Getty Images
Top 21 Kali Linux tools and how to use them
Kali Linux includes many tools tailored to beefing up network security. Getting familiar with them takes a lot of work, but the benefits they provide can be wide-ranging.
Kali Linux is the OS most frequently used by both ethical and malicious hackers for almost every aspect of cybersecurity. It includes almost every imaginable hacking tool, meaning learning to use it is a journey, not a simple skill that can be picked up watching a 10-minute tutorial.
Kali is based on the Debian distribution and contains hundreds of tools for penetration testing, security auditing and digital forensics. These tools help security professionals discover vulnerabilities, address misconfigurations, find exposed data and more. Other security-oriented Linux distributions, including Parrot and BlackArch, contain many of the same tools.
Editor's note: Tools such as those in Kali Linux can be used in ways that are lawful and helpful as a security practitioner, but they can also be used illegally, unlawfully and unethically. Make sure any planned use is ethical, lawful and legal. If you're not sure about the legality, do not proceed until you are. This might require some research on your part, such as an honest discussion with internal counsel about what you have planned.
Top Kali Linux tools
Kali Linux contains just about every type of security-oriented utility you could name, from scanners and password crackers to DoS site testers and web server scanners. In fact, its comprehensive tool list could overwhelm many users.

Kali's menu breaks down its utilities into several categories, including the following:
- Information gathering. This category includes tools that help with everything from identifying all the devices on a network to identifying open ports on targeted servers. Tools include Nmap and Wireshark.
- Wireless attacks. This category includes tools that carry out attacks against wireless systems, including those connected by Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Tools include Aircrack-ng and Kismet.
- Password attacks. This category includes password cracking tools and tools to make password crackers more effective. Tools include John the Ripper and Hydra.
Let's examine some of Kali Linux's most common and useful utilities. The following tools are not listed in any particular order, but similar tools are grouped together. Some tools are probably familiar, such as Nmap and Wireshark, while others might only be known for their specific features, such as Kismet or CrackMapExec.
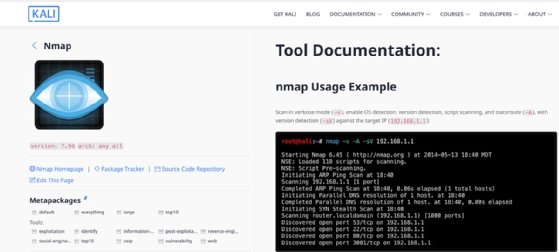
1. Nmap
Network Mapper, or Nmap, has evolved since its release as a port scanner in 1997 to become a ubiquitous tool that not only reports port status, guesses OSes and maps network topologies, but also detects vulnerabilities and performs brute-force password auditing.
Key Nmap features and capabilities
- Identifies devices running on a network.
- Provides visual mapping via its Zenmap GUI.
- Identifies services running on systems, including service versions and types.
- Hosts useful documentation and scripts on its site.

2. Masscan
Masscan is an IP port scanner that offers many of the same features as Nmap. The main difference is that Masscan is designed to scan large networks, multiple machines and the internet quickly, whereas Nmap is meant for more targeted scans on a single network or machine. Masscan's speed can, however, increase network traffic.
Key Masscan features and capabilities
- Supports banner grabbing on multiple protocols.
- Transmits 10 million packets per second from one machine.
- Uses asynchronous transmission, meaning it can send and receive requests separately -- it, therefore, doesn't need to wait for a response from each scan to do the next scan.
- According to Masscan's author, Robert Graham, can scan the entire internet in less than five minutes.

3. Unicornscan
Unicornscan is a stateless port scanner that sends data to potentially vulnerable TCP/IP-enabled devices and analyzes results. It is often faster than Nmap on larger networks and able to hide its scans.
Key Unicornscan features and capabilities
- TCP banner grabbing.
- User Datagram Protocol scanning.
- Packet capture (PCAP) file logging and filtering.
- OS, application and component identification.
4. Wireshark
Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer, sometimes called a packet analyzer, that captures network traffic and displays its constituent parts, such as logical and physical address information. It also displays packet contents unless those contents are encrypted.
Key Wireshark features and capabilities
- Advanced filtering tools enable practitioners to narrow results.
- PCAP capabilities; converts traffic into human-readable content.
- Easy-to-use GUI.

