Data backup explained: A comprehensive enterprise guide
Data backup is the process of copying data in an IT system to another location so it can be recovered if the original data is lost. A backup process aims to preserve data in case of equipment failure, cyberattack, human error, natural disaster or other data loss event. As such, data backup is an important part of an enterprise's data protection strategy, which also typically includes a business continuity and disaster recovery plan.
The scope of data backup has broadened over the years and now encompasses data maintained in the cloud as well as in on-premises systems. Backup also covers a wider range of use cases. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, led to a massive increase in employees working from home, elevating remote data protection as a backup task. In some cases, it also created new backup responsibilities for general IT administrators.
Backup technologies are also evolving, with AI as a key influence. Enterprise Strategy Group, now part of Omdia, has cited the transition of traditional backup offerings into what it calls the "data intelligence market," in which products incorporate automation, AI and machine learning.
This comprehensive guide examines all aspects of data backup, including the importance of backup, the benefits and challenges of providing this layer of data protection, plus an overview of different backup approaches, technologies and vendors. It also describes how to create and implement a data backup plan and includes a planning template. Hyperlinks throughout this page connect to related articles that provide additional insights, new developments and advice from industry experts on what data backup teams must do to implement a successful enterprise data backup strategy.
Why are data backups important?
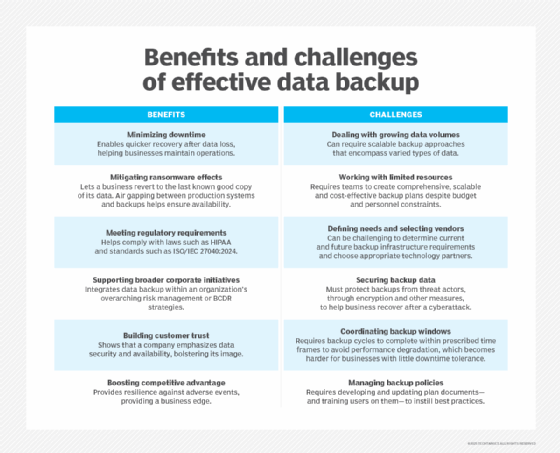
Data is a critical corporate asset: It's analyzed to understand customers, maintained for regulatory compliance purposes and monetized to create new revenue streams, to name a few uses. The increasingly high-stakes nature of data makes backups an important IT infrastructure component. Backups provide a way to restore data, whether the issue is inadvertent deletion, a ransomware outbreak or a data center outage. The ability to recover rapidly from such setbacks is the essence of digital resilience.
The objective is to provide a safeguard against data loss and help organizations recover data in its original form. As businesses become data-centric organizations, they must keep their data consistently available to maintain credibility with employees and external customers who rely on it to do their jobs. Failure to do so results in billions of dollars in annual downtime costs.
What to back up and how often to do it
A backup process can be applied to data stored in various settings, including physical servers, databases, NAS, VMs, public cloud storage, containerized applications, SaaS applications and endpoints such as laptops and mobile devices. Backups can also be file-based or image-based. The file-level method is useful for recovering users' critical documents, while the image backup approach protects data, applications and OSes.
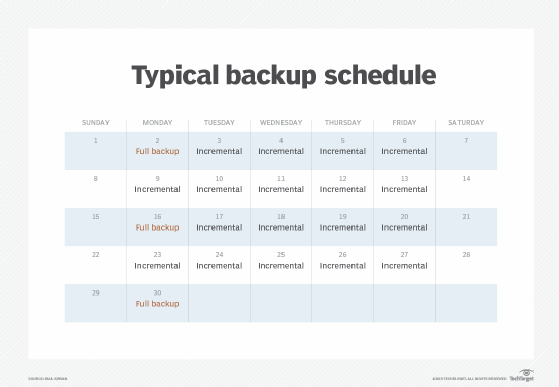
The frequency of full data backup, which covers all the data a business wishes to protect, depends on variables such as the criticality of the data and how frequently it changes. So, a full backup might be scheduled daily, weekly or at some other interval. Such backups typically take place during weekends or off-hours to reduce the performance impact on systems. Data managers can also schedule differential or incremental backups that take place in between the full ones and only back up data that is new or has changed.
