proof of stake (PoS)
What is proof of stake (PoS)?
Proof of stake (PoS) is an approach used in the cryptocurrency industry to help validate transactions.
When a transaction occurs with a cryptocurrency, a corresponding change on the blockchain on which the cryptocurrency is based needs to occur. All cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology at the foundation, providing a distributed ledger of transactions. Blockchain provides a set of distributed nodes in a decentralized approach and validating that a transaction has occurred requires some form of consensus to ensure integrity.
Validating transactions to the cryptocurrency's blockchain ledger can occur in many different distributed approaches known as consensus algorithms, including PoS and proof of work (PoW). Both methods achieve the same result of validating a transaction by adding a new block to the underlying blockchain of the cryptocurrency. While the two consensus mechanisms have the same result, they work in different ways.
As a consensus algorithm, PoS uses validators that have a specific stake, which is a minimum amount of cryptocurrency tokens on the blockchain. The stake held by validators is locked into a smart contract on the cryptocurrency's blockchain to help maintain the required amount of cryptocurrency tokens.
Validators are rewarded by the cryptocurrency, typically with new tokens for participating in the PoW effort. If a validator fails to properly validate a transaction, the stake can be at risk from a reactive action known as slashing, whereby several tokens are revoked.
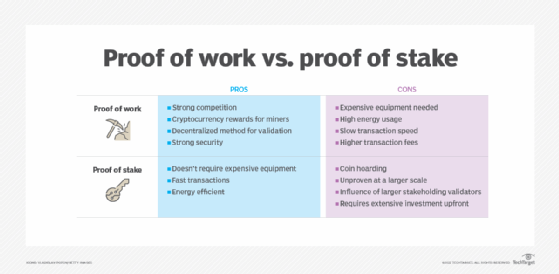
Proof of stake vs. proof of work
Both PoS and PoW are consensus mechanisms for cryptocurrency nodes on blockchain. The method by which the two consensus approaches work varies significantly.
In the PoW approach, the consensus is achieved when an individual node writes the next block in the blockchain to validate the transaction by solving a cryptographic hash in an operation referred to as mining. The process of writing the new block in a blockchain can require significant computing power and energy consumption. PoW was outlined by Bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto in the initial paper released in 2008 that defined the Bitcoin model. It remains the consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin today.
With PoS, consensus is achieved by validators that provide a deposit -- known as a stake -- in the specific cryptocurrency used. PoS requires significantly less energy and computing power than the PoW approach. PoS also has the potential to be faster than PoW, as well as provide more scalability because it requires less computing power to achieve consensus and validate a transaction. PoS was pioneered by the Peercoin cryptocurrency group in 2012.
Benefits of proof of stake
The PoS consensus mechanism offers several benefits to the cryptocurrency platforms that support the approach, including the following:
- Smaller resource requirements. The ability to add a node to the blockchain, requires less computing power.
- Lower energy utilization. With the need for less computing power comes a corresponding decline in the amount of energy consumed in order to validate a transaction.
- Speed. A node can be added quicker with PoS, enabling faster transaction throughput.
- Scalability. The PoS-based approach has the potential to be more scalable than PoW as the requirements and resources to have a stake may be lower than the hardware and energy costs of PoW.
Challenges of proof of stake
While there are numerous benefits to using PoS, there are some challenges, including the following:
- Potential for undue influence. A key promise of cryptocurrencies is that they are decentralized. With the need to stake coins, it is possible that a large stakeholder could exert significant influence on the validation of transactions on a blockchain network.
- Staking conditions. With PoS, it is possible that the stake will be tied up in a smart contract for a longer period.
- Security concerns. There are concerns that PoS is less secure as there is less effort required for validation and the potential for influence from large stakeholders. PoS also does not have the same volume of transactions or history as PoW, and as such has not yet been tested at the same scale.
Proof of stake cryptocurrencies
In the ever-growing world of cryptocurrencies, there is an expanding list of those that use PoS as a consensus mechanism, including the following:
- Avalanche (AVAX). Avalanche aims to help enable the development of dApps (decentralized applications) and was created in September 2020.
- Cardano (ADA). Cardano provides smart contract capabilities and was founded in 2015 by the co-founder of Ethereum, Charles Hoskinson.
- Cosmos (ATOM). Cosmos was created by the Interchain Foundation (ICF) in 2014 to build an open source blockchain technology.
- EOS (EOS). EOS has its own blockchain that was first publicly released in January 2018 with the aim of accelerating smart contracts.
- Ethereum (ETH). Ethereum is one of the most widely owned and used cryptocurrencies and moved to PoS in September 2022.
- Peercoin (PPC). Peercoin claims to have been the first to implement the PoS approach and got its start in 2012.
- Solana (SOL). Solana launched in 2017 and aims to be an efficient platform for transaction processing.
