What is SAP MM (SAP Materials Management)?
SAP MM (SAP Materials Management) is a functional module in the SAP ECC (SAP ERP Central Component) and SAP S/4HANA software suites that provides the logic, data structures and integration needed to support procurement and inventory management. The module, which runs in the background, integrates with other SAP ERP modules to facilitate the procure-to-pay (P2P) process in materials management from the time a purchase requirement is identified to the time the supplier's invoice is sent to finance for payment.
Materials management is a core business function that focuses on planning, sourcing, purchasing, receiving, storing and tracking materials used in production or operations. The primary goal of materials management is to make sure that the right materials are available in the right quantity at the right time and place, while minimizing costs and avoiding shortages, outages or excess inventory.
SAP MM supports materials management by seamlessly integrating materials management tools and data with other core business functions like finance, production planning and warehouse operations. This helps eliminate data silos and provides supply chain visibility for inbound supply chain data across all relevant departments in the organization.
What is the purpose of SAP MM?
In SAP's enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, the MM module acts as a centralized data hub and transactional engine for all materials-related workflows. It provides the database tables for storing materials management master data, the transaction logic that governs P2P processes, and the integration points that ensure consistent and accurate data flow across finance, production, sales and other core business modules.
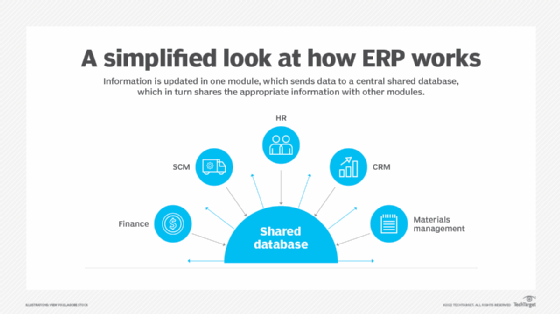
Business benefits of SAP MM
SAP MM helps businesses streamline procurement and inventory management by automating routine purchasing and inventory-related tasks and by providing authorized users with real-time visibility into the inbound supply chain. It provides stakeholders with a single source of truth for all data related to acquiring materials and then managing their movement, storage, valuation and usage across the organization.
Perhaps the biggest business benefit is that SAP MM turns materials management into a strategic business asset that improves supply chain efficiency and drives business value by making it easier for an organization to optimize stock levels, reduce excess inventory and prevent stockouts.
Key features of SAP MM
SAP MM's integrated features support accurate, data-driven decisions that enable organizations to optimize procurement and manage inventory more efficiently. Key features in the SAP MM logistics catalog include the following:
- Purchase requisition creation. An internal request to purchase materials or services based on operational needs.
- Purchase order (PO) creation. A formal order issued to the selected supplier specifying items, quantities and delivery dates.
- Goods receipt (GR). Confirms the physical receipt of materials from the supplier and updates inventory.
- Quality inspection. Verifies that incoming materials meet defined specifications and quality standards.
- Stock posting. Moves materials to the correct inventory category or location.
- Invoice verification. Compares the supplier's invoice with the PO and GR to determine invoice accuracy before payment.
- Vendor payment processing. Ensures timely payment to the supplier after successful invoice verification.
- Material master data management. Keeps all material-related information accurate, consistent and accessible across the SAP platform.
- Vendor master data management. Stores key supplier information such as payment terms, addresses and tax data.
- Source determination and source lists. Helps automatically identify the preferred vendor for specific materials.
- Quota arrangement management. Allocates procurement quantities across multiple suppliers based on predefined quotas.
- Outline agreements. Supports long-term contracts and scheduling agreements for recurring procurement needs.
- Automatic PO generation. Converts approved purchase requisitions or planning proposals into purchase orders automatically.
- Inventory valuation and price control. Assigns a monetary value to materials held in stock.
- Batch and serial number management. Tracks individual material lots or items for compliance, traceability and quality control.
- Physical inventory management. Supports inventory counting and reconciliation processes to ensure data accuracy.
- Subcontracting. Manages and tracks materials sent to subcontractors.
- Service procurement. Enables services to be purchased just like materials.