Backup policies or service-level agreements govern the frequency of backups and how quickly data must be restored. Here, the main criteria include the recovery time objective (RTO), which determines how quickly after an event an organization must recover data, and the recovery point objective (RPO), which determines the age of data that must be recovered to resume operations.
FAQs on different types of data backup
Businesses have several backup methods to consider, with storage capacity and the length of available backup windows among the factors influencing decisions on which to use.
What are the main types of backup methods available for businesses?
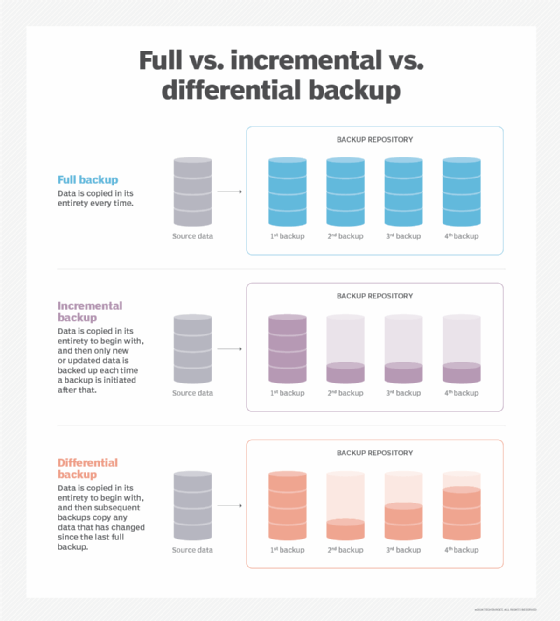
There are three primary backup types:
- Full backup.
- Differential backup.
- Incremental backup.
There are several variations that a business might also use, including the following:
- Synthetic full backup.
- Incremental-forever backups.
- Reverse-incremental backups.
What is a full backup?
Just as it sounds, this method captures a copy of an entire data set. Most organizations run full backups only periodically because the process is time-consuming. Full backups, however, offer rapid data recovery when required.
What is a differential backup?
This backup type copies data that has been changed or added since the last full backup. If an organization creates a full backup on a Monday, differential backups on each of the following days would include all the changes since then on a cumulative basis. Backup time is therefore faster than for a full backup. Data recovery requires the original full backup and the latest differential backup.
What is an incremental backup?
Backups of this kind copy only the data that has changed since the previous backup. After a full backup, the first incremental backup captures the data that has changed since then. The second incremental backup copies the data that has changed since the first one, and so on. Incremental backups take up less storage space than differential backups and complete more quickly than other backup types, but data recovery takes longer because it requires the original full backup plus each incremental backup.
What is a synthetic full backup?
This method combines the original full backup with data gleaned from incremental copies. The synthetic full backup requires a shorter backup window than a conventional full backup because only the changed data is copied.
What is an incremental-forever backup?
A variation on incremental backups, this approach aims to minimize the backup window while providing faster data recovery. An incremental-forever backup captures the full data set and supplements it with incremental backups from that point forward.
What is a reverse-incremental backup?
This method begins with a conventional full backup and creates a series of synthetic full backups, each of which incorporates an incremental backup. When the next full backup is created, the reverse-incremental backups provide multiple data restore points that an organization can roll back to if necessary.
Techniques and technologies to complement data backup
In addition, various data protection and storage techniques can be incorporated into the backup process, including the following:
- Continuous data protection (CDP) technology backs up data every time it changes, providing a series of point-in-time restore points after an initial full backup. This approach provides rapid recovery and eliminates backup windows, but the storage demands might prove expensive for smaller businesses. In addition, CDP requires redundancy to eliminate single-point-of-failure scenarios. Near-CDP is another option that performs backups at set intervals, typically in the range of 30 seconds to 15 minutes.
