
What is VoIP (voice over Internet Protocol)?
VoIP (voice over Internet Protocol) is the transmission of voice and multimedia content over an internet connection. VoIP allows users to make voice calls from a computer, smartphone, other mobile devices, special VoIP phones and WebRTC-enabled browsers. VoIP is a technology useful for both consumers and businesses as it typically includes other features that can't be found on common phone services. These features can include call recording, custom caller ID, and voicemail to email. It is also helpful to organizations as a way to unify communications.
The process works similarly to a regular phone, but VoIP uses an internet connection instead of a telephone company's wiring. VoIP is enabled by a group of technologies and methodologies used to deliver voice communications over the internet, including enterprise local area networks or wide area networks.
A VoIP service will convert a user's voice from audio signals to digital data, then send that data through the internet. If another user is calling from a regular phone number, the signal is converted back to a telephone signal before it reaches that user.
VoIP can also perform routing of incoming and outgoing calls through existing telephone networks. However, some VoIP services may only work over a computer or VoIP phone.
This article is part of
Ultimate guide on enterprise unified communications strategy
VoIP in unified communications
VoIP consolidates communication technologies into one unified system -- meaning that VoIP can enable several audio, video or text-based communication methods. This can be particularly useful for businesses so teams don't have to work with multiple different applications to communicate with one another effectively.
VoIP creates this network by enabling users to make calls and hold web conferences using devices like computers, smartphones or other mobile devices.
Some common features might include the following:
- audio calls;
- video calls;
- voicemail;
- instant messaging;
- team chats;
- email;
- text messaging;
- mobile and desktop apps; and
- mobile and local number portability (enables a subscriber to choose a new telephone carrier without needing a new number).
VoIP telephone equipment
The two main types of VoIP telephones are hardware based and software based.
A hardware-based VoIP phone looks like a traditional hard-wired or cordless telephone and includes similar features, such as a speaker or microphone, a touchpad and a caller ID display. VoIP phones can also provide voicemail, call conferencing and call transfer.
Software-based IP phones, also known as softphones, are software clients installed on a computer or mobile device. The softphone user interface often looks like a telephone handset with a touchpad and caller ID display.
A headset equipped with a microphone connects to the computer or mobile device to make calls. Users can also make calls via their computer or mobile device if they have a built-in microphone and speaker.
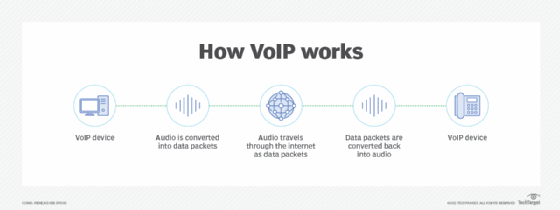
How does VoIP work?
VoIP services convert a user's voice from audio signals to digital data, in which that data is then sent to another user -- or group of users -- over Ethernet or Wi-Fi. To accomplish this, VoIP will use codecs.
Codecs are either a hardware- or software-based process that compresses and decompresses large amounts of VoIP data. Voice quality may suffer when compression is used, but compression reduces bandwidth requirements. Equipment vendors will also use their own proprietary codecs.
The process of sending data to other users includes encapsulating audio into data packets, transmitting the packets across an IP network, and unencapsulating the packets back into audio at the other end of the connection.
Within enterprise or private networks, quality of service is typically used to prioritize voice traffic over non-latency-sensitive applications to ensure acceptable voice quality.
Additional components of a typical VoIP system include an IP private branch exchange (PBX) to manage user telephone numbers, devices, features and clients; gateways to connect networks and provide failover or local survivability in the event of a network outage; and session border controllers to provide security, call policy management and network connections.
A VoIP system can also include location-tracking databases for E911 (enhanced 911) call routing and management platforms. This can collect call performance statistics for reactive and proactive voice quality management.
By eliminating circuit-switched networks for voice, VoIP reduces network infrastructure costs and enables providers to deliver voice services over Broadband and private networks. This should also enable enterprises to operate a single voice and data network.
VoIP also piggybacks on the resiliency of IP-based networks by enabling fast failover following outages and redundant communications between endpoints and networks.
VoIP protocols and standards
VoIP endpoints typically use either International Telecommunication Union (ITU) standard codecs or specifically developed codecs:
- G.711 is the standard for transmitting uncompressed packets.
