What is a chief marketing officer (CMO)?
A chief marketing officer (CMO) is a C-suite executive responsible for overseeing the planning, development and execution of an organization's marketing and advertising initiatives.
With a primary mandate to drive business growth, the CMO bridges the gap between brand perception and consumer engagement, ensuring that products and services resonate with current and potential customers.
Key roles and responsibilities of the CMO
While the role of a C-suite marketing director might seem intuitively succinct, the position is a conglomeration of several roles, covering a broad range of responsibilities. This includes traditional concerns like marketing strategy and research, but also more modern aspects such as analytics, new integrated technology and emerging tools enabled by AI. Those roles and responsibilities incorporate the following key concepts:
- Strategic planning. One of the core tasks of a CMO is to set the strategic direction for the marketing department. This involves strategic planning, setting long-term goals and defining how these objectives will be met.
- Brand management. In an age where brand perception can make or break a company, the CMO ensures brand messages are consistent across all platforms. By leveraging brand equity, they drive growth and position the company favorably in consumers' minds.
- Customer engagement. The CMO understands that marketing activities don't end at acquisition. It's about creating lasting relationships. They craft customer engagement strategies that attract and retain customers, deepening these relationships over time.
- Digital, data-driven marketing & analytics. The CMO leverages analytics to derive actionable insights and oversees the governance of CRM and other customer-related data and processes. By understanding customer behavior, preferences and feedback, they can optimize marketing strategies for maximum return on investment (ROI). As the enterprise proceeds in digital transformation, the CMO is essential to that planning process.
- Market research. The CMO oversees analytics concerning consumer and customer behaviors and the associated analytics -- both those of the enterprise and its competitors. Insights gleaned from this work help identify new opportunities and risks.
- Team leadership. As leaders, CMOs oversee the marketing department, ensuring synergy in campaigns and initiatives. They also collaborate with other business units, ensuring marketing strategies align with overall company objectives.
- Development of new channels. As new digital technologies proliferate, it’s up to the CMO to figure out which can be developed as new marketing channels and how to make that happen.
Required skills for a CMO
The CMO role is a mix of artist and scientist. They possess creativity and analytical skills that help them craft compelling campaigns and measure their effectiveness simultaneously. Their leadership capabilities and interpersonal skills ensure smooth operations within the marketing department and effective collaborations with other teams.
Because marketing is ever changing, a CMO must have a strong grasp of current marketing tools and strategies. They're always on the lookout for the next big trend or tool that can give their company an advantage.
Additionally, understanding the customer journey is crucial. A successful CMO can predict market trends, ensuring their company is always one step ahead in meeting customer needs. They can also integrate innovative technologies and methods into their marketing strategy, ensuring the company remains at the forefront of modern marketing techniques.
The following skills can help make this happen:
- Strategic skills. A CMO must be a good strategist, aligning marketing activities with organizational goals and cultivating a growth mindset, as well as driving digital transformation and institutional evolution.
- Branding expertise. A CMO is the primary brand manager, responsible for the company’s marketplace identity; this expertise must be backed by a strong knowledge of marketing technology and analytics.
- Customer Insight. A CMO must have an in-depth understanding of customer behavior and how to monitor it, including specifics such as personalization and cultural differences.
- Budget management. A CMO works closely with the chief executive officer (CEO), Sales and Finance, and thus must have a command of the organizational big picture as well as budget management, ROI and market position.
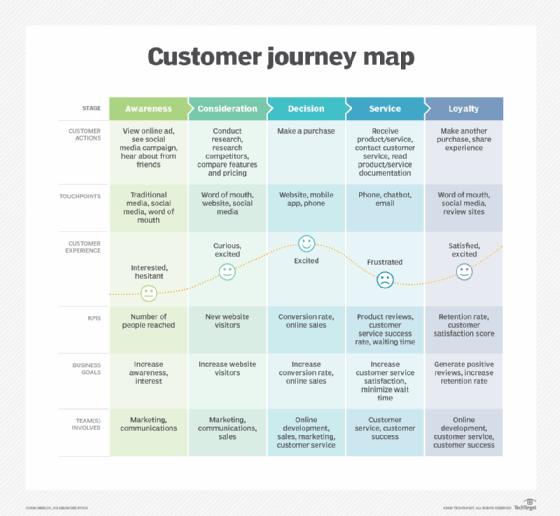
Collaboration with other C-suite roles
The CMO doesn't operate in a silo. They work alongside the CEO, ensuring that the company's vision and values are reflected in every marketing campaign.
