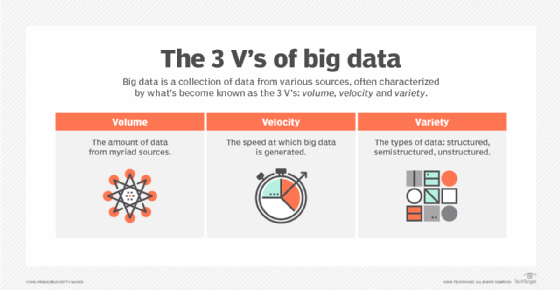
3 V's (volume, velocity and variety)
What are the 3 V's of big data?
The 3 V's (volume, velocity and variety) are three defining properties or dimensions of big data. Volume refers to the amount of data, velocity refers to the speed of data processing, and variety refers to the number of types of data.
According to the 3 V's model, the challenges of big data management result from the expansion of all three properties, rather than just the volume alone or the sheer amount of data to be managed. An organization can be better equipped to deal with big data challenges through understanding the 3 V's of big data management.
Gartner analyst Doug Laney introduced the 3 V's concept in a 2001 Meta Group research publication, "3D Data Management: Controlling Data Volume, Velocity and Variety." More recently, additional V's have been proposed for addition to the model, including variability -- the increase in the range of values typical of a large data set -- and value, which addresses the need for valuation of enterprise data.
Data using the 3 V's is sometimes referred to as 3D data.
Why are the 3 V's important to big data?
The 3 V's help define big data and are how it's measured. Big data refers to data points that are generated frequently, in high volume and in multiple forms.
These characteristics determine the data modeling techniques analysts use, such as how the data is processed and stored. They also play a part in determining the value of the data. In theory, a higher volume, velocity and variety of data is more valuable because it creates a stronger analytical basis and yields stronger insights.
Data with little variety might yield skewed analytics. Low-velocity data can be inefficient and costly to process. Data with too little volume might miss important patterns.
Collecting and analyzing data from various sources improves decision-making. It provides businesses with an enhanced understanding of customer behavior, market trends and organizational performance. Businesses might use artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to process data.
The data model or data architecture used is also important when considering the 3 V's. Certain types of data models lend themselves to higher-velocity data processing. For example, batch processing lets organizations process large amounts of data quickly. It performs jobs in batches, transforming and classifying unstructured data to fit into a conceptual data model.
Data that's mishandled can result in inefficiencies or inaccurate predictions. For example, if numerical data is fed into a logical data model designed for qualitative data, the system might not be able to produce results or the data analysis might be incorrect.
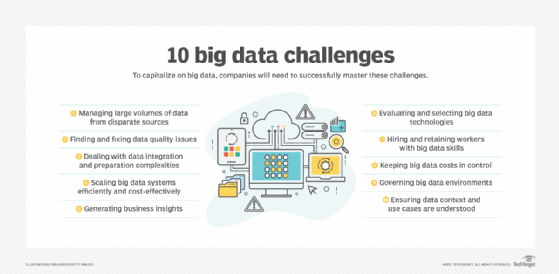
Examples of the 3 V's in big data
Healthcare and cybersecurity are two industries that make heavy use of big data analytics and rely on the 3 V's of big data.
Healthcare
Many medical devices are part of the internet of things (IoT). These IoT devices collect and transmit large amounts of data about patients from a variety of sources, contributing to the big data volume and variety used in healthcare.
Healthcare data sources include genomics data sets, electronic health records, patient data from wearables and biosensors, and third-party data from insurance claims, published literature and even social media. The different data types coming from these various sources must be handled differently, depending on the provider's technical requirements and any compliance restrictions.
There is often an urgency involved in the use of medical data, and that's where processing velocity comes into play. One example is data that reveals drug interactions. Data velocity is also important for research scientists seeking to get potential drug candidates through the regulatory process as fast as possible.
Cybersecurity
Cyberthreats evolve quickly, and that's reflected in the data needs of cybersecurity companies. They must have information on the latest threats in as close to real time as possible. Like healthcare data, cybersecurity data comes from many sources, including IT networks and systems, security and nonsecurity applications, and physical and virtual surveillance systems. Here, too, processing velocity is required so that systems administrators and data scientists can monitor the changing cybersecurity landscape and address vulnerabilities quickly.
Mitre ATT&CK is an example of a cybersecurity database that aggregates threat information from a variety of sources. It's a free framework that provides data-driven cyberthreat information to anyone looking to improve their cybersecurity strategy.
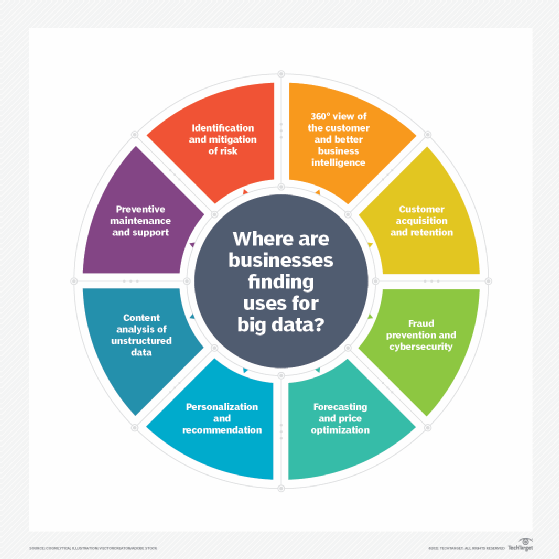
Are there other V's?
Today, big data science experts often cite five V's of big data, and sometimes even six. The additional V's include value, veracity and variability:
- Veracity refers to the quality and accuracy of data, and the level of trust an organization has in its data. Data with missing pieces or unreliable sources can bring its veracity into question.
- Value refers to how useful the data is to the organization collecting and using it. The value depends on the quality and quantity of insights pulled from that data. The specific way an organization derives value from big data is unique to its business requirements and business processes. The other V's often contribute to value.
- Variability relates to the ways in which the data can be used, formatted and structured.
To collect big data effectively, businesses must understand its value and develop a strategy that makes the most of it. Learn how to create an enterprise big data strategy.