Top 9 blockchain platforms to consider in 2026
Get the lowdown on the major features, differentiators, strengths and weaknesses of the blockchain platforms that are getting the most buzz -- and real-world deployments.
Interest in blockchain platforms continues to grow as a way to streamline supply chains, improve traceability, simplify trade and improve financial transactions.
Modern blockchain platforms were developed to help overcome the energy consumption and speed limitations of early cryptocurrency platforms, such as bitcoin, and provide practical value for other business uses and applications. Enterprises have begun to adopt these blockchain platforms for some of their application needs, most often in areas that require multiparty cooperation or data exchange, said Suseel Menon, practice director at Everest Group, an IT advisory firm.
Menon pointed to blockchain applications in supply chain tracking, trade finance, digital assets and identity management as advancing beyond the pilot stage and some activity in using blockchain platforms for certain functions of ERP, such as vendor management and supply chain management (SCM).
Other analysts highlighted a demand for blockchain platforms coming from decentralized finance (DeFi), which enables new business models that pose significant threats to traditional banking, finance and supply chain finance.
Here are nine of the top blockchain platforms to consider.
1. Ethereum
First proposed in 2013 and launched in 2015, Ethereum is one of the oldest and most established blockchain platforms. It provides a truly decentralized blockchain and is considered to have strong support for smart contracts, a type of self-executing program that is considered a potential blockchain killer app. Besides its role as a blockchain platform that underpins enterprise applications, Ethereum has its own cryptocurrency called ether.
 Suseel Menon
Suseel Menon
The Ethereum platform has seen widespread adoption by technologists who build decentralized applications (dApps) that run on the Ethereum network. For example, there are numerous platforms and exchanges for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) -- a type of digital asset that can be exchanged on a blockchain. Ethereum has a mature ecosystem of tools for writing smart contracts using the Solidity programming environment, which runs on Ethereum Virtual Machine.
However, alternative blockchain networks could process transactions faster at potentially lower cost than Ethereum, though many observers expected this to change after Ethereum adopted a more efficient security mechanism in 2022. That's when the Ethereum community migrated from a proof of work (PoW) consensus mechanism to proof of stake (PoS), which is more energy-friendly. The Ethereum Foundation estimated this reduces energy use by 99.95% compared to the older approach.
Ethereum is an actively developed technology, benefiting from a pair of major upgrades in 2025. The Pectra upgrade activated on May 7, 2025, introducing account abstraction through EIP-7702. That update enables wallets to function more like smart contracts with features such as transaction batching and social recovery to help users recover their wallets. The Fusaka upgrade took effect on Dec. 3, 2025, introducing a more efficient method for the network to verify data. Instead of requiring network validators to download complete datasets, the upgrade enables them to verify data by checking small samples, which significantly reduces bandwidth requirements and improves performance for Layer 2 networks built on Ethereum.
Ethereum also has an active developer community orchestrated by the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance, which includes major enterprises such as Accenture, JPMorgan Chase and Microsoft.
2. Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is an open source set of tools for creating blockchain applications. The open source project is part of the Linux Foundation's LF Decentralized Trust group, which helps to champion the technology's development and governance. Hyperledger Fabric was built from the ground up with enterprise distributed ledger use in mind. It has a rich ecosystem of components that can be plugged in to a modular architecture and works well in closed blockchain deployments, which can improve security and speed. It also uses an open smart contract model that can support various data models, such as account and unspent transaction output (UTXO) models.
Hyperledger Fabric can also improve data privacy by isolating transactions in channels or enabling the sharing of private data on a need-to-know basis in private data collections. It also enables high-speed transactions with low latency of finality and confirmation, according to its proponents.
There is an active and diverse community around Hyperledger Fabric that works on adding more features related to consensus algorithms, additional privacy options for GDPR compliance and operational improvements. Version 3.0 of Hyperledger Fabric, released in September 2024, added support for byzantine fault tolerance, a consensus mechanism that can function even when some nodes on a blockchain fail or act maliciously. Version 3.1, released in May 2025, introduced incremental performance optimizations and operational enhancements.
Hyperledger Fabric is supported by several major technology vendors offering enterprise-grade managed services and support. IBM, a founding contributor to the Hyperledger project, provides IBM Support for Hyperledger Fabric with 24/7 support and SLAs. Oracle offers Oracle Blockchain Platform, built on Hyperledger Fabric, with cloud and on-premises deployment options. Amazon provides Amazon Managed Blockchain, a fully managed service for deploying Hyperledger Fabric networks in AWS.
