Ansible
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open source IT automation platform from Red Hat. It enables organizations to automate many IT processes usually performed manually, including provisioning, configuration management, application deployment and orchestration.
The Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform is a Red Hat-supported platform built around Ansible Core. It provides an Agentless framework to create, test and manage automation content. Written in the Python programming language, this command-line IT automation software application provides organizations with a flexible, secure way to automate many IT tasks and complex processes. The platform, available as a subscription, has numerous components integrated into one streamlined product.
IT expert Stuart Burns walks through Ansible basics.
Ansible Automation Platform features
The Ansible Automation Platform components each have a specific purpose and well-defined scope.
Automation execution environments
These environments are packaged as containers. They are defined, consistent and portable, and enable the execution of Ansible playbooks and roles.
Automation controller
The automation controller is a control plane for the Ansible platform. It helps standardize automation deployment, initiation, delegation and audits. Bundled into the platform to manage automation, the controller is the web UI and application programming interface (API). It is based on the upstream project AWX.
Automation mesh
The automation mesh enables organizations to automate at scale and in a cloud-native way. It simplifies the planning of distributed, remote and complex automation deployments, and provides visibility, control and reporting capabilities. The Ansible platform uses the automation mesh to spread automation jobs across execution nodes to increase execution capacity for devices that cannot run modules.
Ansible Content Collections and content tools
Ansible content creators and developers can use Ansible Content Collections, or certified modules, to deploy automations faster and more efficiently. Content tools simplify the process of building and deploying execution environments.
Automation hub
Ansible automation hub enables users to quickly find, use and extend Red Hat-supported content in demanding environments.
Ansible architecture: Nodes and modules
Ansible's architecture is based on the concept of a control node and a managed node. The platform is executed from the control node where a user runs the ansible-playbook command. There must be at least one control node; a backup control node can also exist. The devices being automated and managed by the control node are known as managed nodes. A Microsoft Windows server is an example of a managed node.
Ansible automates Linux and Windows by connecting to managed nodes and pushing out small programs called Ansible modules. Ansible executes these modules, which are the resource models of the desired system state, over Secure Socket Shell (SSH) by default and removes them when finished. There's no need to install an application or service on the managed node because Ansible is agentless and can communicate with devices.
If modules cannot be executed -- say, for automating network devices and other IT appliances -- Ansible will run on the control node.
How does Ansible work?
For transport, Ansible uses OpenSSH, which is an Open Source implementation of the SSH protocol and provides secure encryption for remote logins and file transfers. Apart from SSH keys, other transports, pull modes and authentication mechanisms are also supported in Ansible.
Ansible uses human-readable YAML templates, known as playbooks, with instructions that provide a blueprint of automation tasks. Playbooks allow users to program repetitive tasks to occur automatically, without much training or learning an advanced programming language. Also, the playbooks are executed on a set, group or classification of hosts, which make up an Ansible inventory.
Ansible pushes application code, programs and IT infrastructure setup instructions via modules to managed nodes, which can be clients, physical servers, virtual machines or cloud instances. It connects to managed nodes on a network and sends an Ansible module to that node, then executes the module over SSH and removes it when finished. Simply put, Ansible connects to what a user wants to automate and then pushes programs that execute instructions.
The modules are written based on the endpoint's connectivity requirements, interface and commands. No additional servers, daemons or databases are required, so users can work with their preferred terminal programs, text editors and version control systems to make and track changes.
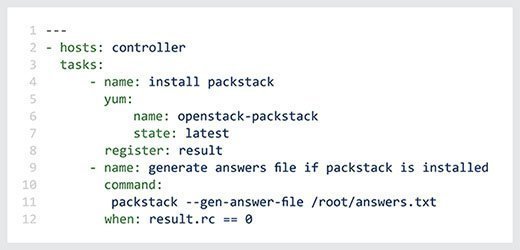
What are Ansible playbooks?
In Ansible, playbooks provide a powerful yet simple automation language. They enable Ansible users to use modules to accomplish automation tasks. Every Ansible playbook is a human-readable and self-documenting configuration file. It is written in YAML and provides instructions to bring a managed node into its desired state. Playbooks are also idempotent, which means they run on a system at any time in the same way without negatively affecting it.
