data center
What is a data center?
A data center is a facility composed of networked computers, storage systems and computing infrastructure that organizations use to assemble, process, store and disseminate large amounts of data. A business typically relies heavily on the applications, services and data contained within a data center, making it a critical asset for everyday operations. The main components of a data center typically include routers, firewalls, switches, storage systems and application delivery controllers.
What is a modern data center?
In the past, data centers were highly controlled physical environments. However, modern infrastructures have shifted away from physical servers to virtualized environments, facilitating the deployment of applications and workloads across diverse multi-cloud environments.
Modern data centers can support a variety of workloads, from traditional enterprise apps to modern cloud-native services. These enterprise data centers increasingly incorporate facilities for securing and protecting cloud computing and in-house, on-site resources. They're designed to meet the growing demands of businesses for computing resources, while optimizing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
As enterprises turn to cloud computing and multi-cloud environments, conventional data centers are evolving, blurring the lines between the data centers of cloud providers and those of enterprises.
How do data centers work?
A data center facility, which enables an organization to collect its resources and infrastructure for data processing, storage and communications, includes the following:
- Systems for storing, sharing, accessing and processing data across the organization.
- Physical infrastructure for supporting data processing and data communications.
- Utilities such as cooling, electricity, network security access and uninterruptible power supplies (UPSes).
- Physical safety mechanisms, such as monitoring across the entire building, safety personnel, metal detectors and biometric systems.
Gathering all these resources in a data center enables the organization to do the following:
- Protect proprietary systems and data.
- Centralize IT and data processing employees, contractors and vendors.
- Apply information security controls to proprietary systems and data.
- Realize economies of scale by consolidating sensitive systems in one place.
Why are data centers important?
Data centers support almost all computation, data storage, and network and business applications for the enterprise. To the extent that the business of a modern enterprise is run on computers, the data center is the business.
Data centers are crucial for the following reasons:
- Information and storage processing. Data centers are essentially huge computers that store and process vast amounts of information, making them indispensable for tech firms and businesses that rely on digital data.
- Support for IT operations. Data centers support IT operations and critical applications, providing infrastructure for computing, storage and networking needs. They can be owned and operated by organizations, managed by third-party or public cloud providers, or rented spaces inside colocation facilities.
- Support for cloud technology. With the increasing reliance on cloud technology, cloud data centers have become popular. Tech companies dedicated to cloud computing typically operate cloud data centers, further emphasizing the significance of data centers in modern technology.
- Proximity and connectivity. Data centers are ideally located in areas that are minimally susceptible to natural disasters and near stable and reliable sources of electricity to ensure better internet connectivity. The closer a data center is to a business, the faster the overall internet speed is.
- Data management and security. Data centers house crucial organizational data, user data and important applications, making their security and reliability essential for businesses. They also offer scalability, security, efficiency and state-of-the-art technology to address the growing demands of businesses.
- Business agility and resiliency. As businesses become increasingly digitalized, data has become the most important asset in a digital economy. Data centers are essential for managing data and ensuring compliance and security, all of which are crucial for organizational adaptability and resilience.
What are the core components of data centers?
Elements of a data center are generally divided into the following primary categories:
- Facility. This includes the physical location with security access controls and sufficient square footage to house the data center's infrastructure and equipment.
- Networking equipment. This equipment supports the storage and processing of applications and data by handling tasks such as switching, routing, load balancing and analytics.
- Enterprise data storage. A modern data center houses an organization's data systems in a well-protected physical and storage infrastructure along with servers, storage subsystems, networking switches, routers, firewalls, cabling and physical racks.
- Support infrastructure. This equipment provides the highest available sustainability related to uptime. Components of the support infrastructure include the following:
- Power distribution and supplemental power subsystems.
- Electrical switching.
- UPSes.
- Backup generators.
- Ventilation and data center cooling systems, such as in-row cooling configurations and computer room air conditioners.
- Adequate provisioning for network carrier connectivity.
- Operational staff. These employees are required to maintain and monitor IT and infrastructure equipment around the clock.
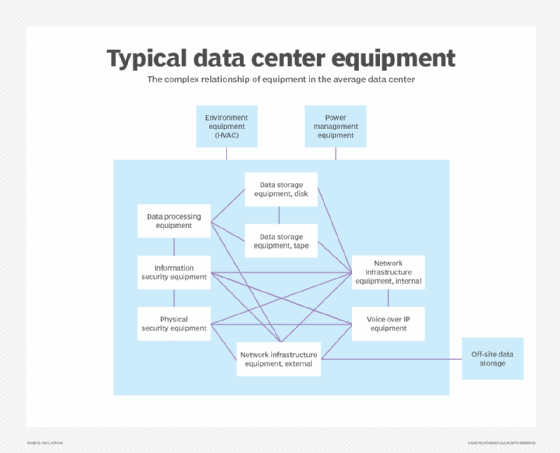
What are the types of data centers?
