What are global area networks (GANs)?
A global area network (GAN) is a type of network that connects devices and users on a global scale.
GANs consist of multiple smaller interconnected networks, such as wide area networks (WANs) and local area networks (LANs). These networks create a web that spans a country, continent or even the globe. The internet, for example, is considered a global area network.
GANs are the most expansive type of network, as they are designed to connect businesses, individuals, applications and services on a nationwide or global scale. This type of network acts as the backbone for the internet and many other services that are used daily, including email, cloud-based applications and video conferencing.
How do global area networks work?
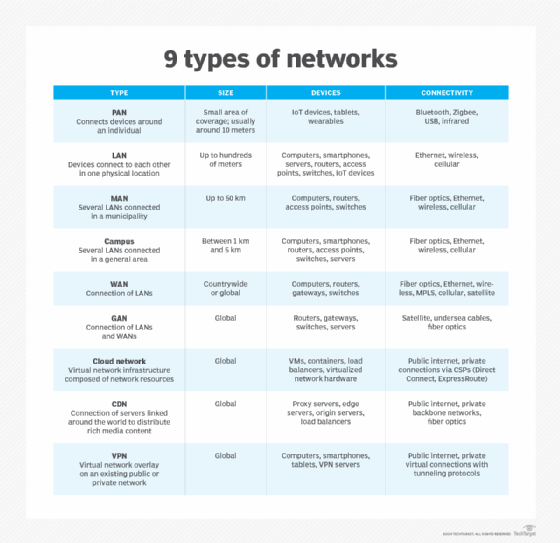
GANs are made up of multiple smaller types of interconnected networks. These can include WANs, LANs, metropolitan area networks (MANs) or any other type of network.
As an example, LANs are typically smaller networks for home or corporate use cases. WANs are a larger-scale network that can connect networks around large geographical areas. They are typically used by organizations to connect office locations or users in widely distributed areas. MANs are typically town or city-wide networks used by a municipality to provide a service or utility. However, GANs could also be made up of other network types, such as cloud or content delivery networks.
The underlying infrastructure used to transfer data can include satellites, fiber-optic cables, 4G and 5G cellular networks and the infrastructure of internet service providers (ISPs). How each technology is used depends on the specific network. For example, satellite transmissions might be used in remote or oceanic areas; 4G and 5G technology would be used to transfer data from mobile devices; and fiber-optic cables can be used for low-latency data speeds on land or below the sea. ISP infrastructure, like data centers, might also be used.
GANs will also use commonly accepted standards, such as the Internet Protocol, and different routing protocols, such as the Border Gateway Protocol.
Types of global area networks
GANs can be implemented and categorized using the following technologies:
- Public internet. The internet is the largest and most common example of a GAN, connecting millions of devices and users online. Services and business operations such as email, cloud applications and VoIP use the internet.
- Satellite GANs. These GANs use a network of satellites to provide connectivity across the globe. Starlink and Inmarsat are two examples of satellite-based GANs. Satellite-based networks are ideal for providing service in places where physical infrastructure is lacking.
- Mobile broadband global area network. These GANs use 4G, LTE and 5G mobile services. ISPs typically provide global mobile networks. Vodafone Global Enterprise, for example, provides businesses with a mobile-based GAN that uses its global cellular networks. It spans across Africa, Asia, Europe and the U.S.
- Fiber. These GAN networks are created using terrestrial and submarine cables to create a network. Lumen Technologies, for example, has a GAN that operates on fiber and on-net as well as in data center and edge locations.
Industry use cases for global area networks
Global area networks have a wide range of applications for businesses and individuals, including the following:
- Internet access. The internet enables businesses and individuals to access online services worldwide.
- Multinational enterprise connectivity. Global organizations use GANs to connect with international offices and data centers worldwide.
- Connectivity for global network configurations. GANs can facilitate connectivity for any network configuration that requires global infrastructure, such as cloud, satellite and international telecom networks.
- International financial services. Banks and other financial businesses use GANs to enable global transactions.
- Supply chain management. GANs are commonly used in SCM to facilitate the management of inventory and tracking of shipments.
Future trends and challenges in global networking
Global area networks are likely to be shaped by the following current and ongoing trends and challenges:
- 5G. 5G networks will continue providing fast speeds and low latency as 5G infrastructure continues to be rolled out and the adoption of 5G networks becomes more common.
- AI. GANs will also likely adopt AI and machine learning processes to improve network optimization and predictive analytics.
- Edge computing. Pushing data processing closer to end users is also likely to enable efficient data processing and reduced latency within GANs.
- IoT integration. Global networks will further enable internet of things technologies, but this will also mean increased data traffic and require secure data transfer methods.
- Satellite GANs. Deployment of more satellite-based GANs will continue to expand internet access to remote areas.
A global area network is the largest type of network. Learn more about GANs and other types of networks.





