
Getty Images/iStockphoto
AI governance can make or break data monetization
As pressures mount for businesses to get the most value from their data, AI governance ensures the data to be monetized is secure, protected, trustworthy and used responsibly.
Today's AI-enabled enterprise relies on the timely availability of quality data. But beyond availability, the data itself and how it's governed can affect revenue streams as businesses find new ways to generate value from vast quantities of historical, real-time and synthetic data.
Businesses monetize their data in many ways. They use it to enhance operations, improve productivity, develop products and services, and analyze business opportunities. They can also monetize data externally by selling it as a product to other organizations.
But data monetization demands careful governance, especially as AI systems use ever-growing volumes of data and exert more control over the data storage and management environments that are key to any data monetization initiative. AI governance establishes the rules, policies, frameworks and controls needed to responsibly and effectively convert meaningful business data into value.
The importance of AI governance
Data monetization and data governance synergistically converge within AI. Good data governance affects the quality, reliability, organization and management of data. In turn, good data impacts the performance and accuracy of AI systems.
AI governance is a major area of concern for business leaders. The "AI Governance Profession Report 2025" notes that 77% of organizations surveyed -- nearly 90% of organizations currently using AI -- are building or refining AI governance programs for process automation, data analysis, automated decision-making, customer interactions and personalizing experiences. These high percentages suggest that AI governance is viewed as a strategic imperative in several key areas, including the following:
- Business ethics. AI governance ensures the responsible use of AI through appropriate use policies, fair application of AI, and bias mitigation in data sets and machine learning (ML) models. f a business chooses to sell or use a data set, for example, AI governance can ensure it represents a fair and unbiased cross-section of users, customers or other constituent data sources.
- Explainability and transparency. AI governance requires that AI decision-making processes are understood, readily explainable, transparent and repeatable. Explainability and transparency can help determine the origin of data, how long it has been retained and how it has been processed.
- Risk mitigation. AI governance can help AI-driven data monetization initiatives adhere to data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA and the EU's AI Act. Governance measures can include strong access controls, human approval before data is processed or shared, and data encryption and anonymization techniques to maintain global compliance and safeguard sensitive data from misuse.
- ML model operations. AI governance should encompass the entire lifecycle of the ML models and greater AI system to ensure they're performing well and delivering accurate outcomes. Metrics and KPIs can help oversee operational behavior and guide ongoing actions, such as algorithmic updates and model retraining.
Ultimately, AI governance demands comprehensive frameworks that let organizations implement data monetization initiatives while maintaining security and compliance, especially when using AI and ML to derive value from business data.
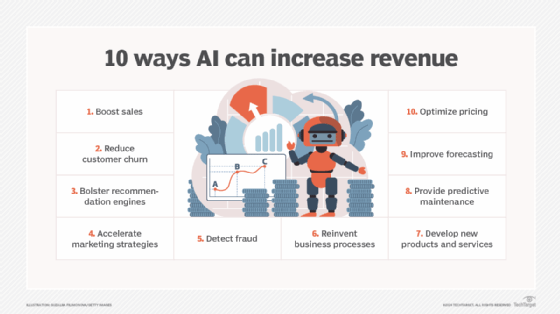
Data monetization strategies
Data monetization is poised to become a major revenue source for modern businesses. The global data monetization market is estimated to grow 25.8% annually and surpass $16 billion by 2030, according to a report by Grand View Research.
There are two fundamental approaches to data monetization: direct and indirect monetization.
Direct data monetization
Direct data monetization involves direct provisioning of data to outside businesses. The data might be sold outright as a one-time revenue source or licensed as a recurring revenue stream. This sort of monetized data includes the following:
- Raw data is collected directly from a source, such as client sales histories or purchasing patterns.
- Preprocessed data has been vetted for quality standards, including completeness, integrity and accuracy, or otherwise prepared using techniques like normalization, feature enhancement, tagging and anonymization.
- Analyzed data is raw data that has been preprocessed and analyzed to provide meaningful insights that can then be sold to other businesses.
Direct data monetization can also use data resources to create data-driven business products and services. A medical analytics company, for example, might create a service that collects and aggregates patient data and performs the analytics to render diagnostic or treatment recommendations for clinicians. Similarly, a business might collect performance data from equipment across a manufacturing floor that can be analyzed to provide optimization and routine maintenance recommendations.
Building a meaningful strategy is a critical part of data monetization. Direct monetization efforts generally follow these six steps:
- Identify the data to be monetized. Not all data is worth monetizing. Consider where the data comes from, what it's used for and whether it has the potential to bring value to the business. Sometimes, data that has little direct value can be coupled with other data to create worthwhile data resources such as analyzed outcomes.
