The ERP HR module: Key features explained
ERP typically includes an integrated HR module. Learn what the HR module in ERP does, how it relates to other components and how it compares to standalone HRMSes and HCM suites.
The ERP HR module is the software component that enables organizations to handle human resource management for the entire employee lifecycle in their ERP software, from hiring to termination and everything in between. It centralizes employee information and HR processes in one common system and has become even more critical as companies increasingly focus on career development and the employee experience.
What is a human resource module and how does it play into ERP?
An HR module helps an organization use an ERP system to manage everything related to employees. This includes -- but is by no means limited to -- employees' personal information (date of birth, address, nationality, contact information, etc.); employment and job information (position, manager, compensation, grade, etc.); actions and events (transfers, promotions, termination, etc.); employee and manager self-service; performance reviews; compensation planning; and benefits management.
Most ERP HR modules also contain talent management applications to enable companies to manage functions such as recruitment, onboarding, performance management, training and development, and succession planning.
The HR module relates to the rest of the ERP system by enabling companies to manage important employee information while providing the employee data the ERP needs for several business processes, such as logistics and shift scheduling.
The ERP HR module is more commonly known as the human capital management (HCM) module. Traditionally, a standalone HR system was called a human resources management system (HRMS) or human resources information system (HRIS). While these terms are still used, they generally refer to the core HR component that handles basic HR functions, such as employee records and self-service, as part of a larger HCM system.
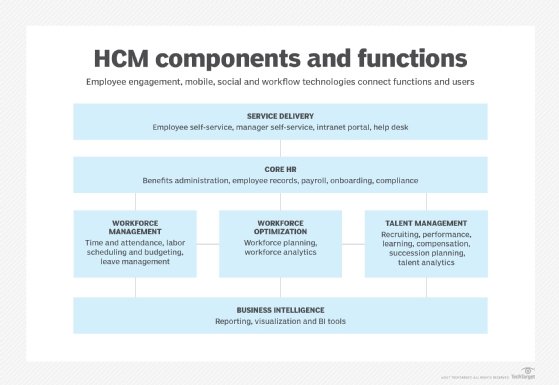
Key features of ERP HR modules
The following are the main features and submodules of an ERP HR module:
- The core HR module is the central repository for managing employees and employee information. It enables designated individuals to access information about employees, make changes and execute various actions, such as promotions, transfers and terminations. Most systems contain capabilities such as employee profiles, org charts, and manager and employee self-service, including built-in workflow capabilities for approvals. Core HR can also manage different types of employment, such as global assignments, concurrent employment (working more than one job) and contingent workers.
- Time and attendance helps track employee attendance, work hours and time off, and manage short- and long-term absences. Some systems also handle work schedules. Time evaluation for payroll processing, which involves calculating the effect of hours worked on certain policies, such as overtime rules and labor contracts, is another important feature of a time and attendance module.
- The payroll module is a comprehensive system for running payroll, including tax calculations, deductions and compliance reporting. In some companies, payroll is considered a responsibility of the finance department, but the payroll system itself is always a standalone system or part of the ERP HR module. Very few ERP finance modules include a payroll system.
- Benefits administration manages employee benefits, such as health insurance and retirement plans. It also provides compliance reporting and can often integrate with insurance carriers and other benefits providers.
- The compensation management module handles compensation planning, bonus management and variable pay programs. Some vendors provide spot bonus functions.
- Recruiting manages the entire hiring process, including raising job requisitions, creating and posting job postings, evaluating candidates and issuing offers. Many vendors also offer career websites and interview scheduling.
- The onboarding component supports the steps involved in bringing new employees into the organization, including completing compliance forms, issuing equipment and providing system access and other credentials.
- Goals management supports creating, assigning and tracking the progress of company and individual goals. Many systems enable cascading goals from the company and team levels. In some cases, goals are managed in the performance management module.
- Performance management tracks employee performance through goal setting, performance evaluations and feedback mechanisms, and helps with performance reviews and skill development. It is usually tightly integrated with the goals management module.
- Career development enables employees to identify future roles, career paths and training opportunities to develop their careers. Some advanced software uses marketplaces to provide access to career opportunities, such as mentoring and internal projects.
- Learning management provides training delivery, course catalogs, evaluations and additional features.
- Succession planning Helps identify key positions, plan for successors and build talent pools.
- Reporting and analytics generates customizable reports and analytics on various HR metrics, which helps in strategic decision-making and workforce planning.
- Workforce planning enables companies to plan current and future workforce needs using data from across the ERP HR module.

Advantages of integrating an HR module to your ERP system
Strong integration between an ERP system and the HR module -- whether it's part of the same ERP system or in a separate HRMS or HCM suite -- helps organizations do useful things, such as the following:
- Use employee data in other ERP processes.
- Generate reports and analytics that combine various ERP and HR data for a holistic view of operations.
- Enable cross-ERP workflows.
- Integrate cost center data with HR data for payroll and other cost assignment processes.
- In a logistics or distribution module, align staff scheduling with business needs.
- Improve workforce planning to better meet current and future needs across the business.
- Support upskilling and reskilling to realize workforce plans.
- Manage job position budgets and recruitment based on business needs.
Traditionally, ERP software vendors included an integrated HR module in their ERP system. In recent years, with the move to the cloud, some of the large vendors have built or acquired standalone HR modules and integrated them with their ERP. This newer architectural model enables vendors of older, legacy ERP systems to acquire cutting-edge capabilities and cloud expertise while taking advantage of years of integration experience to support modern, end-to-end business processes in their ERP systems.
Luke Marson is a principal architect and part of the management team of a global SAP SuccessFactors consulting partner, where he focuses on SuccessFactors Employee Central, extensibility and integration technologies.







