What is a firewall and why do I need one?
A firewall is a network security device that prevents unauthorized access to a network by inspecting incoming and outgoing traffic using a set of predetermined security rules.
The main purpose of a firewall is to act as a barrier between a trusted internal network, such as a home or business network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet, to help prevent unauthorized access, cyberattacks and data breaches. A firewall can be physical hardware, digital software, software as a service (SaaS) or a virtual private cloud.
Firewalls are used in both personal and enterprise settings, and many devices, including Mac, Windows and Linux computers, come with a built-in firewall. They're widely considered an essential component of network security.
History of Firewalls
The history of firewalls mirrors the evolution of the internet and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Here's a timeline of the key stages of firewalls:
- The origins of firewalls. In the 1980s, as networks began to connect, routers played a basic role in separating these networks and could filter packets that crossed between networks based on fundamental information. These basic systems laid the foundation for more advanced security measures in the future.
- First-generation firewalls. The first dedicated firewall technologies emerged in the late 1980s. These early firewalls, known as packet filters, analyzed network traffic at the network layer by inspecting individual packets based on their source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols. They would permit or block traffic according to a predefined set of rules, called an access control list. While this was an important initial step in network security, these early firewalls were stateless, meaning they did not retain information about past traffic or the context of a connection. As a result, they were vulnerable to various attacks, as they could not inspect the actual content of the packets.
- Second-generation firewalls. In the early 1990s, stateful inspection firewalls emerged as a significant advancement in network security. These firewalls maintained a table of active connections and made decisions based on the state and context of network traffic. By tracking the status of these connections, they could determine whether a packet was part of an existing, legitimate connection or a potential threat. One of the first commercially available stateful inspection firewalls was Check Point's FireWall-1, which was released in 1993.
- Third-generation firewalls. As web-based applications became increasingly prevalent and threats grew more complex, application-layer firewalls, also known as proxy firewalls, emerged. These firewalls operate at the application layer or Layer 7 of the OSI model, enabling them to analyze the actual content of network traffic. These firewalls provide more granular control and the ability to block threats specific to certain apps, such as HTTP or File Transfer Protocol (FTP). They serve as intermediaries, inspecting traffic in both directions.
- Fourth-generation firewalls. Around 2008, the concept of next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) gained prominence. These firewalls combined traditional firewall functionalities with advanced security features, including deep packet inspection (DPI), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application awareness and control, user identity awareness and URL filtering. NGFWs marked a major shift toward more proactive and comprehensive security measures.
- Fifth-generation firewalls. Beginning in the early 2020s, the latest advancement in firewall technology has involved the integration of machine learning (ML) to improve threat detection and response. ML-powered firewalls analyze network traffic patterns in real time to identify anomalies and potential threats. This proactive approach enables the detection of zero-day vulnerabilities and other sophisticated threats that traditional methods might overlook.
Why are firewalls important?
Firewalls serve as the first line of defense against external threats, such as hackers and malware attacks. In particular, firewalls combined with an IPS are crucial in preventing malware and certain application layer attacks.
Firewalls first emerged in the early days of the internet when networks needed new security methods that could handle increasing complexity. They've since become the foundation of network security in the client-server model -- the central architecture of modern computing.
Overall, firewalls play an important role in preventing cyberattacks, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining the privacy and security of computer systems and networks.
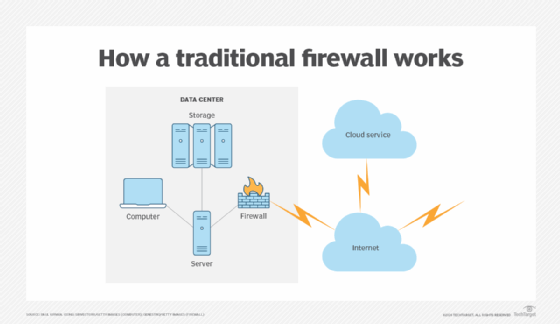
How does a firewall work?
A firewall establishes a border between an external network and the network it guards. It's inserted inline across a network connection and inspects all packets entering and leaving the guarded network. As it inspects, it uses a set of preconfigured rules to distinguish between benign and malicious traffic or packets.
The term packet refers to a piece of data formatted for internet transfer. Packets contain the data itself and information about the data, such as where it came from, source and destination IP addresses, the port numbers being used and the protocols such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Firewalls can use this packet information to determine whether a given packet abides by the rule set. If it doesn't, the packet is barred from entering the guarded network. Rule sets can be based on several things indicated by packet data, including source, destination and content.
