20 must-have HR software features and system requirements
The demands on HR software are only growing more complex. Here's what to focus on to meet your requirements in recruiting, onboarding, employee benefits, compensation and more.
While the long-term goals can vary tremendously, broadly speaking, an HR team implements HR software to support the needs of multiple constituencies: managers, employees, the HR team itself, and departments within the organization that rely on employee data, such as payroll and IT. The immediate goals typically include automating manual tasks, making information available to people when they need it and being able to analyze HR data to make informed decisions.
HR software functions are typically arranged in various modules, each designed to perform a specific task. For example, an HR system might include a core HR module to track employee data, as well as modules for performance management and compensation. You can usually select the modules you need from one vendor and add others from that vendor later, or license software from separate vendors to fill certain gaps. The core HR module is often the first implemented since it feeds employee data to the other modules, whether licensed from the same vendor or third-party vendors.
Before beginning the process of evaluating HR systems, it's important to build a list of requirements and understand the different software features and modules available to address them.
When determining the features to include in the requirements document, consider your company's culture and plans for the future. If the organization seeks to foster a learning culture, for example, a learning management system (LMS) may be more essential than performance management software.
It's also important to consider features that affect the entire system. This includes the usability of the software and its UIs, its security model, how configurable it is, and whether the software can scale with your organization as it grows. The HR and IT teams might also be interested in knowing how easy it is to integrate the software with other applications used in the organization. This could be other HR software, email, a calendar, internal communications technology or single sign-on.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another feature that can have a major impact on a variety of modules and the HR processes they support. While AI has become mainstream and is incorporated in many HR applications, the journey is still a work in progress. Understanding the AI features that vendors have already implemented and their future plans will assist in evaluating vendors.
Consider the following HR software features when compiling your HR system requirements checklist.
1. Cloud based vs. on premises
Most new HR systems are cloud based. The software is hosted by the vendor, and employee access to the application and data is available through a web browser or mobile device. Alternatively, vendors offer HR software that's installed and managed on premises in the enterprise, typically by IT. Both options have advantages, but cloud based is now the preferred model and many vendors do not sell an on-premises version.
2. Core HR
A key component of HR software, the core HR module stores information about employees and is often the hub for functions that apply to the whole HR system, such as security and reporting. An HR team will often access this module on a daily basis to find or update information. When evaluating the core HR functionality, confirm the following points:
- One centralized database rather than multiple databases, which can happen when the software has been pieced together from vendor acquisitions.
- All the necessary employee information can be entered and reported on, such as employee name, address, emergency contacts, salary, job and department.
- Ability to create custom fields to track information specific to the organization.
- Role-based security with the ability to restrict data based on parameters, such as by country. This simplifies the assigning of access rights to employees and eliminates the need to have the same role multiple times to restrict data access.
- Entries can be future dated and back dated.
- The system is configured to meet all government compliance requirements for each country and region where the organization operates.
- Non-employee data, such as contractor information, can be recorded in the system.
- Interfaces can be set up to allow access to employee data in other systems, such as payroll and IT applications.
- AI chatbots are available to answer employee questions, thereby reducing the number of requests sent to HR.
3. Time and attendance
HR software typically provides features to track absences and capture hours worked on a time sheet. Make sure the system can accommodate corporate policies and practices. Also validate that it can do the following:
- Provide the ability to configure all the absence types used by the company.
- Define which absence types apply to which employee populations.
- Produce schedules and time sheets that capture and display required information.
- Make timekeeping simple to use on a mobile device or browser.
- Provide exception reporting to highlight missed shifts, missed clock-outs and overtime.
- Specify statutory holidays by country and region and configure eligibility requirements.
- Provide approval workflows and reminders for absence requests and completed time sheets.
- Provide a mechanism to capture where an employee spent their time, such as training, meetings and projects.
