network vulnerability scanning
What is network vulnerability scanning?
Network vulnerability scanning is the process of inspecting and reporting potential vulnerabilities and security loopholes on a computer, network, web application or other device, including switches, routers, firewalls and wireless access points.
Vulnerabilities are triggered for various reasons, including open ports, network misconfigurations or outdated software running on the network. Vulnerabilities can be either known or unknown and can be easily exploited by hackers and used as entry points into a system.
Why is network vulnerability scanning important?
Network vulnerability scanning helps mitigate the numerous cybersecurity risks and challenges that exist within an organization. If vulnerabilities in an organization's IT infrastructure remain undetected, cybercriminals can easily exploit these weaknesses.
Even with protective measures in place, enterprises can still encounter data breaches. However, conducting regular vulnerability scans and promptly applying patches can help to prevent cyber attacks.
Vulnerability scanning is a vital part of a company's security posture, as it provides the following benefits:
- Detects anomalies. A vulnerability scan detects and classifies system weaknesses in computers, networks and communications equipment and predicts the effectiveness of countermeasures. A scan can be performed by an organization's security team or a security service provider, possibly as a condition imposed by some authority. An approved scanning vendor, for example, is a service provider that's certified and authorized by the Payment Card Industry to scan payment card networks. On the flip side, attackers also use vulnerability scans to look for points of entry.
- Provides proactive mitigation. Since most vulnerability scanning can be scheduled and automated, it can proactively detect weaknesses in a system. Once vulnerabilities are identified, organizations can promptly prioritize, address and mitigate the most critical risk factors.
- Inspects the entire attack surface. A vulnerability scanner runs from the endpoint of the person inspecting the attack surface in question. The software compares details about the target attack surface to a database of information about known network security holes in services and ports, anomalies in packet construction, and potential paths to exploitable programs or scripts. The scanner software attempts to exploit each vulnerability that's discovered.
- Complies with cybersecurity regulations. Most organizations are subject to cybersecurity compliance and legislation. By conducting regular vulnerability scanning, they can meet these requirements and ensure adherence to standards.
- Provides cost savings. Early detection of vulnerabilities can save organizations expenses associated with data breaches, network downtime and legal penalties.
- Offers continuous monitoring. Regular scans provide insights into the ever-changing security landscape and enable organizations to successfully change their security measures in response to emerging threats.
- Safeguards reputation. By performing regular scans, a business ensures that its assets are protected and conveys to stakeholders and customers that it's taking all necessary measures to safeguard their data and trust.
However, running a vulnerability scan can pose its own security risks, as it's inherently intrusive on the target machine's running code. As a result, the scan can sometimes cause issues such as errors and reboots, diminishing productivity.
Types of network vulnerability scanning
There are several types of vulnerability scanning and each comes with a specific purpose. Some common vulnerability scanning approaches include the following:
- Unauthenticated scanning. The tester performs the scan as an intruder would, without trusted access to the network. Such a scan reveals vulnerabilities that can be accessed without logging into the network.
- Authenticated scanning. The tester logs in as a network user, revealing the vulnerabilities that are accessible to a trusted user or an intruder that has gained access as a trusted user.
- Host-based scanning. This type of scanning inspects individual servers or computers to detect weaknesses in the operating system (OS), applications and configurations that are specific to each host.
- Network-based scanning. This scanning identifies vulnerabilities such as weak passwords in network devices, including routers, servers, firewalls and switches. Limited penetration testing is also conducted through network scanning without affecting the underlying system or network performance.
- Web application scanning. This targeted scanning of web apps aims to identify security flaws in their code, configurations and authentication mechanisms, which helps mitigate common web-based security breaches.
- Database scanning. This type of scanning focuses on identifying flaws in database management systems.
- Port scanning. Port scanning entails making connection requests to network servers to locate open ports and then monitoring the responses to assess their activity. Port scan attacks are conducted by threat actors to get illegal access by locating open or underutilized ports.
- Cloud vulnerability scanning. Cloud-based vulnerability scanning is designed to pinpoint weaknesses that are specific to Cloud services and configurations.
