What is enterprise content management? Guide to ECM
Enterprise content management is a set of defined processes, strategies and tools that enables a business to obtain, organize, store and deliver critical information to its employees, business stakeholders and customers.
ECM has evolved rapidly as different forms of content have been introduced to the work ecosystem. However, ECM tools continue to focus on digitally managing a company's information in a centralized repository and using the digital content to support business processes.
Enterprise content management does not refer to a single technology or process. It's an umbrella term that describes a combination of methods, tools and strategies that support capturing and managing content, as well as the storage, retention and delivery of information throughout its lifecycle.
The definition of content can range significantly, but it generally refers to any information that employees use to do their work. In the context of traditional ECM, content often took the form of paper documents, such as invoices, resumes and contracts. As technology has advanced, however, the definition of content has broadened to include video and audio files, social media posts, email, web content and more.
ECM can handle both structured and unstructured content:
- Structured content. Data that is contained and defined, such as databases and code repositories.
- Unstructured content. Information that doesn't have a predefined format and can include content such as Microsoft Office documents, PDFs and emails.
Enterprise content management software helps streamline the information lifecycle with a document management system and the automation of process workflows. It's critical for any organization with large volumes of content to define an ECM plan to eliminate operational inefficiencies, reduce costs and adhere to regulatory compliance mandates.
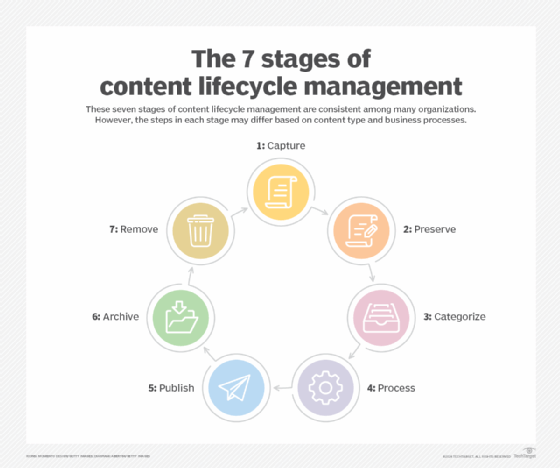
Some specific areas of business that benefit from ECM software include the following:
- Contracts management. ECM software enables users to digitally collaborate and ensure contracts are reviewed, edited and approved on time by automatically routing the documents and notifying the appropriate people when contracts need attention.
- HR automation. ECM software can remove the need for paper-based employee files while also improving new hire processes, streamlining the organization of HR-related information and guaranteeing compliance with HR onboarding mandates.
- Accounts payable automation. ECM software enables users to accurately match, distribute and approve purchase orders, delivery tickets and invoices, resulting in reduced late fees and enhanced efficiency.
- Accounts receivable automation. ECM software provides users with immediate access to purchase orders, invoices and signed receipts, thus reducing the time for days sales outstanding by accelerating the speed of customer payments.
How does ECM work?
Enterprise content management refers to a collection of strategies, methods and tools used to capture, manage and store key business process management information throughout its lifecycle.
Organizations can use ECM software to identify duplicate and near-duplicate content, enabling the organization to keep a few copies of a particular piece of content instead of hundreds. This variety of information is organized in a central location with document metadata stored in folders, ensuring the content is available to the right people at the right time.
Users with the proper approvals can find specific documents using full-text searches. The ECM platform retrieves the document and presents it to users, allowing them to read, edit or print a copy of the information regardless of their location or the device they're using. With ECM software, users can also look for specific words or phrases within the stored documents, decreasing the time spent scanning content and increasing productivity.
Why is ECM important?
In recent years, ECM has become increasingly important and complex for various reasons. Financial fraud and data breaches -- and the regulations designed to prevent them -- have made information governance essential for compliance reasons and to help protect an organization's reputation. Organizations also need to manage content effectively for integration with business intelligence/business analytics applications that help them to use the information to guide business decisions.
Furthermore, productivity and efficiency within companies increase when they reduce their dependence on paper documents and create an organized, secure repository of unstructured information that considers business needs. Companies that don't implement ECM risk losing time and productivity as well as potential noncompliance with corporate policies and regulations. If disaster strikes, companies that don't securely store content can lose that information, leading to significant business interruptions.
Technological advancements are also making a content management system more important than ever. The proliferation of remote work has necessitated the business continuity and collaboration features that ECM provides. Advancements in machine learning, mobile and cloud technology are creating new opportunities for businesses.
New types of content are also emerging in the form of social media, video and audio. ECM software must continue to adapt with these new forms of unstructured information so it can continue to organize data and optimize business performance.
What are the components of ECM?