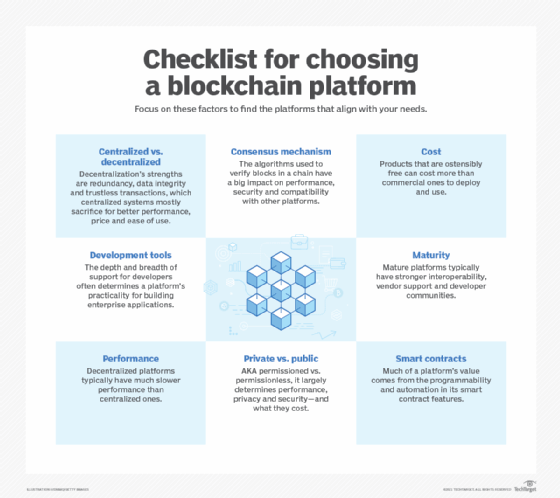
Key features to consider
Blockchain platforms consist of a wide range of components, which enables enterprises to select the appropriate components for different kinds of capabilities, said Chris Georgen, founder and partner of Change Code and co-founder of Amersand Labs.
 Chris Georgen
Chris Georgen
Georgen recommended examining four features when evaluating platforms:
- Whether a platform is open (public) or closed (private) and how that affects speed and security. Anyone can join a public blockchain, which can make it easier to set up. The downside is open blockchains aren't as fast. Many blockchain codebases can be modified to be either open or closed.
- Consensus mechanism, such as PoW, PoS or Byzantine fault tolerance. PoW is the older mechanism used in bitcoin. The others are newer and less proven but faster and more efficient, Georgen said.
- Ledger technology and how it records transactions. Popular approaches include an account model and UTXO. An account model records the balance, whereas UTXO is analogous to cash with serial numbers. The account model is used in Ethereum, Stellar, Tron and EOSIO. IBM Blockchain and Hyperledger Fabric use UTXO.
- Smart contract functions for capturing business logic on the blockchain. Popular programming languages include Ethereum Solidity, WebAssembly languages and Digital Asset Modeling Language.
3. R3 Corda
David E. Rutter, Todd McDonald and Jesse Edwards founded R3 in 2014. In September 2015, nine major banks, including Barclays, Goldman Sachs and JPMorgan Chase, formed a consortium with R3 to develop distributed ledger technology for financial markets. The consortium expanded to over 200 financial institutions, regulators and technology companies. R3 developed Corda as an open source distributed ledger platform specifically designed for regulated financial services. There is some debate whether R3 Corda is technically a blockchain or an alternative type of distributed ledger. It uses a novel consensus mechanism in which transactions are cryptographically linked, but does not periodically batch multiple transactions into a block. One of the key benefits of this approach is that all transactions are processed in real time, which can improve performance compared to other types of blockchains.
The R3 consortium has a strong following in the financial industry, since Corda provides an attractive approach for financial transactions and smart contracts with strong security. Leading proponents include Bank of America, HSBC, Intel and Microsoft. It supports tools that automate business logic that can execute across company boundaries.
One key innovation is a delivery-versus-payment mechanism designed to improve settlement with other distributed ledger platforms.
Corda has become a popular choice in the insurance industry for automating and streamlining common processes, such as claims processing, closing and settlement.
R3 reached a significant milestone in February 2025 with more than $10 billion in tokenized real-world assets on Corda-based platforms, processing over one million transactions daily. In May 2025, R3 announced a strategic partnership with Solana Foundation to bridge permissioned and public blockchain networks. In December 2025, R3 revealed specific plans for this collaboration, announcing that the Corda protocol would launch on Solana in the first half of 2026 as a yield vault platform for tokenized real-world assets, enabling institutional investors to access vetted yield opportunities while meeting compliance requirements.
4. Tezos
In development since 2014, Tezos is an older platform that supports dApps, smart contracts, and novel financial instruments, such as NFTs, which can be thought of as a modern variation on trading cards tied to digital assets. The platform supports a dynamically upgradable protocol and modular software clients, enabling it to adapt to new uses. It supports a PoS consensus mechanism that improves efficiency compared to bitcoin and the original Ethereum implementation. An on-chain upgrade mechanism enables developers to add new features without forking, which requires spinning up a new blockchain and migrating users over.
The Tezos community has been upgrading the platform at a rapid pace, introducing enhancements that improve performance and increase the size limit on smart contracts. It has also developed tools to help automate the process of weaving NFTs into enterprise supply chains.
Tezos completed three protocol upgrades in 2025. The Quebec upgrade in January reduced block creation time from 10 seconds to 8 seconds and improved staking features. The Rio upgrade in May introduced faster network cycles and allocated rewards to support Layer 2 networks. The Seoul upgrade in September added native multisig capability for institutional users and reduced network bandwidth requirements.
5. Vaulta (formerly EOSIO)
The EOSIO blockchain platform was first launched as an open source project in 2018. It was originally optimized for developing dApps and smart contracts and used a complex consensus mechanism based on PoS. The platform featured fast transaction processing, advanced account permission controls and on-chain governance for voting on network changes.