4. Recruiting
Often referred to as an applicant tracking system, the recruiting module covers the lifecycle of finding and hiring new employees. Most HR systems include functions that support the recruiting process, though they're not always as advanced as products from vendors who specialize in this area. Key features to consider include the following:
- A job library that contains a job description and key information about the job, such as salary range, job family and job level.
- Configurable requisition and offer-approval workflow.
- An easy process for posting open positions to multiple websites, job boards and social media.
- Reports, tags and custom groups to track candidates.
- Functions for hiring managers to view and rate candidates and add comments.
- Support for multiple offer templates to meet the unique needs of the organization, especially when the organization operates in multiple countries or regions.
- Support for the entire offer process, including sending offers, candidate signatures and returning signed offers electronically.
- Easy for job seekers to find relevant job postings and apply with the ability to ask knockout questions.
- Support for advanced digital signatures like those offered through Docusign.
- Ability to add attachments to offers.
- Ability to integrate with standard office applications, such as email and calendar and tools to easily add candidates from popular websites, such as LinkedIn.
- Ease of sending regular communications to passive candidates.
- AI features that help draft job descriptions and job offers as well as rank candidate resumes based on specific criteria.
5. Onboarding
An onboarding module can enhance the onboarding process for new hires and provide a positive first impression. At a minimum, new hires use the onboarding module to complete forms and review policies. Look for the following features when developing an HR system requirements checklist:
- Simple process to move new hires from recruiting to onboarding and avoid rekeying data.
- Customized landing page that allows adding company information, videos and organizational charts.
- Employees can easily complete and sign forms and policies.
- Before their first day, new hires can access and complete all the necessary paperwork.
- Task lists for everyone involved in the onboarding process.
- Signed documents are easily accessible for future reference.
6. Performance management
Many vendors have added features to support informal feedback options, while continuing to provide functions for a traditional performance review process. Regardless of the performance management approach, consider the following points when evaluating HR software features:
- A configurable form to capture required data from employees and managers.
- Configurable workflows to bring the process and approvals in line with the company's performance management process.
- Concurrent filling of forms, which reduces the amount of back-and-forth required to complete the review process.
- Reports and dashboards to track progress and analyze results.
- 360-degree feedback.
- Integration with calibration, compensation and succession.
- AI to summarize feedback and provide recommended wording for comments entered by employees and managers.
- Features that make it easy for managers and employees to view past ratings and feedback, such as feedback from the rewards and recognition platform or 360 feedback.
7. Employee benefits
Incorporating a feature that captures employee benefits information can save significant time during the onboarding process and open enrollment. After examining your organization's requirements, confirm that an employee benefit feature supports the following actions:
- Configure multiple plan options.
- Upload data to insurance providers rather than rekeying the data.
- Allow employees to choose their coverage based on the options presented and provide costs.
- Push data to payroll to avoid rekeying data.
- Recommend plan options based on an employee’s specific situation, such as a plan more aligned to families versus options for single employees.
8. Reporting, dashboards and analytics
While reviewing HR software features, allocate sufficient time for reporting and dashboards. Too often, those capabilities are left until the end of a demo. Look for the following:
- Enough standard reports to meet most needs.
- Dashboards that include charts and graphs to provide actionable insights.
- Ability to create custom reports and dashboards and have access to all data entered into the system.
- Scheduling reports and dashboards to be emailed to specific employees on a regular basis.
- Restricting access to data using role-based permissions.
- Ability to pull data from multiple data sources. This is important if the HR software is acquired from multiple vendors, however it may require licensing a third-party reporting application.
9. Learning and development
Incorporating an LMS and learning experience platform (LXP) can streamline the administrative tasks of scheduling and running courses, provide online courses and reinforce a corporate learning culture. Consider the following features when exploring an LMS and LXP:
- Support for online and instructor-led training.
- Ability to combine courses, articles and videos into a curriculum.
- Integration with third parties that license online courses.
- Detailed reporting and dashboards.
- Ability to add content.