Depending on the ownership and precise requirements of a business, a data center's size, shape, location and capacity can vary.
Common data center types include the following:
- Enterprise data centers. These proprietary data centers are built and owned by organizations for their internal end users. They support the IT operations and critical applications of a single organization and can be located both on premises and off-site.
- Managed services data centers. Managed by third parties, these data centers provide all aspects of data storage and computing services. Companies lease, instead of buy, the infrastructure and services.
- Cloud-based data centers. These off-site distributed data centers are managed by third-party or public cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services, Google or Microsoft. Based on an infrastructure-as-a-service model, the leased infrastructure enables customers to provision a virtual data center within minutes.
- Colocation data centers. These rental spaces inside colocation facilities are owned by third parties. The renting organization provides the hardware, and the data center provides and manages the infrastructure, including physical space, bandwidth, cooling and security systems. Colocation is appealing to organizations that want to avoid the large capital expenditures associated with building and maintaining their own data centers.
- Edge data centers. These are smaller facilities that solve the latency problem by being geographically closer to the edge of the network and data sources. Edge data centers also enhance application performance and customer experience, particularly for real-time, data-intensive tasks, such as big data analytics, artificial intelligence and content delivery.
- Hyperscale data centers. Synonymous with large-scale providers, such as Amazon, Meta and Google, these hyperscale computing infrastructures maximize hardware density, while minimizing the cost of cooling and administrative overhead.
- Micro data centers. Micro data centers are compact design data centers associated with edge computing. While smaller than traditional data centers, micro data centers deliver comparable functionalities. They simplify edge computing setup through quick deployment, needing less space and power. A standard micro data center container or locker typically houses less than 10 servers and 100 virtual machines.
What are the standards of a data center?
Small businesses can operate successfully with several servers and storage arrays networked within a closet or small room, while major computing organizations might fill an enormous warehouse space with data center equipment and infrastructure. In other cases, data centers can be assembled in mobile installations, such as shipping containers, also known as data centers in a box, which can be moved and deployed as required.
However, data centers can be defined by various levels of reliability or resilience, sometimes referred to as data center tiers. In 2005, the American National Standards Institute and the Telecommunications Industry Association published standard ANSI/TIA-942, "Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard for Data Centers," which defines four tiers of data center design and implementation guidelines.
Tiers can be differentiated by available resources, data center capacities or uptime guarantees. The Uptime Institute defines data center tiers as follows:
- Tier I. These are the most basic types of data centers, and they incorporate a UPS. Tier I data centers don't provide redundant systems but should guarantee at least 99.671% uptime.
- Tier II. These data centers include system, power and cooling redundancy and guarantee at least 99.741% uptime. An annual downtime of 22 hours can be expected from a Tier II data center.
- Tier III. These data centers provide partial fault tolerance, 72 hours of outage protection, full redundancy and a 99.982% uptime guarantee.
- Tier IV. These data centers guarantee 99.995% uptime -- or no more than 26.3 minutes of downtime per year -- as well as full fault tolerance, system redundancy and 96 hours of outage protection.
Beyond the basic issues of cost and facility size, sites are selected based on a multitude of criteria, such as geographic location, seismic and meteorological stability, access to roads and airports, availability of energy and telecommunications, and even the prevailing political environment.
Once a site is secured, the data center architecture can be designed with attention to the mechanical and electrical infrastructure, as well as the composition and layout of the IT equipment. All these issues are guided by the availability and efficiency goals of the desired data center tier.
How are data centers managed?
Data center management encompasses the following:
- Facilities management. Managing the physical data center facility can include duties related to the real estate of the facility, utilities, access control and personnel.
- Data center inventory or asset management. Data center facilities include hardware assets, as well as software licensing and release management.
- Data center infrastructure management. DCIM lies at the intersection of IT and facility management and is usually accomplished through monitoring the data center's performance to optimize energy, equipment and floor space use.
- Technical support. The data center provides technical services to the organization, and as such, it must also provide technical support to enterprise end users.
- Operations. Data center management includes day-to-day processes and services that are provided by the data center.
- Infrastructure management and monitoring. Modern data centers use monitoring tools that enable remote IT data center administrators to oversee the facility and equipment, measure performance, detect failures and implement corrective actions without ever physically entering the data center room.
- Energy consumption and efficiency. A simple data center might need less energy, but enterprise data centers can require more than 100 megawatts. Today, the green data center, which is designed for minimum environmental impact through the use of low-emission building materials, catalytic converters and alternative energy technologies, is growing in popularity.
- Data center security and safety. Data center design must also implement sound safety and security practices, including the layout of doorways and access corridors to accommodate the movement of large IT equipment and employee access. Fire suppression is another key safety area, and the extensive use of high-energy electrical and electronic equipment precludes common sprinklers.
