analog telephone adapter (ATA)
What is an analog telephone adapter (ATA)?
An analog telephone adapter (ATA) is a device used to connect an analog telephone, fax machine or similar equipment to a computer or network to enable communications over the internet. ATAs let users talk on their telephones like they do when connected to a traditional telephone network. In this way, they get the flexibility of the internet, can continue to use their existing analog equipment and often reduce their overall phone expenses.
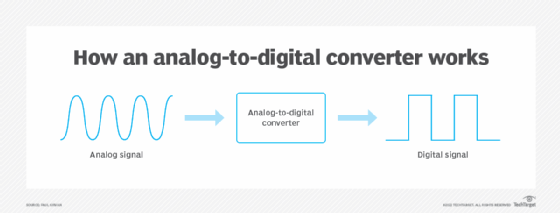
Most of today's ATAs connect directly to an IP network without needing a computer to establish the connection. The ATA is physically connected to a network device, such as a modem, router, hub or switch, and the ATA communicates directly with a voice over IP (VoIP) server, whether on the local network or accessed through the internet. The ATA converts a phone's analog signal to a digital format when transmitting the signal and converts the digital signal to analog when receiving the signal. An ATA that connects telephones to an IP network is sometimes called a VoIP adapter or VoIP gateway.
In some cases, an ATA connects directly to a computer, usually via a USB port, rather than connecting directly to the network. Although this configuration is less common than it was in the past, when it is used, the computer typically runs a softphone program that acts as an intermediary between the ATA and VoIP server. The software converts the data between the digital and analog signals and handles any other operations necessary to support internet communications.
Modern analog telephone adapters
Most of today's ATAs connect directly to network devices; however, the devices differ in important ways. One of those differences is the number of analog devices that can connect to the ATA. Connectivity is established through a combination of port types, including the following:
- Foreign exchange station (FXS). This is a port that uses an RJ-11 connector to physically connect the ATA to an analog device, such as a phone or fax, thereby enabling VoIP communication. An ATA often includes multiple FXS ports.
- Foreign exchange office (FXO). An FXO port uses an RJ-11 connector to physically connect the ATA to a plain old telephone service phone line. An FXO port is sometimes included in an ATA to provide alternative access to a public switched telephone network.
- Ethernet. An Ethernet port uses an RJ-45 connector to physically connect the ATA to an IP network device. In some cases, the ATA includes two Ethernet ports: one to connect to the internet and another to connect to a downstream device, such as a router or computer.
In today's market, the simplest ATA has one FXS port, one Ethernet port and one jack for a power adapter. However, an ATA in a business setting often includes many FXS ports, along with two Ethernet 10/100 megabits per second ports. Some internet telephony service providers, such as Vonage, provide an ATA to their customers as part of the service package.
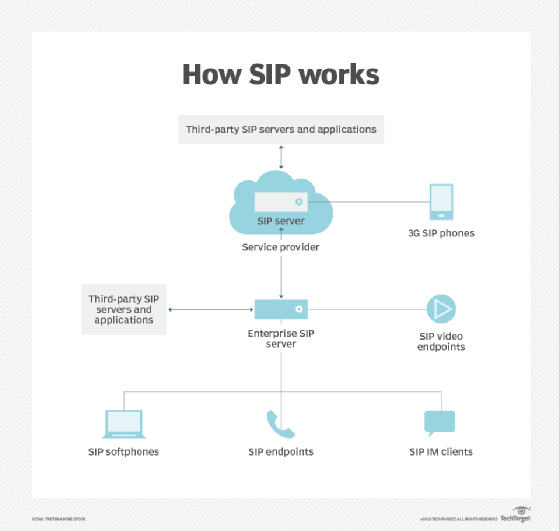
An ATA carries out communications through the use of a VoIP protocol. One of the most common is Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), a signaling protocol that can initiate, maintain, modify and terminate real-time communications. Other common protocols include H.323, Inter-Asterisk eXchange and Media Gateway Control Protocol. An ATA also uses codecs to convert phone signals from analog to digital, and vice versa. Common codecs include G.711, G.729 and Internet Low Bitrate Codec.
Learn how VoIP platforms offer a wide range of benefits to the enterprise.