- Auto-assigning courses based on predefined rules and employee data, such as assigning new hire orientation training based on an employee's hire date.
- Curate content for employees based on the types of articles they've read in the past and the content viewed by others in a similar role.
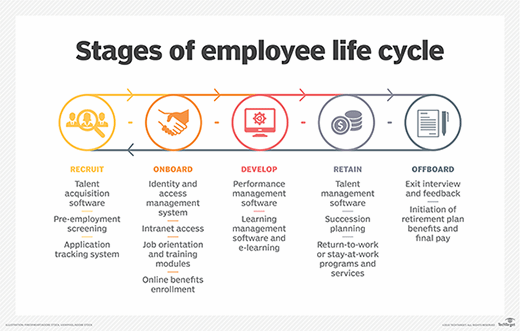
10. Self-service portals
A significant benefit of using HR software is the ability to securely share information with employees and managers. Consider the following self-service features:
- Employee self-service that enables employees to view and update personal information.
- Manager self-service where managers can view and update information about their direct reports.
- Role-based permissions to control access to sensitive data.
- An approval process that ensures all employee- and manager-initiated changes are acceptable.
- A landing page that offers the option to display company-specific information, such as policies and company holidays.
- An organizational chart with control over what details an employee can see.
11. Integration options
The ability to integrate an HR system with other software used in the work environment can be very valuable. IT systems managers, for example, might benefit from knowing about new hires and terminations. The following two options are typically available:
- Custom integrations, which allow data to be pulled from the HR software. These can be APIs or file transfers using Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
- Partner integrations, which offer prebuilt integration with specific third-party applications.
12. Data management
You can edit and audit data with HR software's built-in tools. The following valuable features may be available:
- Data import when multiple changes are required at once, such as in a large reorganization.
- Quick entry to list multiple employees and a subset of fields requiring an update.
- Error checking to ensure data is cleanly entered and valid.
- Audit report functionality that can track changes across the system, displaying the name of the user that made the change, the date and time, and the data that was updated.
13. Payroll
The data between HR and the payroll department is closely related and warrants consideration, regardless of whether payroll reports to HR or finance. Many HR systems offer a payroll module in addition to prebuilt integrations with the major payroll providers. Consider the following payroll features:
- Tight integration with core HR to avoid rekeying data.
- Support for multiple currencies.
- Enough payroll codes to meet current and future needs.
- Employee self-service access to pay statements and other tax-related forms.
- Integration with the time and attendance and benefits modules.
- Simple data validation tools to ensure data is correct before being submitted.
- Payroll comparison to highlight significant changes from one pay cycle to the next.
14. Compensation
Although it happens just a once or twice a year, compensation planning is critical to get right, and the often-used spreadsheet can be problematic and not very secure. A good compensation management module will provide the following benefits:
- Eligibility rules to determine which employees will be part of the compensation process.
- Budgets that can prevent managers from overspending.
- Workflows and approval processes.
- Data security and control to protect sensitive data.
- Comprehensive reporting to understand who will receive a pay increase and how budgets are being spent across the organization.
- Performance management ratings that default to a recommended salary increase.
- Ability to plan non-base-pay-related compensation items, such as bonuses, options and stock grants.
- Ability to budget and report in one currency when the organization operates in multiple countries.
- The ability to generate total rewards statements that incorporate all compensation elements awarded through the process.
15. Calibration
For companies using a rating system as part of performance management, it is preferable to have a step in the process where HR managers and senior leaders can review ratings at a high level and adjust them before the ratings are final. This helps avoid the time-consuming process of opening each review one at a time to make edits. Consider the following features when looking at calibration:
- Integration with the performance management module.
- Ability to see employees listed on a rating scale, such as a nine-box grid.
- Employees can be moved from one rating to another with drag-and-drop controls, which simultaneously updates the employee’s rating on their performance review.
- The software records the original and new rating.