Learn how to use Wireshark to sniff and scan network traffic.
5. Tcpdump
Tcpdump is a protocol analyzer often installed on Linux distributions by default. It only operates via CLI. It offers many filtering options and is easily scripted and efficient at capturing network packets for analysis.
Key tcpdump features and capabilities
- Offers speed and scriptability.
- Via PCAP, enables practitioners to write results to a file for analysis in Wireshark, tcpreplay or other tools.
- Provides extensive documentation.
6. Metasploit
Metasploit Framework is one of the most well-known pen testing tools. It is a comprehensive framework for gathering information and executing exploits against targeted systems. It contains prebuilt exploit code and payloads to exploit known vulnerabilities.
Key Metasploit features and capabilities
- Includes exploits and payloads, as well as auxiliary tasks that don't use payloads.
- Normalizes how practitioners work with exploit code by fostering payload reuse and using a common methodology to interact with exploits.
- For those starting with Metasploit, can use Metasploitable, an intentionally weakened VM to test exploits on and learn about Metasploit.
Learn how to use Metasploit commands and exploits for pen tests.
7. Burp Suite
Burp Suite is a web application vulnerability scanner from security testing software vendor PortSwigger. It identifies issues, performs intensive website scans and can send modified HTTP calls to discover exploits.
Key Burp Suite features and capabilities
- Includes spidering tools, a randomness tool, a request repeater and an intercepting proxy.
- Checks for SQL injection, cross-site scripting, OS command injection, HTTP request smuggling, broken authentication and more.
- Supports static and dynamic testing.

8. John the Ripper
John the Ripper is an offline password recovery and cracking tool. It uses various hashes, ciphers, encryption formats and word lists to test password strength via dictionary attacks, brute forcing and other methods.
Key John features and capabilities
- Is known for its ubiquity and accessibility.
- Helps in instances where online brute-force cracking is impractical, such as a remote system with user login rate limiting.
- Offers Johnny, a GUI for John the Ripper.
9. Hydra
Hydra is an online password cracking utility that uses brute-force and dictionary attacks to expose weak passwords or poor password practices. It targets SSH, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, Remote Desktop Protocol, HTTP, HTML forms, virtual network computing and other protocols.
Key Hydra features and capabilities
- Can run multiple threats in parallel to increase efficiency and speed.
- Has a simple and intuitive interface.
- Offers prebuilt and customizable word lists.

10. Aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a suite of wireless security tools that consists of multiple applications for monitoring, interception and injections. It includes Airdecap-ng, a Wired Equivalent Privacy, Wi-Fi Protected Access and WPA capture file decryptor; Airodump-ng, a tool that collects packets and WPA handshakes; Airtun-ng, a virtual tunnel interface creator; and Besside-ng, a WEP and WPA cracker.
Key Aircrack-ng features and capabilities
- Focuses on 802.11 wireless LANs.
- Provides command-line tools that enable heavy scripting.
- Performs WEP dictionary attacks and fragmentation attacks.
11. Kismet
Kismet is a wireless and Bluetooth network monitor and war driving tool that sniffs networks, intercepts traffic and acts as a wireless intrusion detection system (IDS).
Key Kismet features and capabilities
- Detects rogue access points (APs).
- Supports radio frequency sensors, Zigbee and multiple beacons.
- Is compatible with tcpdump and Wireshark.
12. Wifite
Wifite is a wireless network penetration testing and auditing tool written in Python. It gathers service set identifiers, signal strength and other information. It also attacks WEP, WPA and WPA2 keys.
Key Wifite features and capabilities
- Includes brute-force PIN attacks, handshake captures and hash captures.
- Decloaks hidden APs automatically.
- Maintains a directory of cracked passwords and handshakes.
13. Fern Wifi Cracker
Fern Wifi Cracker is a wireless testing and attacking tool written in Python. It uses a GUI to scan wireless networks. It can expose WEP, WPA and WPA2 keys.
Key Fern Wi-Fi Cracker features and capabilities
- Has a straightforward and easy-to-use GUI.
- Monitors network activities in real time.
- Conducts dictionary attacks, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) request replay attacks, brute-force attacks and Wi-Fi Protected Setup attacks.