- Storage snapshots periodically capture and record data changes over time. CDP and near-CDP, for example, create high-frequency snapshots, while other methods might produce a daily snapshot.
- Mirroring replicates data across two or more disks. The goal is to protect the data against disk drive failure.
- Data replication copies data from one location to another, using a SAN, LAN, WAN or the cloud. An organization could use it for disaster recovery (DR), replicating data between a primary storage location and an off-site facility. Both hardware and software replication technologies are available.
- Data reduction shrinks an organization's storage footprint. There are two primary methods: data compression and data deduplication. Reducing the size of data has implications for backup windows and restoration times. Minimization also supports sustainable data management because smaller volumes use less energy.
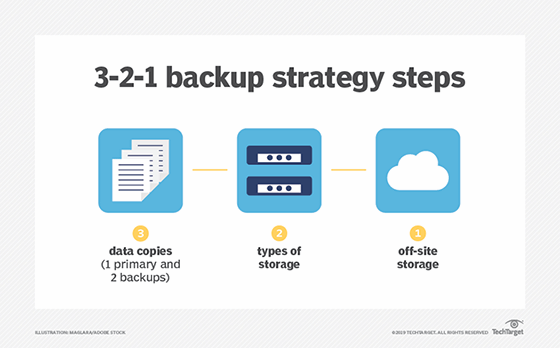
What is a 3-2-1 backup strategy?
Under the 3-2-1 backup strategy, an organization makes three copies of the data it wants to protect. Two copies are stored on two different types of storage media, and at least one copy resides in a remote facility. The off-site backup copy provides a safeguard against on-site system outages and data loss.
The 3-2-1 method, considered one of several key data backup best practices, aims to ensure organizations have no single point of failure for data backups. While the strategy has become a de facto industry standard, IT managers might need to refine it for current circumstances. The capacity required to store multiple copies can prove expensive -- particularly amid tightening IT budgets -- so data reduction methods might become necessary to complement 3-2-1 backup.
Another tweak on the strategy is the 3-2-1-1-0 rule. In this variation, the second "1" calls for one copy to be maintained offline, providing an air-gapped backup as a defense against ransomware attacks and other incidents. The "0" refers to verifying that a backup contains zero errors to ensure proper restoration.
Data backup storage options
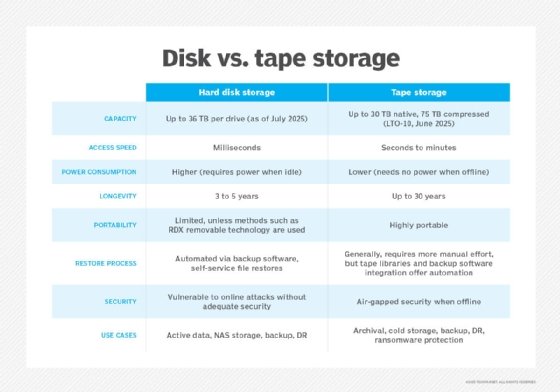
Different storage media options for backups include tape, disk and removable storage. In addition, cloud backup can serve as both a storage media alternative and an off-site storage resource. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages.
Tape
A computer storage medium since the 1950s, tape endures as a backup technology. Its advantages include security: Tape is inherently offline, so it provides air-gapped data protection. In addition, the latest tapes store a high volume of data. The LTO-10 generation of tape products can store up to 30 TB native and 75 TB compressed.
On the other hand, tapes require maintenance and management to ensure they are safe and secure. Businesses must make sure the hardware used to read tapes still works, and tape backup media should ideally be shipped to an off-site storage center. As a result, tape is more often used for archival purposes now.
Disk
Disk has become a common backup technology, offering more attractive pricing than in the past and generally providing faster performance compared with tape. Hard disk drives trail solid-state drives in performance but maintain a cost advantage, which makes them more widely used for backups.
Disk storage, however, often physically resides in an organization's office and is, thus, more susceptible to damage in the event of a natural disaster. That scenario highlights the importance of adopting the 3-2-1 backup approach to help avoid permanent data loss.