- Filters to narrow the number of employees displayed, such as by department, job title or job level.

16. Succession planning
Adding a succession planning module to an HR system can help identify and prepare rising stars in the company for senior roles. However, before dedicating time and money to implement and license this module, be sure there's a companywide commitment to succession planning. Consider the following capabilities when evaluating a succession planning feature:
- Integration with performance management, calibration, core HR, and employee recognition tools.
- A user interface that makes it easy to see employee details without switching to another module, such as performance ratings and job families.
- Ability to incorporate job data, such as job grades, families and descriptions.
- A security model that allows managers at different levels in the organization to participate in the planning process without divulging sensitive data, such as preventing a director from seeing data about their peers.
- Filtering tools, which enable those doing reviews to focus on certain employee groups filtered by criteria like job title, department or position.
17. Rewards and recognition
Providing employees with tools to recognize each other's contributions helps build a culture of appreciation and boost employee engagement. The data can also be helpful when employees and managers meet to discuss performance. When the recognition includes points that can be redeemed for rewards, employees benefit further from the chance to spend points on things they really value. Some features to consider include the following:
- Software that handles both recognition and rewards.
- Ability to customize the number of points awarded when someone is recognized by a peer versus someone in a leadership position.
- A customizable catalog of rewards and associated points.
- Integration with online pay systems, such as PayPal, which enables employees to purchase items with a combination of points and their own money.
- Reporting tools to measure use of the system and track tax implications for individual employees and the company.
- Functionality that supports companies with employees in more than one country, such as reporting that makes it easy to track and report on the tax implications of each employee purchase.
18. Marketplace
It's not uncommon for an HR team to select a vendor that offers most of the functions they need, while not meeting all their requirements. In this case, the team might look for other vendors who can fill the gap. For example, HR might select a vendor for core HR, performance management and learning management but prefer a third-party provider for recruitment. The primary vendor might offer a marketplace of partners who are certified and offer functionality that is complementary to the core system. In some cases, the vendors in this marketplace might offer competing software that is more specialized, or they offer a service not available through the primary vendor. Consider these points when listing your requirements:
- A substantial list of vendors.
- Integrations between the third party and primary vendor have been tested and work correctly.
- Availability of a wide variety of software and services.
- The sales team for the primary vendor is aware of the vendors in the marketplace and will recommend their services when appropriate.
19. Organization chart
Many core HR modules provide basic organizational charts, but there are vendors who specialize in this area and offer advanced features typically not available by default. The following are features to consider:
- Integration with core HR to avoid rekeying employee data.
- Security model that restricts what users can see and allows for roles to be auto-assigned to employees based on their position.
- Ability to create custom organizational charts, such as one that displays and rolls up salary information, or one with performance ratings for each employee.
- The ability to create and generate reports on a subset of the organization based on specific needs, such as producing a one-page chart of the senior management team.
- The software provides features to support workforce planning, such as designing an organizational chart based on a proposed restructure, then migrating the changes to the core HR module.
20. Compensation survey data
Organizations have a need to compare their total compensation practices with those of competitors to validate that they are rewarding employees sufficiently to retain and attract top talent. Vendors in this market often use surveys to collect data, but some payroll vendors and other large organizations with access to compensation data produce the results using data within their domain. The data is always anonymous at the granular level, but survey participants are often listed. Users of the data can filter the survey results by country, region, company size, market segment and potentially others. The following are items to consider when looking for compensation data:
- The survey data includes participants from similar organizations and regions.
- The survey has taken place over many years and has a track record of producing reliable results.
- The data can be analyzed using multiple parameters, such as by job family, location and country.
- Job descriptions are well defined and facilitate matching jobs in the organization to those from the survey.
- It is possible to record job matches for future iterations of the survey.
Eric St-Jean is an independent consultant with a particular focus on HR technology, project management and Microsoft Excel training and automation. He writes about numerous business and technology areas.