Budgets are crucial in marketing. Therefore, the CMO will often find themselves collaborating with the chief financial officer to manage finances and ensure a good ROI for their marketing initiatives.
Furthermore, with the rise of digital marketing tools, the CMO frequently partners with the chief technology officer and IT departments. This collaboration ensures that the company's marketing tech stack is up-to-date, functional, and provides the necessary data for informed decisions.
Chief marketing officer salary ranges
Salaries for CMOs can vary widely based on several factors, including the size, location and industry of the company, as well as the CMO's level of experience and expertise. The following is a generalized overview of CMO salaries:
- Startups and small businesses. CMOs at smaller firms, especially startups, might have a lower base salary supplemented with equity or stock options. According to a 2025 survey by recruitment platform Wellfound, CMO salaries can range from $54,000 to $427,000 annually.
- Mid-sized companies. As businesses grow, so do the complexities and responsibilities of the CMO role. Per Glassdoor USA, for mid-size companies, CMOs might expect annual salaries in the range of $228,000 to $416,000.
- Large corporations. At top-tier corporations, especially those operating internationally, CMOs play a pivotal role in shaping global strategies. According to Salary.com, annual base salaries in the U.S. can range from $333,000 to $416,000, with bonuses and equity pushing total compensation over $1 million. Additionally, bonuses, stock options and other compensation perks can significantly increase the total package.
Salaries can vary based on the cost of living in a particular region or country. For instance, a CMO in San Francisco or New York City might command a higher salary than one in a smaller city given the higher living costs in those areas.
Certain industries, especially tech, pharmaceuticals and finance, might offer higher compensation packages due to the high stakes and profitability of these sectors.
Companies looking to hire and professionals seeking CMO roles should conduct thorough research, consult industry benchmarks and potentially engage with executive search professionals to get an accurate and current understanding of salary expectations in their specific context.
Measurable impact and key performance indicators for a CMO
For any executive role, measurable impact is crucial. The CMO is no different, as their effectiveness is measured by the following:
- Key performance indicators. The effectiveness of a CMO is measured by how successfully they manage KPIs. These include brand equity, which measures the value of the brand in the market, and customer lifetime value, which indicates the total worth of a customer over the duration of their relationship with the company. Additionally, the return on marketing investment provides insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Customer satisfaction metrics. The ultimate testament to a CMO's success is the tangible affect they have on a company's growth and profitability. By driving brand awareness, ensuring customer satisfaction (CSAT) and optimizing marketing strategies, they play a pivotal role in a company's success. Is customer lifetime value increasing? Is the customer retention rate strong? What are the CSAT numbers?
- Digital campaign effectiveness. Are lead generation metrics strong? What is the typical campaign ROI? Is social media engagement high?
How to become a CMO
The road to the CMO's office is a long one. It is the culmination of a career spent acquiring marketing expertise, leadership skills and strategic acumen. Education is key; most CMOs have degrees in marketing, communications, business administration or related fields, and many have MBAs.
There are several viable roles that can help prepare someone for the CMO's office. These include marketing assistant, a specialization in digital marketing, brand management and public relations roles, product marketing assistant and market research experience. Moving more deeply into these career paths, management in these areas is a strong step and executive roles such as director or vice president of marketing or communications are often a common final step.
The evolving role of the CMO
The role of the CMO was created at the beginning of the business era when merchants understood the need to differentiate their goods from competitors. The modern CMO, however, has evolved drastically since.
Initially, marketing leadership primarily revolved around traditional advertising: billboards, TV commercials and print ads. These methods were effective in their time, providing a broad reach and creating brand recognition and recall.
However, with the rapid growth of the internet and digital technologies in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the landscape of advertising transformed. Marketers had many channels from which to choose, ranging from email campaigns to social media marketing ads. This diversification in the marketing world led to increased complexity when managing and optimizing these channels.
Companies soon realized the need for a dedicated role at the executive level to not just oversee marketing but also align it with broader business goals. The CMO rose in prominence, ensuring brand messages were consistent, impactful and drivers of growth.
The role of the CMO is not static. It's always adapting to the demands of the market. Today, there's a shift from traditional marketing practices to dynamic, data-driven strategies. This change demands a CMO who's agile, informed and ready to adapt.
Finally, the significance of the CMO extends beyond marketing. They influence business strategies, growth trajectories and even company culture. As ambassadors of the customer within the company, their insights and strategies are shaping the future of businesses globally.
Sustainable marketing has grown in popularity and importance. Learn what strategies organizations can implement to align their marketing campaigns with customer values and reduce harm to the environment.