Cloud
As part of a 3-2-1 strategy, off-site data backup often equates to subscription-based cloud storage as a service. This option provides low-cost, scalable capacity and eliminates a customer's need to purchase and maintain backup hardware. Using the cloud can also ease remote backup processes, but that cost edge is subject to change when large amounts of data are backed up in the cloud.
As an off-site storage tier, cloud shields businesses from disasters affecting in-house data centers. But cloud's online nature makes it vulnerable to cyberattacks, and cloud service outages can temporarily leave businesses without access to backup data.
Cloud backup is divided into the following categories:
- Public cloud storage. Users ship data to a cloud service provider (CSP) that charges them a monthly subscription fee based on the storage they consume. Additional fees are commonly charged for data ingress and egress.
- Private cloud storage. Data is backed up to different servers inside a company's firewall, typically between an on-premises data center and a secondary disaster recovery site.
- Hybrid cloud storage. A company uses both local on-premises and off-site cloud storage. Businesses customarily use public cloud storage selectively for data archiving and long-term retention. Private storage is used for faster access to backups of their most critical data.
In addition, the following backup-related services have emerged from the evolution of cloud storage:
- Disaster recovery as a service. DRaaS also backs up data via a third-party CSP, enabling failover in the event of a business disruption. DRaaS lets customers avoid the cost of maintaining secondary data centers.
- Cloud-to-cloud (C2C) backup. This practice copies data located on one cloud service to a second cloud service, which functions as an off-site backup. C2C backup can protect a range of cloud workloads. It has become increasingly important for businesses that depend on SaaS applications such as Microsoft 365 and Salesforce.
- Backup as a service. BaaS involves purchasing backup and recovery services from an online data backup provider, typically through a subscription. BaaS providers, representing one example of cloud-native backup, manage the backup infrastructure, which resides in a private, public or hybrid cloud.
Backup options for PCs and mobile devices
The rise in remote work has further expanded the scope of backup tasks for individual users. PC users can consider local backup from a computer's internal hard disk to an attached external hard drive or removable media, such as a thumb drive. Another alternative for users is to back up data from smartphones and tablets to cloud storage.
Selecting the right backup offering
The scope of enterprise backup often encompasses a combination of on-premises environments, cloud-based infrastructure and SaaS applications. Use cases are wide-ranging as well: Requirements might include data protection, disaster recovery, cyberthreat defense, remote work, regulatory compliance and long-term archival storage.
Backup technology options in this varied market include software applications, hardware offerings such as backup appliances and other backup storage devices, and cloud services such as BaaS and DRaaS. Enterprises might need to use a mix of backup software, hardware and cloud technologies to address complex, hybrid IT environments.
In this context, backup vendors are evolving to provide offerings that span a range of technologies and use cases. Market research companies group such vendors under different headings. Forrester Research, for example, defines them as "data resilience solution providers," while Gartner uses the "backup and data protection platform" label, and IDC covers the "data protection software" market.
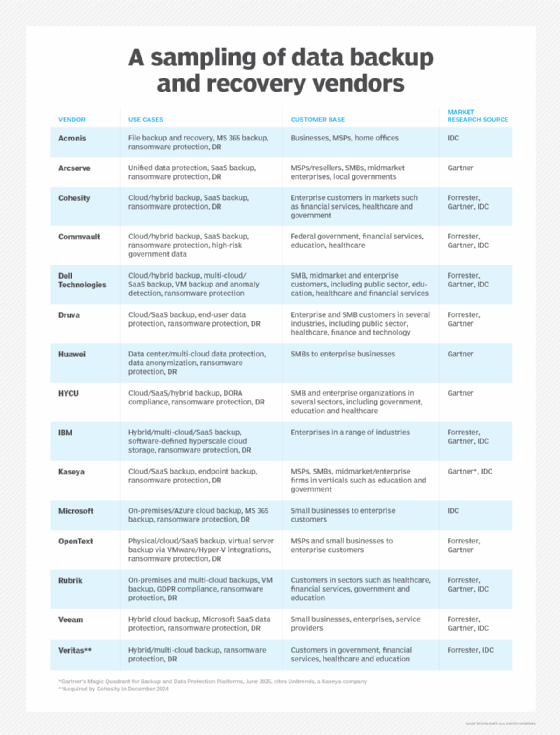
A recent report from Forrester Research on data resilience vendors, published in November 2024, identified Cohesity, Commvault, Dell Technologies, Druva, IBM, OpenText, Rubrik, Veeam Software and Veritas as the vendors "that matter most" in the market. Forrester's evaluation considered a vendor's current offering, strategy and customer feedback.