- Determine the beneficiaries of the data. Consider the target audience -- those willing to buy or benefit from the available data. Make a strong business case for each audience as data buyers.
- Ensure high-quality data. Every AL and ML process demands high-quality data that's accurate, complete, timely and consistent. Data might need to be curated, tagged, normalized and enhanced with key features to achieve quality levels worthy of monetization.
- Set a value or price on the data. Not all data has the same value, so it's important to put a value or price on the data set that's competitive in the data marketplace. Perform a competitive market analysis to ensure the data is unique, highly relevant, timely and in demand, so it will likely command a higher value.
- Implement suitable governance. Data has value and might contain sensitive information. Plan and implement appropriate data and AI security, protection and compliance policies to manage data risks, ensuring it's used properly and adheres to regulatory requirements.
- Market the data. Business leaders can work with sales and marketing teams to set pricing and establish a marketing plan to get the data into the hands of interested customers.
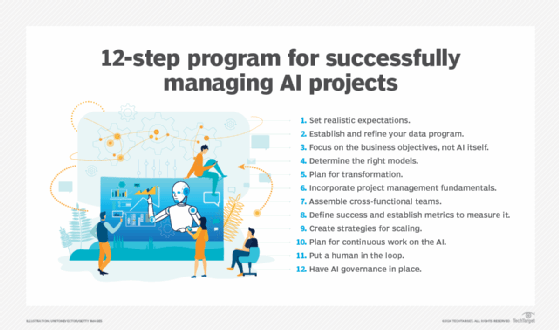
Indirect data monetization
While direct data monetization focuses on external sales, indirect data monetization primarily focuses on potential business value derived from the in-house use of data and analytics. Internal efforts can take many forms, but common initiatives seek to enhance a process, a product and the customer experience in the following ways:
- Data analysis. Businesses can analyze data to improve efficiency, ease bottlenecks and lower costs. For example, a logistics company can analyze data to lower fuel costs and optimize delivery schedules.
- New features. Data can be used to add features to a company's existing products or services. An e-commerce business, for example, can use its data to add purchasing recommendations for returning shoppers, or a manufacturer can analyze quality control data to reduce defects and build more reliable products.
- Better customer service. Organizations can collect and analyze customer behavior, feedback and purchasing data and use it to improve the customer experience, drive new sales and build customer loyalty.
Direct and indirect data monetization aren't mutually exclusive. They can be used simultaneously to yield even more value for a business. A company that collects and analyzes data to provide insights to third-party businesses can also sell or license the underlying data to outside parties for their own unique applications.
GenAI and data monetization
Generative AI (GenAI) is playing an increasingly important role in data monetization. It can vastly extend AI capabilities by supporting decision-making and synthesizing the creation of new content and workflows based on known data. GenAI provides benefits in several areas of data monetization, including the following:
- Synthetic data. GenAI can create almost limitless amounts of high-quality data that can be used to train ML models or test software applications. Since the synthesized data can be tailored and curated for almost any purpose, it can be generated on-demand and monetized as a product. Synthetic data is free from the data privacy and regulatory compliance risks that restrain real world data.
- Data preparation. AI routinely deals with complex unstructured data, such as audio, text and images. It requires significant computing power and a clear purpose to process this data into clean, high-quality structured data. GenAI can take orders, perform the processing and deliver high-quality data sets for internal or external monetization with high levels of autonomy.
- Operational improvements. With little, if any, human intervention, GenAI can be combined with agentic AI to support dynamic workflows capable of adjusting on-demand to meet the needs of each customer. GenAI can use real-time and historical data to bolster indirect data monetization by providing workflows that maintain security and compliance while lowering operational costs.
Who makes data monetization decisions?
Business leaders are responsible for generating value from data, yet they're also responsible for maintaining data privacy, providing governance, meeting compliance obligations and ensuring the ethical use of data. A dedicated cross-functional business team typically makes data monetization decisions. That team includes the following roles:
- The CEO is ultimately responsible for the strategic decisions involved in data monetization and business outcomes.
- The chief data officer (CDO) typically sits at the forefront of a data monetization initiative and is responsible for data protection, data governance and the ethical use of data, as well as getting business value from data.
- The CIO is mainly responsible for the storage, security and protection of business data and the infrastructure within which the data is moved and processed.
- The product owner and group manager are familiar with the mechanics of the workflows or product, such as an e-commerce web presence, that generates or uses the data being monetized.