SAP MM in SAP ECC vs. SAP MM in SAP S/4HANA
SAP ECC is SAP's legacy ERP system. On the back end, it uses a relational database and has a modular structure with separate components like materials management and finance. In contrast, SAP S/4HANA, the next-generation ERP suite, was built for the SAP HANA in-memory database. It has a simplified data structure, can process data faster, has embedded analytics tools and groups modules together in SAP Fiori apps.
SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA both have materials management components, but the way that users interact with MM functions is different. SAP ECC users interact with SAP MM by entering a transaction code or navigating through the SAP GUI menu to access specific materials management functions.
SAP S/4HANA on-premises and Cloud Private Edition users can interact with SAP MM in the same way, but they also have the option of interacting with MM functions by clicking and opening a Fiori app. In contrast, SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition users can only take advantage of SAP MM's capabilities through Fiori apps.
SAP MM submodules
SAP ECC platforms include submodules for SAP MM, each of which supports specific business processes related to procurement and inventory management:
- MM-PUR. Supports the operational processes related to manual or automated purchasing.
- MM-IM. Supports inventory management.
- MM-MD. Supports centralized records management for materials and vendors.
- MM-IV. Supports invoice verification.
- MM-CBP. Supports consumption-based planning.
- MM-SRV. Supports procurement for external services.
S/4HANA implementations and documentation do not use the label submodule, but the underlying business processes and functional areas still exist. To take advantage of the SAP HANA in-memory database and architecture, SAP S/4HANA organizes submodule functions around end-to-end business processes in Fiori apps. For example, purchasing functions are part of the Sourcing and Procurement line of business, and inventory management is part of Inventory Management and Warehouse Management.
The importance of roles within SAP MM
SAP MM uses roles to define each user's access rights. The purpose of roles is to control what data and transactions a user can access, and what actions they are allowed to perform.
In SAP ECC, roles are created and managed using the transaction code PFCG (Profile Generator). ECC roles are customized, and authorization profiles provide a list of the other transaction codes that a user is allowed to run.
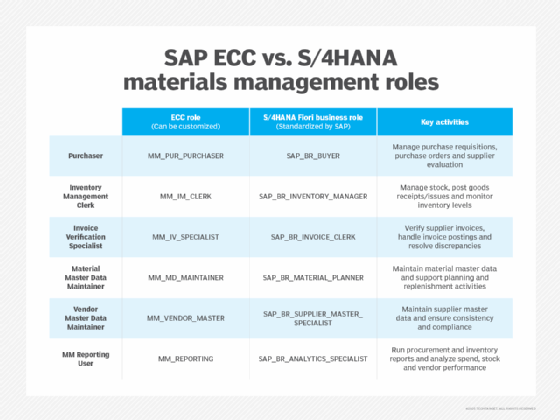
Important ECC roles include the following:
- SAP MM Purchaser. This role can use transaction codes for creating purchase requisitions, purchase orders and goods receipts, and viewing material and vendor master data.
- SAP MM Clerk. This role can use transaction codes for goods receipts, stock transfers and viewing stock levels across various storage locations.
- SAP MM Master Data Specialist. This role is able to use transaction codes for creating and managing material master records, vendor master records and purchasing info records.
- SAP MM Invoice Verifier. This role can verify invoices against purchase orders and goods receipts, resolve discrepancies, and prepare invoices for payment.
- SAP MM Reporting User. This role can use transaction codes to run procurement and inventory reports and analyze transactions within MM to gain insight into specific transactions like procurement spend, inventory turnover and vendor performance.
In SAP S/4HANA on-premises or SAP S/4HANA Cloud Private Edition, roles can still be created and managed with the transaction code PFCG, but SAP encourages organizations to adopt SAP's Fiori-based roles, which are preconfigured by SAP and tied to specific Fiori apps.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition roles are always tied to specific Fiori apps. On the back end, authorization and access rights are still managed in PFCG, but the user's interaction points are determined by which apps they see in their Fiori Launchpad.
SAP is encouraging customers to move to S/4HANA because it will stop mainstream support for SAP ECC on Dec. 31, 2027. Learn about the advantages and challenges of migrating to S/4HANA in this comprehensive guide.