Ansible playbooks can be simple -- for example, to install an Apache Hypertext Transfer Protocol server on a node in a web server group -- or complex -- for example, to orchestrate an entire network of managed nodes. Complex playbooks can include conditionals and variables. Even so, they are usually brief, readable and clear because Ansible modules do most of the "real" work.
Important use cases for Ansible
According to Red Hat, Ansible enables organizations to "scale automation across the enterprise with control and insight." It is particularly useful for these use cases:
Infrastructure provisioning
Ansible replaces ad hoc scripting or manual infrastructure management with an automated and repeatable process. Since everything is written in simple script form, it enables organizations to adopt infrastructure as code (IaC).
Using Ansible playbooks, users can build one instance and use it for multiple additional servers employing the same infrastructure details. After the environment is provisioned, it can be easily configured as part of the IT operational lifecycle. Ansible automation eliminates the need to provision hundreds or thousands of servers manually.
Configuration management
Routine IT tasks can be easily automated with Ansible. It is minimal, consistent, reliable and secure. And it uses simple data infrastructure descriptions that are human- and machine-readable. These capabilities allow system administrators, developers and IT managers to easily understand and automate routine configuration tasks.
Application deployment
Ansible provides a common framework to configure services; deploy applications, including multi-tier applications; and push application artifacts easily, reliably and consistently. There's no need to write custom code to automate app deployment. Instead, teams only need to write simple task descriptions in YAML files that are easy to read, implement and update as required.
Advantages and benefits of Ansible
Ansible enables system administrators, developers, architects and DevOps teams to automate tasks such as software installations, infrastructure provisioning, system configurations, updates and patching. Ansible can also orchestrate advanced workflows for application deployment. It improves security and compliance, and makes it easy to deploy and share automation across the organization.
Other possible benefits that organizations can expect from Ansible include the following:
- Rich and visual insights to identify, troubleshoot and resolve operational and security issues across the IT ecosystem.
- A collaborative and scalable approach to enterprise automation.
- Infrastructure codification for both on-premises and cloud deployments.
- Easy to transfer automation into multiple domains and across a range of use cases.
- Analytics, policy and governance, and content management tools to streamline and scale automation.
Who are Ansible users?
Enterprise users such as these can also benefit from the Ansible platform:
- Automation architects can use Ansible to expand automation across the enterprise and manage automation policy and governance.
- Automation developers can create Ansible playbooks, roles, modules and pre-built automation content for development use cases.
- Automation admins can use Ansible's automation controller and automation hub to manage and share automation projects.
- Operations and DevOps teams can automate repetitive tasks and free up time to focus on more strategic, higher-value work.
Ansible vs. Chef, Puppet and other tools
Several products offer competing approaches to infrastructure automation, application deployment and configuration. Ansible and its competitors offer various open source, supported open source and proprietary commercial offerings, which IT organizations should investigate before choosing a tool.
While these products compete for users, IT organizations also deploy them together. For example, Puppet will run configurations that Ansible then orchestrates, or the developers will use Chef while the operations team uses Ansible.
Competitors to Ansible include the following:
- Chef. Open source systems management and cloud infrastructure automation platform.
- Puppet. Open source systems management tool that centralizes and automates configuration management.
- PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC). PowerShell feature that automates the configuration of Windows and Linux operating systems.
- SaltStack. Configuration management and orchestration tool for provisioning IT infrastructure through a central repository.
- Terraform. DevOps open source IaC tool for programmatically provisioning physical resources to run applications.
- Vagrant. Automates the consistent creation of a small set of virtual machines, most often to replicate development environments.
Ansible and Salt use YAML, while Chef uses JSON and Ruby, and Puppet relies on a declarative domain-specific language. PowerShell DSC users must know PowerShell programming. Ansible uses an agentless approach, while the competing offerings from Chef, Puppet, Salt and PowerShell DSC install agents, although certain agentless configurations are possible.
Configuration management tools, including Ansible, also compete with Docker and other orchestration technologies to manage workloads in containers. An Ansible user can build a container and define the container's payload. Ansible Container is an open source project that builds, deploys and manages containers.
While there is also overlap with continuous integration technologies, such as Jenkins, Ansible and its competitors work alongside these tools, handling deployment once the CI pipeline delivers ready code.
Explore the differences between Ansible vs. Terraform vs. Vagrant and learn more about how Ansible vs. Chef vs. Puppet vs. SaltStack compare. Also explore how to maximize Ansible scalability and performance as IT deployments grow.