- Data and analytics teams, typically under the direction of the CDO, provide a clear understanding of the data's value, meaning, availability and use, so it can be effectively monetized.
- Compliance and legal teams ensure proper data and AI governance in accordance with the prevailing regulations and legislation, in addition to the preparation of data sales, leasing and acceptable use agreements.
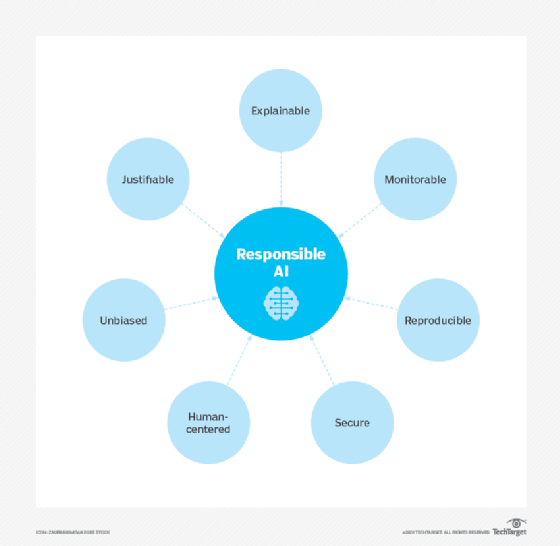
AI governance challenges in data monetization
Data monetization initiatives inevitably involve AI systems in one of two ways: The data being monetized will be used to train and operate AI systems or the AI system will be used to select, process and deliver the data being monetized. In either case, AI governance builds upon existing data governance, such as privacy and security, and becomes inseparable from data monetization. However, AI governance comes with several challenges, including the following:
- Security and regulatory compliance. AI governance must meet prevailing regulatory obligations to ensure monetized data conforms to the GDPR, HIPAA, the EU AI Act and other national and regional legislation. Depending on the regulation, AI systems can be required to ensure data is properly organized, filtered, anonymized and encrypted to prevent personally identifiable information (PII) from being distributed outside the enterprise.
- Ethics and transparency. AI governance must ensure the data being monetized is used ethically in alignment with appropriate business purposes. AI systems might be required to emphasize monitoring, transparency and explainability to prove to regulators and stakeholders that AI systems handling monetized data are mitigating bias and performing at acceptable levels.
- Data quality and provenance. Data quality is the key to trustworthy AI. AI governance must ensure the monetized data, which will ultimately train other AI systems, is accurate, complete, timely and relevant. The data's origins should also be validated to ensure it's suitable for monetization. Third-party or open source data elements, for example, might be ineligible for data monetization because the company doesn't own rights to the data.
- Data rights and ownership. Data is intellectual property and will have value beyond its immediate sale to an external buyer. Compliance and legal teams should frame monetization agreements that outline how the data being provided is used and what rights are retained and conveyed with its sale.
- Workflow limitations. AI governance is often unclear and distributed across varied departments, such as IT, business and legal, potentially weakening AI governance and disrupting data monetization initiatives. Clearly defined workflows and ownership across the entire enterprise are required.
Best practices for AI governance in data monetization
AI governance demands can vary among industries and business types, but there are common best practices that can enhance AI governance and facilitate successful data monetization initiatives. They include the following.
- Implement a strong AI governance framework. Use a combination of tools and policies to establish and enforce AI governance that aligns with existing data security, data protection, regulatory compliance and governance efforts.
- Monitor the model and data quality. Continually monitor data quality while applying metrics and KPIs to the ML models and AI system. That way, any disruptions in data quality and performance can be detected and addressed before data monetization initiatives are implemented.
- Focus on transparency and explainability. ML models and AI systems must be transparent and explainable to bolster stakeholder support, regulatory acceptance and customer adoption of data monetization initiatives.
- Automate AI governance tasks. Use automation to build consistent AI workflows and enforce AI governance tasks, such as data classification, versioning, security and compliance, to ensure adherence to AI governance guidelines.
- Create a dedicated AI governance team. Establish a strong cross-departmental AI governance team that includes business, technology, regulatory and legal representation. The team should regularly review AI system performance, address concerns and ensure data monetization projects conform to AI governance guidelines.
- Build a strong data collection strategy. Data monetization initiatives are often safer and more successful when data collection focuses on security and privacy from the start. Limit data collection to the most meaningful elements, maintain data security with strong authentication and encryption, and ensure data privacy with anonymization and other techniques that can obscure PII and keep important data tagged and curated.
Stephen J. Bigelow, senior technology editor at TechTarget, has more than 30 years of technical writing experience in the PC and technology industry.