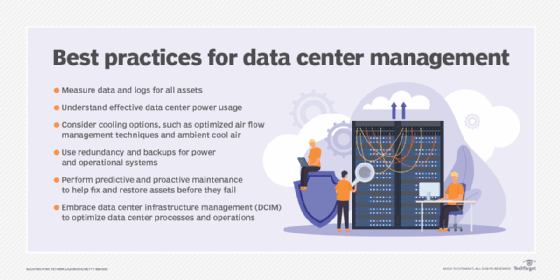
What is data center consolidation?
Data center consolidation is the process of downsizing or consolidating many servers, storage systems, networking systems or even locations into a more efficient set of systems. Consolidation typically occurs during mergers and acquisitions when the majority business doesn't need the data centers owned by the subordinate business.
There are many benefits of consolidating data centers, including the following:
- Reduced latency. Modern businesses might use two or more data center installations across multiple locations for greater resilience and better application performance, which lowers latency by locating workloads closer to users.
- Cost reduction. A business with multiple data centers could opt to consolidate data centers, reducing the number of locations to minimize the costs of IT operations. By reducing the operational costs of multiple data centers and energy expenses, businesses can gain significant cost savings.
- Improved efficiency. Consolidating data centers can streamline operations, simplify infrastructure and make it easier for IT staff to control, optimize and manage the organization's infrastructure.
- Optimize IT governance and compliance. Data center consolidation enables easier compliance with regulatory measures. With fewer data centers to operate, organizations can more easily adhere to regulatory requirements, data protection standards and industry best practices, reducing compliance risks and potential penalties.
- Improved business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR). Centralizing data and backup infrastructure enhances BCDR capabilities. Organizations can apply more thorough backup and replication strategies, ensure data availability across geographically dispersed locations, and reduce recovery time objectives and recovery point objectives.
- Environmental benefits. Due to the fewer number of data centers being used, data center consolidation reduces energy consumption and carbon footprint. It also optimizes server efficiency through virtualization, minimizes electronic waste and extends hardware life span. This plays a crucial role in the sustainability strategies of businesses, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
- Enhanced security. Consolidation reduces the attack surface and enables more effective use of security measures, which strengthens the overall security posture of an organization.
Data center vs. cloud vs. server farm: What are the differences?
How and where data is stored play a crucial role in the overall success of an organization. Over time, businesses have transitioned from simple on-site server farms and large enterprise data centers to cloud infrastructures.
The key differences among enterprise data centers, cloud service vendors and server farms include the following:
- Enterprise data centers are designed for mission-critical businesses and are built with availability and scalability in mind. They offer everything required to maintain seamless business operations, including physical computer equipment and storage devices, as well as DR and backup.
- Cloud vendors enable users to purchase access to the cloud service provider's resources without having to build or buy their own infrastructure. Customers can manage their virtualized or nonvirtualized resources without having physical access to the cloud provider's facility.
The main difference between a cloud data center and a typical enterprise data center is scale. Because cloud data centers serve many different organizations, they can be huge. - Server farms are bare-bones data centers. Many interconnected servers live inside the same facility to provide centralized control and easy accessibility. Even with cloud computing gaining popularity, many businesses still prefer server farms because they offer cost savings, security and performance optimization. In fact, cloud providers also use server farms inside their data centers.
Further blurring the lines between these platforms is the growth of hybrid cloud. As enterprises increasingly rely on public cloud providers, they must incorporate connectivity between their own data centers and their cloud providers.

Evolution of data centers
Data centers have undergone a significant evolution over the years, adapting to technological advancements and changing business needs:
- 1940s. The origins of the first data centers can be traced back to early computer systems, such as the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, or ENIAC. These machines, which were used by the military, were complex to maintain and operate. They required specialized computer rooms with racks, cable trays, cooling mechanisms and access restrictions to accommodate all the equipment and execute the proper security measures.
- 1960s. The creation of the mainframe computer by IBM led to the development of dedicated mainframe rooms at large companies and government agencies, some of which needed their own free-standing buildings, marking the birth of the first data centers.
- 1990s. The term data center first came into use when IT operations started to expand and inexpensive networking equipment became available. It became possible to store all of a company's necessary servers in a room within the company. These specialized computer rooms were dubbed data centers within the organizations, and the term gained traction. Around the time of the dot-com bubble in the late 1990s, the need for internet speed and a constant internet presence for companies necessitated bigger facilities to house the large amount of networking equipment needed. It was at this point that data centers became popular and began to resemble the ones described above.
- Recent years. Current data centers reflect a shift toward greater efficiency, flexibility and integration with cloud resources to meet the evolving demands of modern computing and storage needs.
Learn the essentials of designing a data center efficiently. Explore key components, infrastructure and industry standards before embarking on the project.