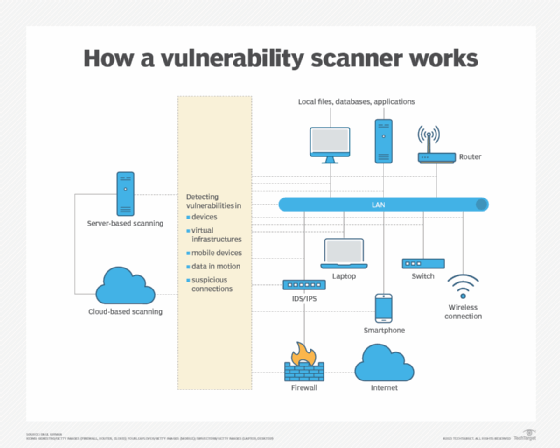
Key features of a network vulnerability scanner
Network vulnerability scanners should include the following features:
- Vulnerability detection. The scanners should be able to recognize well-known vulnerabilities in network hardware, OSes, software and configurations.
- Comprehensive database. A network vulnerability scanner should have access to a vast and current database of identified vulnerabilities to ensure precise screening and detection.
- Scalability. This feature enables a scanner to efficiently scan vast and complicated networks that are comprised of a variety of devices.
- Scanning automation. The scanner should be able to plan and carry out automated scans without human intervention.
- Asset discovery. This involves locating and cataloging all connected devices to create a complete inventory of all network assets.
- Customizable scanning policies. The scanner should let users set up scanning policies in accordance with their own requirements and compliance standards.
- Prioritization and risk assessment. The scanner should be able to rank vulnerabilities according to their seriousness and potential consequences, enabling organizations to prioritize important issues.
- Remediation advice. Vulnerability scanners should offer practical suggestions and actions to fix discovered vulnerabilities successfully.
- Seamless integration. Scanners should be able to integrate seamlessly with different security platforms. They should also be able to produce thorough reports for analysis and regulatory compliance.
- Continuous monitoring. A scanner should be able to carry out continual scans and monitoring to find vulnerabilities as they appear.
- Support for vendors and compliance. The vulnerability scanner should also offer custom checks for the organization's specific vendor products and compliance requirements.
Network vulnerability scanning best practices
For the network vulnerability scanning process to produce relevant results, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
- Check each device that interacts with the ecosystem, including both internal and external resources.
- Scan often; weekly or daily scans are preferred to yearly ones.
- Owners should be assigned to critical assets and scanning activities should be prioritized accordingly.
- To increase coverage and accuracy, agent-based and agentless scanning techniques should be combined.
- To reduce false positives and negatives, organizations should optimize the configuration and performance of the asset discovery system. They should also include online application scanning in the overall approach for vulnerability scanning.
Network vulnerability scanning vs. network scanning
Network scanning and network vulnerability scanning are separate but related techniques. While network vulnerability scanning is especially focused on discovering flaws in those linked devices that could be exploited by attackers, network scanning involves identifying all devices connected to a network.
In a nutshell, network vulnerability scanning focuses on potential security threats, whereas network scanning gives a broad overview of the devices on a network.
Network scanning tools
Numerous network vulnerability scanning tools are available, ranging from open source to premium options. To make the best choice, organizations should carefully assess their specific requirements and vet a tool that aligns well with their needs.
Examples of network vulnerability scanning tools include the following:
- Burp Suite. This web vulnerability scanner from PortSwigger conducts automated enterprisewide scans to check for SQL injection, cross-site scripting and other vulnerabilities besides being used for compliance and security auditing. Although the Burp Suite Enterprise Edition has the most features, a free version is also available.
- Falcon Spotlight. This cloud-based next-generation antivirus tool from CrowdStrike protects networks and endpoints but also comes with a network threat-hunting module.
- Nessus. Nessus from Tenable is an industry-standard platform that scans for security flaws in hardware, software, OSes, cloud services and other network resources. Its enterprise edition transitioned from being an open source tool in 1998 to a commercial offering in 2005.
- Nmap. Short for Network Mapper, this open source tool offers network exploration, security audits and network discovery. Nmap is specifically designed to scan large networks rapidly, although it can also be used on smaller single-node networks.
- Wireshark. This open source packet analyzer is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development as well as for educational purposes. Wireshark lets users capture and interactively browse the contents of network traffic.
- Wiz. Wiz is an agentless vulnerability management tool for all cloud resources. It continuously assesses workloads to detect and prioritize vulnerabilities at scale and also extends vulnerability management into the CI/CD pipeline, scanning virtual machine and container images before deployment to prevent vulnerabilities from reaching production.
An effective vulnerability management program equips an organization to identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities in both processes and technologies. Explore the steps to build an effective vulnerability management program.