- G.729 is the standard for compressed packets.
- Transmission Control Protocol is used to break a message down into smaller packets. Meanwhile, the IP deals with the sending and delivery of the packets.
- The ITU T.38 protocol will send faxes over a VoIP or IP network in real time. VoIP typically uses this to support non-voice communications.
- The Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) is used once voice is encapsulated onto IP.
- The Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol acts as an encrypted variant of RTP.
- The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a rigorous standard for signaling most often used to signal to create, maintain and end calls.
- The H.248 protocol describes a Gateway Control Protocol, which defines a centralized architecture for creating multimedia applications.
- H.323 is a signaling protocol that is used to control and manage calls.
- Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol is a protocol for contact list maintenance, instant messaging and presence information.
- Skinny is another signaling protocol, which is proprietary to Cisco.
- Session Description Protocol is used for initiation and announcement of sessions for multimedia communications as well as WebSocket transports.
What are the advantages of VoIP?
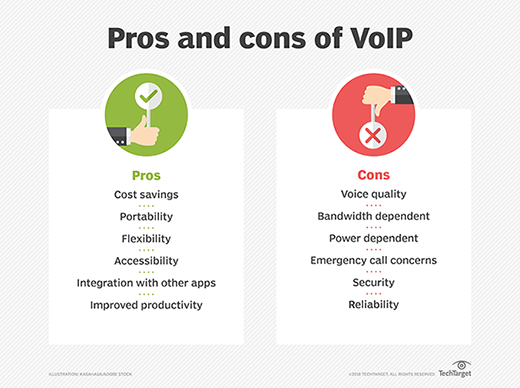
Benefits of VoIP include the following:
- Lower cost. Price is lower than typical phone bills.
- Higher-quality sound. With uncompressed data, audio is less muffled or fuzzy.
- Access for remote workers. Good for employees who work remotely as they have a number of options to call into meetings or communicate to other teammates.
- Added features. These features include call recording, queues, custom caller ID or voicemail to email.
- Low international rates. When a landline makes an international call, it rents the wired circuit for the call to transfer overseas. VoIP doesn't require a wired line and uses the internet to make calls, which means it's treated like normal traffic and is less expensive.
What are the disadvantages of VoIP?
Despite these advantages, VoIP services may still come with some disadvantages:
- Not all these services may connect directly to emergency services.
- VoIP needs a high-speed internet connection.
- Services will not work during power outages.
- There may be a lack of directory assistance depending on the VoIP service.
What is the history of VoIP?
The term VoIP historically referred to using internet protocols to connect PBXs but is now used interchangeably with IP telephony. Paul Baran and other researchers worked on early developments of packet network designs. In 1973, Danny Cohen was the first to demonstrate a form of packet voice over an early Advanced Research Projects Agency Network. One year later, the first successful real-time conversation was had over ARPANET. Three years after this, in 1977, User Datagram Protocol was added to carry real-time traffic.
The 1990s
In 1991, the first VoIP application release was Speak Freely. A year later, InSoft launched a desktop conferencing product namedCommunique. Communique notably included options for video conferences. InSoft is often credited for creating the first generation of commercial VoIP services in the United States.
In 1994, the FCC placed a requirement on VoIP providers to comply with the Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act of 1994. In addition, VoIP providers had to now contribute to the Universal Service Fund.
In 1995, Intel, Microsoft and Radvision began to standardize VoIP systems. One year, later the ITU-T developed standards for transmission and signaling voice over IP networks, creating the H.323 standard. The G.729 standard is also introduced. SIP was standardized in 1999.
The 2000s
In 2005, the FCC began imposing VoIP providers to provide 911 emergency call abilities. This began opening up the ability for VoIP to make and receive calls from traditional telephone networks. Emergency calls do work differently with VoIP, however. For example, a provider with the right hardware infrastructure can find the approximate location of the calling device by using the IP address that is allocated to the network router.
Another codec, the G.729.1 protocol, was unveiled in 2006. A year after this, VoIP device manufacturers began to expand in Asia. The SILK codec was introduced in 2009, notable for being used for voice calling in Skype.
In 2010, Apple introduced the LD-MDCT-based AAC-LD codec, which is notable for being used in FaceTime.