Gartner's report on backup and data protection platforms, published June 2025, listed Arcserve, Cohesity, Commvault, Dell Technologies, Druva, Huawei, HYCU, IBM, Kaseya's Unitrends business, OpenText, Rubrik and Veeam as top vendors. Evaluation criteria for this report included product/service capabilities, customer experience and the vendor's overall viability.
IDC's top 10 data protection software vendors, based on 2024 vendor revenue, include Acronis, Cohesity, Commvault, Dell Technologies, IBM, Kaseya, Microsoft, Rubrik, Veeam and Veritas.
Leading vendors have begun integrating AI into their products, which will influence backup automation and potentially transform data recovery. Gartner predicts that 90% of backup and data protection platforms will incorporate generative AI by 2029.
Some specialized products, however, fall outside these broad backup system vendor categories. In the long-term data retention market, for instance, options include tape and cloud archive technologies. Based on 2023 data, Straits Research identified the following companies as "key players" in the North American tape storage market: Dell Technologies, HPE, IBM, Lenovo, Oracle, Overland Tandberg, Qstar Technologies, Qualstar, Quantum and Spectra Logic. Overland Tandberg, however, ceased operations in 2025.
In addition, cloud market share leaders AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google offer cloud archive products: Amazon S3 Glacier, Azure Blob Storage and Google Cloud Storage's archive storage service, respectively.
Backup planning, testing and training
Backup methods, types, and technologies are only effective when businesses support them with comprehensive backup policies and plans. The following sections provide details on how to create an overarching structure for managing backup and recovery.
Develop a data backup policy and plan
Businesses should create a backup policy to detail the methods and types of data protection they deploy and to ensure critical business data is backed up consistently and regularly. That policy must be coordinated with any overarching data governance framework an enterprise might have. The backup policy also creates a checklist that the IT department can monitor and follow.
The steps for building such a document include the following:
- Conduct a risk assessment and business impact analysis (BIA). The risk assessment identifies issues that could negatively affect an organization's ability to conduct business, while the BIA determines the potential effects of a disruption.
- Define the scope of the backup plan. IT managers incorporate the risk assessment and BIA findings to determine what data the organization must back up and how often.
- Document the process of performing data backups: who is involved, what tools they should use and the planned storage location of backups. This part of the plan should also include the cost of the data backup strategy.
- Identify the types of backups to be used. Typically, this step will include an initial full data backup, with a series of differential or incremental backups between additional full ones.
- Document the process of moving data to and from disk, cloud and tape, since it differs for each backup target.
- Set data retention rules to automate the deletion of data -- or migration to different media -- after it has been kept for a specific period. Consider setting rules for individual users, departments and file types.
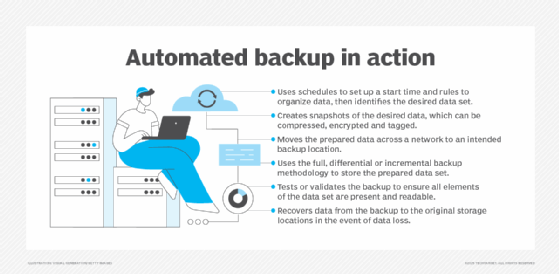
Implement a data backup plan
With a backup plan in place, the next phase is implementation. The data backup policy offers guidance, detailing the process for executing and authenticating backups. It should also specify measures to ensure that data is backed up safely and securely. The steady rise of quantum computing adds another wrinkle to securing backups: Quantum machines could crack classical encryption algorithms within a few years, which puts stored data at risk of harvest-now-decrypt-later attacks.