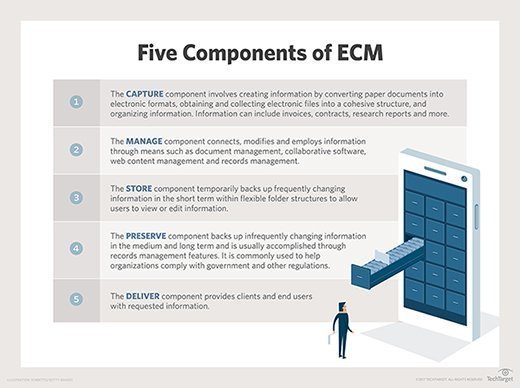
Traditionally, the five main components of ECM are: capture, manage, store, preserve and deliver. The purpose of each component, as originally defined by the Association for Intelligent Information Management, is as follows:
- Capture. The capture component creates information by converting paper documents into electronic formats, obtaining and collecting electronic files into a cohesive structure, and organizing information. With document capture, information can include content such as invoices, contracts and research reports.
- Manage. The manage component connects, modifies and employs information through means such as document management, collaborative software, web content management and records management.
- Store. The store component temporarily backs up frequently changing information in the short term within flexible folder structures to let users view or edit information.
- Preserve. The preserve component backs up infrequently changing information in the medium and long term, and it is usually accomplished through records management. It's commonly used to help organizations comply with government regulations and other directives.
- Deliver. The deliver component provides clients and end users with requested information.
These five elements largely make up the ECM architecture, which encompasses both front-end and back-end functionalities for end users and software support teams, respectively.
What are the benefits of ECM?
An effective enterprise content management system provides everyone in the organization with easy access to all the information they need to make business decisions, complete projects, collaborate and perform their jobs with efficiency.
In addition to the obvious benefits of organization and efficiency, ECM provides a wealth of other benefits, including the following:
- Minimized compliance and regulatory risk. ECM provides a centralized platform where content can be held and disseminated in a way that meets regulatory compliance requirements and risk management guidelines. An ECM achieves this by eliminating ad hoc processes that can expose an enterprise to regulatory compliance risks and other potential problems.
- A single source of truth. ECM software can provide organizations with a single source of truth by structuring information so it's only stored once -- in a secure digital content repository. This reduces the risk of duplication and ensures the entire enterprise has access to a single, approved and authoritative piece of information. An ECM system also enables effective knowledge management due to an organization's ability to create, share and optimize the total knowledge in the content management platform.
- Reduced cost. ECM reduces costs across the organization by automating previously manual processes, reducing compliance penalties, minimizing storage needs and reducing postal requirements. It also reduces the cost of e-discovery in the event of a legal or compliance incident when lawyers or compliance officers would require access to the organization's content.
- Improved customer satisfaction. When resolving customer issues, customer service representatives require access to the right content at the right time, which is one of the major goals of ECM. An ECM system enables employees to help customers more quickly and efficiently, thus improving customer satisfaction.
- Business continuity. An ECM platform that is properly implemented enables a business to have high availability and uptime for its content. ECM incorporates archives, disaster recovery and account backups.
- Increased productivity. Effective ECM can streamline access and business processes, optimize security, maintain integrity, minimize overhead and eliminate bottlenecks by reducing storage as well as paper and mailing needs. All of these can lead to increased productivity.
- Improved content accessibility. ECM provides data search and analytics tools, thus improving data mining. Users can set search ranges and parameters that enable them to narrow search results and find information more efficiently.
What is an example of an ECM?
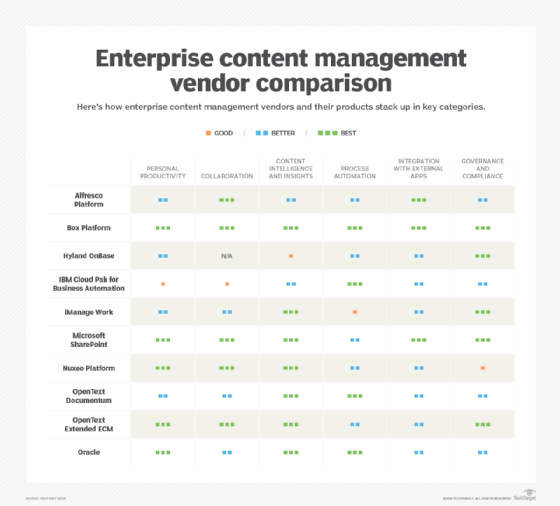
Some examples of ECM software products include Alfresco, Box Platform, Hyland OnBase, IBM Cloud Pak for Business Automation, iManage Work, Microsoft SharePoint, Nuxeo Platform, OpenText Extended ECM, Newgen and SER Group's Doxis. Free and open source ECM services are available.
Organizations can deploy ECM software on premises or in the cloud. The benefits of cloud-based ECM include flexible licensing models, easier remote and mobile access, and integration with other cloud services.
ECM software provides several capabilities. But companies that want more flexibility in choosing content management tools or don't need all the components of an ECM suite can purchase one-off apps from software providers to meet their needs. This approach to managing enterprise content -- which includes content services applications, platforms and components -- falls into the content services classification.
