and where it is being stored.
- Storing all privileged information in secure locations.
- Indexing/tagging/labeling information to enable easy search and retrieval.
- Optimizing the processes and policies for ESI capture, storage, access and use.
- Assigning proper roles and responsibilities to manage and protect ESI.
- Ensuring that there is a clear audit plan for all ESI so it can be tracked at any time during its lifecycle and its validity cannot be questioned.
- Implementing controls to prevent potentially important ESI from being deleted inadvertently or maliciously and ensuring its preservation for future legal purposes.
Per FRCS Rule 34, requested parties must produce ESI within 30 days. A comprehensive ESI management program can save organizations from having to scramble to find the requested information during litigation. It ensures smooth and hassle-free e-discovery within the mandatory timeline, and it lets the organization export and deliver the ESI in the format requested by the requesting party.
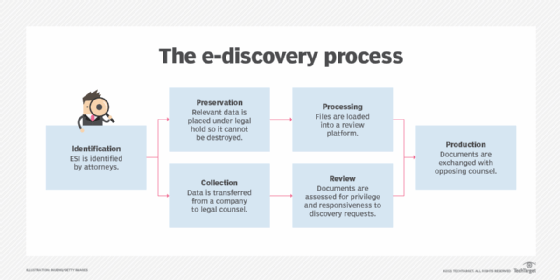
ESI management for e-discovery can be a complex process, so organizations may benefit by using e-discovery software. Applications are now available to easily preserve ESI; maintain its accuracy; and simplify the various parts of the e-discovery process, including ESI identification, collection, processing, review, production and presentation.
See why e-discovery in the cloud introduces security and compliance issues. Explore best practices to implement when preparing for an e-discovery request. Learn more about computer forensics and its role in risk management.








