802.11
What is 802.11?
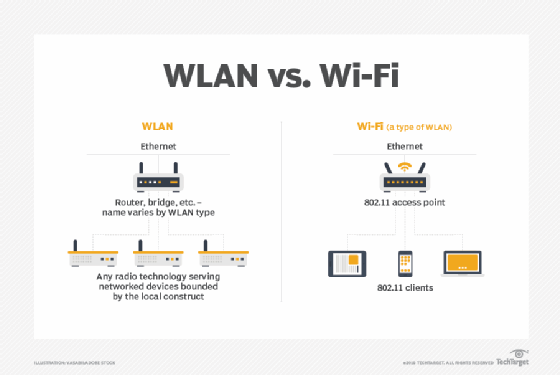
802.11 is a family of evolving specifications for wireless local area networks (WLANs) developed and maintained by a working group of IEEE. There are several specifications in the family, and new ones are occasionally added.
802.11 is the first wireless networking standard to be broadly adopted. The technical specifications govern the implementation of Wi-Fi networks for optimal device compatibility and connectivity. Built into the 802.11 specification family are best practices, physical hardware-layer requirements and algorithms to address resource contention on shared networks.
802.11 technologies originated from a 1984 Federal Communications Commission decision to release the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band for unlicensed use. The original 802.11 standard was ratified in 1997. Dozens of amendments and revisions have been made since its inception.
A similar set of IEEE standards exists for wireless metropolitan area networks; 802.16 outlines physical-layer requirements. All the 802 standards have gone through many rounds of updates.
What is the purpose of the 802.11 wireless standard?
802.11 specifies the interface that enables over-the-air signaling between two or more wireless clients. It is the main bearer of communication for different electronic devices, including actuators, laptops, tablets and televisions.
Each version of 802.11 spells out a theoretical performance limit, such as data throughput, signal range, network bandwidth and radio frequencies. Network vendors use this information to guide product design and identify which generations of Wi-Fi technologies are supported.
What does 802.11 mean?
802.11 refers to the numbering scheme adopted by IEEE. The 802 committee within IEEE oversees the development of industry protocols for wireless networks, including Ethernet networks. The 11 in 802.11 refers to a WLAN standard working group within the 802 committee.
The earliest 802.11 iterations focused on improving speeds and data rates. The initial 802.11 spec specified operations in the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) ISM band, with a top speed of about 2 megabits per second (Mbps), well below the gigabit-level data rates of a modern WLAN.
With each technological advance, the amended specification was identified by adding a suffix of one or two letters to the 802.11 nomenclature. Over time, the string of letters and numbers created confusion for enterprises trying to evaluate the capabilities of vendor products.
To simplify matters, the nonprofit Wi-Fi Alliance in 2018 rebranded 802.11 technology under its Wi-Fi trademark, applying it retroactively to earlier releases. The trade group also oversees certification of vendor products.
The numeric naming designation mirrors the branding of cellular technologies. The current version, 802.11ax, is designated as Wi-Fi 6 to signify sixth-generation wireless.
How does 802.11 work?
WLAN channels rely on networking equipment engineered for high performance. 802.11 deploys six half-duplex, over-the-air modulation techniques that share the same network protocol layer.
802.11 makes several radio frequencies that Wi-Fi devices use to communicate, including the 900 megahertz, 2.4 GHz, 3.6 GHz, 4.9 GHz, 5 GHz, 5.9 GHz, 6 GHz and 60 GHz bands. Each frequency can be subdivided into multiple channels. The amount of spectrum available for licensing varies by country.
The original modulation used in 802.11 was binary amplitude-shift keying, binary frequency-shift keying, binary phase-shift keying and other schemes, such as complementary code keying. Those methods were simpler with regard to designing circuits, but they provided a limited bit rate. Newer modulation methods have emerged that provide higher data speed and reduce a network's vulnerability to interference.
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) has gained increasing prominence since the launch of 802.11a, as it expands the number of clients that can connect to a shared wireless access point. OFDM may be used in tandem with other modulation techniques, such as quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM).
802.11 specifies the use of carrier sense multiple access/collision avoidance, an algorithm that manages path sharing between two transmitting stations. The methodology is similar to IEEE's 802.3 standard for Ethernet networks, although it differs in implementation.
Ethernet uses a full-duplex model for collision avoidance, where the network can listen and talk to devices at the same time. To prevent signals from colliding, Ethernet only allows a signal to be sent once acknowledgement is received that the transmission line is clear.
By contrast, a Wi-Fi network uses a half-duplex model, where it can listen or speak but not do both simultaneously. Wi-Fi uses a media access protocol known as the distributed coordination function (DCF) to monitor signal traffic. If a client on the receiving end doesn't acknowledge a transmission, DCF presumes a collision has occurred and waits a given amount of time before attempting to retransmit the wireless signal.
Why are 802.11 specs important?