At a high level, key elements of ECM incorporate the following:
- Content lifecycle management.
- Workflow management.
- Information governance.
- Content management systems.
- Collaboration tools.
- Enterprise document management.
- Digital asset management.
Reliable ECM software includes the following features:
- Automated workflows. A workflow engine pushes content through a set of defined steps that support business processes and the content lifecycle.
- Integration with other applications. It's useful for ECM to interoperate with an organization's existing platforms, such as CRM and ERP applications. Many ECM platforms use RESTful APIs to integrate with other web services. Generally, cloud-based ECM tools easily integrate with other cloud services.
- Disaster recovery planning. ECM software incorporates disaster recovery planning, enabling organizations to digitally secure and protect their content from theft, fire or natural disaster, while also ensuring operations proceed as normal in case of a disaster.
- Document scanning. ECM software lets users easily convert paper-based documents into digital information, store those documents in the ECM system, and share, manage and mine them with efficiency.
- Search capabilities. One of the primary goals of ECM is to make content more accessible to users. Advanced search capabilities should be a top priority, enabling users to perform a full-text search and filter the results.
- Metadata support. Advanced ECM platforms include support for automated metadata and tagging driven by an AI engine. They also support multiple enterprise taxonomies.
- Versioning. ECM can track and store multiple versions of files. These tools might also incorporate the ability to revert to a previous version of a document.
- User access controls. For security reasons, an ECM platform often has capabilities to prevent unauthorized users from viewing or editing certain documents. Many ECM platforms incorporate role-based access controls to achieve this.
How to implement an ECM platform
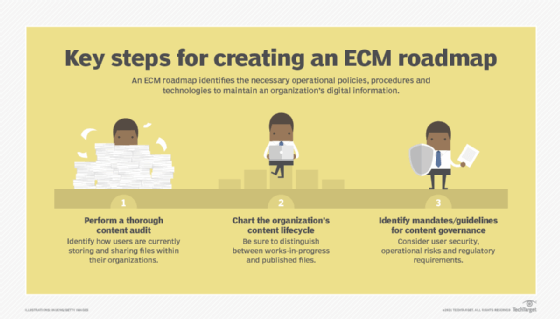
An ECM implementation is often a complex and challenging process that involves a variety of stakeholders and departments. Before implementing ECM, it's important for organizations to develop an ECM roadmap or strategy to identify the priorities of the ECM implementation and get clarity on the necessary procedures and technologies it entails.
The first step of creating an ECM strategy is to perform a content audit by documenting all the types of content the organization deals with, the business processes it's part of and who handles the content.
Once an organization clearly understands the ECM strategy, the next step is implementation. The following are essential steps to successfully implement an ECM system:
- Involve key stakeholders. A single employee -- or even a single department -- should not try to implement an ECM system alone. Multiple departments must be involved due to the collaborative nature of ECM. Businesses should create a team centered around multiple groups, including implementation, governance and executive teams.

- Define goals. Organizations should have a clear understanding of what an ECM implementation will achieve. Regardless of the industry or department implementing ECM, users likely have common goals:
- Eliminate the dependency on paper.
- Streamline all business processes.
- Reduce organizational risk.
- Optimize productivity.
- Improve customer service.
- Plan how to reach those goals. Next, businesses should determine how to reach the goals they've set. They should consider whether they need to migrate content, train users or build a new ECM system. During this step, businesses should evaluate which processes are high priority.
- Build, test and deploy. Ideally, businesses should drive an ECM implementation using Agile or Scrum methodology. This enables stakeholders to be fully engaged as they evaluate biweekly or monthly releases.
- Iterate. An ECM implementation never truly ends. Businesses should build in the capability to refine an ECM system over time to maximize business value.
The future of ECM
In 2016, Gartner declared enterprise content management had been replaced by content services -- the strategic concept that involves content services applications, platforms and components but is less concerned with centralizing all information into one enterprise-wide platform. As part of that initiative, Gartner replaced the ECM Magic Quadrant with a content services Magic Quadrant in 2017.
However, organizations still frequently use ECM to organize their information and achieve goals faster.
Content services platforms (CSPs) and ECM are not equivalent terms, and one will not likely replace the other. A CSP focuses on managing transactional content in the context of solving a particular problem. ECM is broader in scope; it seeks to manage all forms of content within the enterprise, regardless of its type or where it resides.
ECM has also evolved to become an approach rather than a single technology. In the future, enterprise content management strategies and tools will continue to change to adapt to the demands of organizations looking for more agility and integration. As technology evolves, ECM vendors add more features.
More organizations are incorporating team collaboration tools into their ECM approach. Plus, constant advancements in cloud, mobile and analytics technology continue to increase users' expectations of ECM capabilities. Automation and machine learning are becoming key complements to ECM, and it is becoming more and more likely that cloud deployment will be the key to maximizing an ECM system's effectiveness.
Editor's note: This article was republished to improve the reader experience.