Effective backup scheduling is also key to backing up the right data -- and the right amount of it -- in an organization. In many cases, it's likely unnecessary -- as well as impractical -- to schedule a full backup every day or more often than weekly. Not all data is mission-critical, and the required storage space and cost would get very hefty.
Data backup plan template
This free template provides a documented outline for building a data backup plan.
Creating the plan should be a team effort: One person might document it, but the plan should be shared with other key stakeholders, such as IT and business executives, for their review and input.
Data backup planning is an essential business activity -- and one that's expanding in scale. Data sets are growing exponentially, and increasingly large backup data sets naturally follow that trend. With so many threats and risks, an organization must have a ready copy of its critical data in the event of an unplanned incident, so it can continue business operations as expeditiously as possible.
Build a restore and disaster recovery plan
A backup strategy is only as good as its ability to restore critical data. As a result, an organization also needs a restore and DR plan that includes the following steps:
- Outline how the organization plans to restore its backed-up data. Data restoration techniques include restoring from traditional backups, as well as using CDP, data replication and instant recovery.
- Document how much data the organization must recover to function and how quickly that needs to happen, using the RTO and RPO metrics. It's important to be honest about these parameters: Organizations must take a close look at what data they need in a recovery situation and how fast they can get it.
- Align backup and recovery planning with the broader DR plan, which is designed to restore business operations after an emergency. Data recovery is key to that effort.
Train employees on backup protocols
Training is essential to educating staff on the data backup strategy, scheduling and what to expect in a data recovery situation. A training program, including commercially available backup courses, should extend beyond backup administrators to include IT generalists and remote employees. A backup administrator might be unavailable in the event of a business disruption. If that's the case, other IT employees will be assigned to backup work they won't be familiar with -- unless they have been cross-trained on the company's backup processes and technologies.
A well-documented backup process provides a starting point for employee training. In addition, a business's backup vendors might be able to provide training on its products. Third-party training providers with backup and recovery courses are another option.

Remote workers, meanwhile, should receive training on secure storage and backup. A suggested network compliance checklist for remote work includes documenting procedures for data backup and recovery. A company's remote site backup vendor can also provide documentation and guidance on its offerings.
Test and review backup systems regularly
Organizations must regularly test their backup process and technologies to confirm they're working properly. Testing doesn't need to be overwhelming, but it must be consistent. The core elements of backup testing include documenting a test plan, using automation and ensuring accuracy. Backups can fail, but it's better to have them fail in a test than in a live recovery situation.
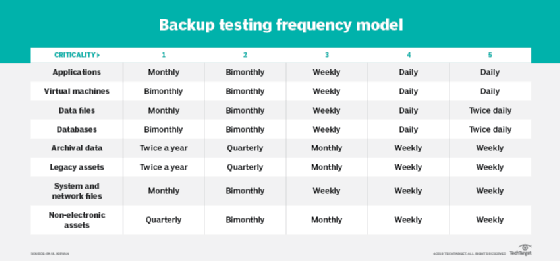
The frequency of backup testing should track with the frequency of data backups. Mission-critical data, for example, will get backed up most often; thus, those backups should receive the most frequent testing. Assigning a criticality value to each backup data set will help determine testing frequency.
Testing results must be analyzed to determine whether any changes are needed. As an additional step, an organization can hire an outside agency for backup auditing to further detail backup effectiveness. This review can help administrators update backup plans and ensure backups are secure.
Editor's note: This article was updated in August 2025 to reflect the latest developments in data backup and recovery.
John Moore is a writer for Informa TechTarget covering the CIO role, economic trends and the IT services industry.
Informa TechTarget executive editor Paul Crocetti and freelance technology writer Brien Posey contributed to this article.