14. Bettercap
Bettercap is a reconnaissance and attack tool for wired and wireless networks that captures packets, performs man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks and more. It includes a CLI, web-based interface and built-in scripting engine.
Key bettercap features and capabilities
- Works on Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth Low Energy devices, Controller Area Network bus, wireless human interface devices and Ethernet networks.
- Supports ARP, DNS, Neighbor Discovery Protocol and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6 spoofing MitM attacks on IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
- Can be used as a network protocol fuzzer.
15. Arpwatch
Arpwatch is a tool that monitors Ethernet and ARP traffic. It maintains a database of MAC and IP address relationships. If a change is detected, such as a new address or an address modification, it alerts administrators.
Learn how to use arpwatch.
Key Arpwatch features and capabilities
- Produces logs and can send email alerts to practitioners.
- Helps detect ARP spoofing.
16. Sqlmap
Sqlmap is an automated tool for exposing and exploiting SQL injection vulnerabilities. It works with Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle and others.
Key Sqlmap features and capabilities
- Conducts Boolean-based, time-based, error-based, union-based and stacked queries, as well as out-of-band SQL injection attacks.
- Includes password cracking capabilities using dictionary attacks.
- Supports user privilege escalation and arbitrary command execution.
17. Social-Engineer Toolkit
Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) is a Python-based tool that exploits human vulnerabilities rather than application or system weaknesses. It enables practitioners to send phishing, website and wireless AP attacks, among other attacks.
Key SET features and capabilities
- Offers options for social engineering, pen testing and post-exploit lateral movement.
- Conducts spear phishing, QR code phishing, mass email phishing, SMS phishing and other phishing attacks.
- Performs tabnabbing and other browser-based attacks to gather information or assess employee responses to social engineering attempts.

Learn how to use SET.
18. Netcat
Netcat is a powerful network utility that scans ports, transfers files, makes web requests and reads/writes across network connections. It's a flexible tool often used beyond security audits for regular network management.
Key netcat features and capabilities
- Acts as a data transfer agent.
- Provides full DNS forward/reverse checking.
- Offers loose source-routing capabilities.
19. BloodHound
BloodHound is a network reconnaissance tool that performs attack path mapping in Active Directory (AD) environments to expose potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
Key BloodHound features and capabilities
- Exposes domain trusts.
- Identifies user and group relationships.
- Identifies users with local admin privileges.
- Enumerates domain computers, including domain controllers.

20. CrackMapExec
CrackMapExec is a pen testing tool for exploiting vulnerabilities in AD environments. It enumerates users, groups, computers, domain controllers and other targets before performing attacks.
Key CrackMapExec features and capabilities
- Performs credential brute forcing.
- Performs post-exploit lateral movement.
- Integrates with Metasploit, BloodHound and other Kali Linux tools.
21. Nikto
Nikto is a web server scanner that identifies vulnerabilities, misconfigurations and unpatched software, including more than 6,700 malicious file types and outdated web server versions.
Key Nikto features and capabilities
- Performs dictionary attacks on web servers to exploit user accounts.
- Has built-in support for HTTP and SSL proxies, as well as IDS evasion.
Other Kali tools
Kali contains hundreds of additional utilities, many of which are for specialized use or specific situations. You can also add new utilities to supplement its inventory -- remember to use the Advanced Package Tool manager, as Kali is based on Debian Linux.
As you become more familiar with the basic Kali Linux tools, you'll soon discover more ways to use these additional applications in your security audits.
The Kali website contains documentation on all tools, so it's a great place to get started.
Using Kali Linux tools: Getting started
You can run Kali Linux on bare metal, as a VM, from bootable media, from cloud images or even as a container. Kali's comprehensive tool list can help you perform security audits more efficiently.
Learning to use Kali Linux effectively can be daunting, especially if you're an administrator with additional responsibilities. Gaining familiarity with the available tools helps you understand when and how to use Kali for best results.
Damon Garn owns Cogspinner Coaction and provides freelance IT writing and editing services. He has written multiple CompTIA study guides, including the Linux+, Cloud Essentials+ and Server+ guides, and contributes extensively to Informa TechTarget Editorial, The New Stack and CompTIA Blogs.