In March 2025, the EOS Network Foundation announced a complete rebrand to Vaulta, representing a pivot from general-purpose blockchain to Web3 banking. The rebrand was officially completed on May 14, 2025. The platform maintained its underlying blockchain infrastructure but shifted focus to financial services, including wealth management, consumer payments, portfolio investment and insurance.
There is also a fork of the original EOSIO, known as EOSIO-Taurus, which was first released in 2023 by cryptocurrency exchange Bullish. EOSIO-Taurus features high availability with automatic failover, disaster recovery capabilities, zero-downtime upgrades and enhanced debugging tools for smart contract development.
6. Stellar
Stellar was launched in July 2014 by Jed McCaleb, Joyce Kim and David Mazières as an open source blockchain platform designed to facilitate fast and low-cost cross-border payments. McCaleb previously co-founded Ripple blockchain and the failed Mt. Gox crypto exchange.
The platform initially used a modified version of the Ripple consensus algorithm but switched to the Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP) in November 2015. SCP utilizes the Federated Byzantine Agreement, which enables nodes to select which other nodes to trust, rather than relying on proof-of-work or proof-of-stake mechanisms. Stellar's native cryptocurrency, Lumens (XLM), serves as a bridge currency for cross-border transactions.
Stellar includes security mechanisms to block bad or suspicious actors in financial transactions. It has been adopted by several companies for international trade and exchanging money across borders. Examples of applications built on the Stellar blockchain include MoneyGram for money transfer, Circle for payments and treasury infrastructure, and Flutterwave for integrating payment processing into enterprise applications. The Soroban smart contract platform, launched in March 2024, helps streamline the development of Web 3.0 and DeFi applications on Stellar.
7. Consensys Quorum
Quorum is a customized version of Ethereum originally developed by financial services company JPMorgan Chase in 2016. In August 2020, ConsenSys acquired Quorum from JPMorgan and rebranded the platform as ConsenSys Quorum.
ConsenSys Quorum is built as a fork of Go Ethereum (Geth) and offers two Ethereum clients: GoQuorum for permissioned networks and Hyperledger Besu, which supports public and permissioned deployments. The platform uses the Tessera private transaction manager to permit privacy for transactions and smart contracts. Unlike public Ethereum, Quorum supports alternative consensus mechanisms better suited for enterprise use.
It uses the core work on the Ethereum blockchain platform and repackages it into a hardened environment suitable for banks. It has been optimized to support high-speed transactions between institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, on a private network.
Consensys partnered with Visa to help bridge central bank digital currencies with existing payment networks and make it easier to create new services. Consensys also worked with Mastercard to improve rollup mechanisms that bundle multiple transactions together to improve efficiency. Quorum also adds various privacy enhancements to Ethereum to improve support for regulations such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California.
The company has developed an extensive ecosystem of supporting tools and services to enhance Quorum's value. Infura is a suite of blockchain APIs and developer tools. MetaMask is a cryptocurrency wallet and gateway to blockchain apps for end-users. Diligence supports smart contract audit and security services.
8. Polygon
Polygon was originally founded as the Matic Network in 2017 and rebranded as Polygon in 2021.
Polygon uses a modified proof-of-stake consensus mechanism where validators stake POL tokens (formerly MATIC) to process transactions. The platform processes transactions through sidechains that run parallel to Ethereum, periodically committing checkpoints to the Ethereum mainnet for security.
The platform's enterprise adoption has been substantial. Starbucks launched its Odyssey loyalty program on Polygon in 2022, allowing customers to earn and trade NFTs. Nike built its SWOOSH digital collectibles platform on Polygon. Reddit deployed its NFT avatar marketplace on the network, minting millions of NFTs for users. Other major implementations include Disney's accelerator program participants, Adobe's content credentials and Meta's Instagram NFT integration.
9. Solana
Solana launched its mainnet beta in March 2020, founded by Anatoly Yakovenko and developed by Solana Labs.
The platform addresses blockchain scalability through Proof of History, a cryptographic clock that timestamps transactions before consensus. This approach eliminates the extensive node communication required by traditional blockchains to agree on transaction ordering, allowing validators to process transactions in parallel rather than sequentially. Solana uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Tower BFT with Proof of History as its timing source.
Enterprise implementations include Visa's USDC settlement pilot, launched in 2023; Shopify's Solana Pay integration for merchant payments; and Polymarket's prediction market platform, which processes billions of dollars in trading volume.
Editor's Note: This article was updated in January 2026 to add new platforms and add updates to the current listings for reader clarity.
George Lawton is a journalist based in London. Over the last 30 years, he has written more than 3,000 stories about computers, communications, knowledge management, business, health and other areas that interest him.
Sean Michael Kerner is an IT consultant, technology enthusiast and tinkerer. He has pulled Token Ring, configured NetWare and been known to compile his own Linux kernel. He consults with industry and media organizations on technology issues.