802.11 led to established network protocols and is now a universally adopted standard that contributes to broad deployment of WLANs. For vendors, 802.11 and its amendments provide a blueprint for designing compatible and interoperable networking hardware and devices.
Business and society have felt its influence as well. Through amendments and revised editions, the 802.11 standards have spurred research and development of commodity technology, such as high-speed Wi-Fi routers with redundant security. This development has led to increased availability of secure Wi-Fi hotspots at public venues, such as airports, libraries, school campuses, shopping malls and stadiums.
The benefits extend to consumers and home office users, who rely on wireless routers to stream and share data among multiple smart devices on private networks.
What is the 802.11 family?
Here are the IEEE 802.11 specs, listed in chronological order of release:
- 802.11 (1997) is now obsolete. Legacy technology specified two spread-spectrum methods in the 2.4 GHz band: frequency hopping and direct sequence, each at 1 Mbps or 2 Mbps, along with diffuse infrared at 1 Mbps.
- 802.11b (1999) boosted speed to 11 Mbps using direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) in 2.4 GHz. It also accommodated weak signals by maintaining lower DSSS modes and emerged as the signature WLAN technology.
- 802.11a (1999) used an OFDM physical layer in the 5 GHz band to transmit up to 54 Mbps. The advantage of 5 GHz is it's less crowded, but the higher frequency can limit its effective signal range.
- 802.11g (2003) used OFDM in the 2.4 GHz band to achieve similar 54 Mbps transmission, excluding forward error correction. However, this approach also is subject to signal interference from nearby devices. 802.11g and 802.11b equipment are compatible, and vendor equipment carries both designations.
- 802.11n (2009), also called Wi-Fi 4, marked the start of new Wi-Fi standards branding. All 802.11n wireless products support multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) technology, in which multiple transmitters and receivers are used to transfer more data at the same time. The addition of multiple antennas boosts the theoretical data rate to 450 Mbps in 2.4 GHz operation. 802.11n reportedly is backward-compatible with 802.11a, 11b and 11g networks.
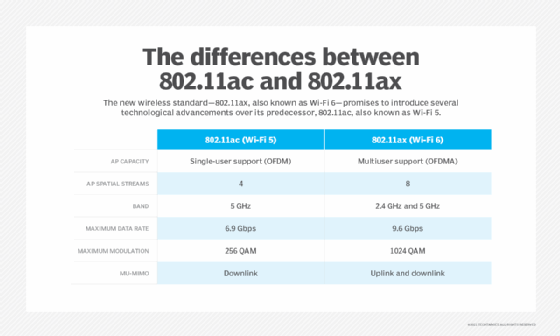
- 802.11ac (2013), also known as Wi-Fi 5, pivots off amendments to 802.11n. Maximum data rates reach the gigabyte level in 5 GHz operation, with expanded channel width, twice the number of spatial streams, 256 QAM bandwidth increases and enhanced multiuser MIMO.
- 802.11af (2014) enables WLAN operation in very high frequency and ultra high frequency bands normally reserved for TV broadcast signals.
- 802.11ah (2017) describes WLANs with low power consumption that could power extended-range hotspots or serve to handle traffic overloads on a cellular network. 802.11ah-enabled WLANs can provide an alternative to short-range Bluetooth connectivity.
- 802.11aj (2018), also called the Chinese Millimeter Wave frequency band, is for WLANs in China and other regions. It provides backward compatibility with 802.11ad, which is in review.
- 802.11ax (2019), also known as Wi-Fi 6, is the current standard. It uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands but has the option to use 6 GHz.
What is Wi-Fi 6?
Certified Wi-Fi 6 products augment MIMO antennas with OFDM to enable routers to broadcast four spatial streams, leading to a fourfold increase in maximum theoretical bandwidth per stream. 802.11ax radios can transmit and receive from either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz.
Follow-on standards for faster WLAN technology are already under consideration by IEEE engineers, including the following:
- Wi-Fi 6E or Wi-Fi 6 Extended enables Wi-Fi 6 to operate in newly licensed 6 GHz spectrum for high-efficiency WLANs.
- The 802.11be draft proposal describes requirements for Extremely High Throughput networks, known as Wi-Fi 7.
- The 802.11ad amendment describes the physical layer needed for networks to operate in the 60 GHz spectrum.
- 802.11bd addresses wireless standards that enable vehicles in proximity to autonomously share safety and traffic information.
- 802.11bf is a task group within the IEEE 802.11 committee studying WLAN sensing that will enable devices to become aware of their environments and elements within those environments.
- 802.11bh is an amendment to an earlier release to study how randomized and changing media access control address mobile client security affects the performance of wireless network services.
- 802.11bi is an outgrowth of an earlier project regarding privacy concerns, particularly standardized steps that prevent networks from tracking a user's location or movement.
Find out everything you need to know about wireless communication in our Tech Accelerator guide.