These characteristics can be represented differently at different levels of the network. As a packet travels through the network, it's reformatted several times to tell the protocol where to send it.
Different types of firewalls exist to read packets at different network levels.
Benefits of using firewalls
Firewalls are used in both corporate and consumer settings. Modern organizations incorporate them into a security information and event management strategy along with other cybersecurity devices.
Firewalls are often used alongside antivirus applications. Unlike corporate ones, personal firewalls are usually a single product rather than a collection of various products. They can be software or a device with firewall firmware embedded.
The following are some use cases of firewalls:
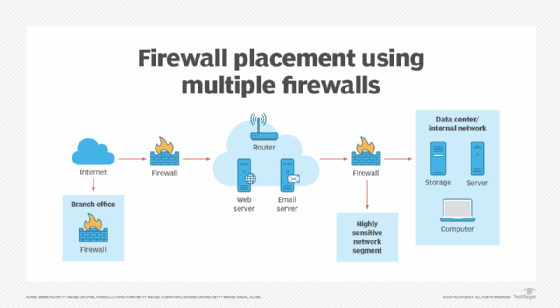
- Threat defense. Firewalls can be installed at an organization's network perimeter to guard against external threats, such as malware attacks or hacking attempts, or within the network to create segmentation and guard against insider threats.
- Logging and audit functions. Firewalls keep a record of events that administrators can use to identify patterns and improve rule sets. Rules should be updated regularly to keep up with ever-evolving cybersecurity threats. Vendors discover new threats and develop patches to cover them as soon as possible.
- Traffic filtering. In a single home network, a firewall can filter traffic and alert the user to intrusions. They're especially useful for always-on connections, such as Digital Subscriber Line or cable modems, because those connection types use static IP addresses. A firewall ensures that only intended and nondestructive content from the internet passes through.
- Controlling and blocking access. Firewalls can be used for controlling and blocking access to certain websites and online services to prevent unauthorized use. For example, an organization can use a firewall to block access to objectionable websites to ensure employees comply with company policies when browsing the internet.
- Secure remote access. Firewalls can be used to grant secure remote access to a network through a virtual private network (VPN) or other secure remote access technology.
- Network segmentation. Firewalls enhance security by separating different parts of a network into distinct security zones with varying access levels. This isolates sensitive data and systems from general network traffic. Virtual LANs can be employed for improved network management.
Types of firewalls
Firewalls are either categorized by the way they filter data or by the system they protect.
When categorized by what they protect, the two types are network-based and host-based. Network-based firewalls guard entire networks and are often hardware. Host-based firewalls guard individual devices -- known as hosts -- and are often software.
When categorizing by filtering method, the main types are as follows:
- Packet-filtering firewalls. For examining data packets in isolation and don't know the packet's context.
- Stateful inspection firewalls. For examining network traffic to determine whether one packet is related to another packet.
- Circuit-level gateway firewalls. For providing security by monitoring TCP handshaking between packets from trusted clients or servers to untrusted hosts and vice versa.
- Proxy firewalls, or application-level gateways. For inspecting packets at the application layer of the OSI reference model.
- NGFWs. They use a multilayered approach to integrate enterprise firewall capabilities with an IPS and application control.
- Threat-focused NGFWs. For combining traditional firewall technology with enhanced functionality to thwart modern threats, including application layer and advanced malware attacks.
- Virtual firewalls. Also known as cloud firewalls, they provide traffic filtering and monitoring for virtual machines (VMs) in a virtualized environment.
- Cloud-native firewalls. For automated scaling features that enable networking and security operations teams to run at fast speeds.
- Web application firewall. WAF protects web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP/HTTPS traffic between a web application and the internet.

Each type of firewall in the list above examines traffic with a higher level of context than the one before; for example, a stateful firewall has more context than a packet-filtering firewall.
Packet-filtering and network layer firewalls
When a packet passes through a packet-filtering firewall, its source and destination address, protocol and destination port number are checked. The packet is dropped, meaning it isn't forwarded to its destination if it doesn't comply with the firewall's rule set. For example, if a firewall is configured with a rule to block Telnet access, then the firewall drops packets destined for TCP port number 23, the port where a Telnet server application would be listening.
A packet-filtering firewall works mainly on the network layer of the OSI reference model, although the transport layer is used to obtain the source and destination port numbers. It examines each packet independently and doesn't know whether any given packet is part of an existing stream of traffic.
The packet-filtering firewall is effective, but because it processes each packet in isolation, it can be vulnerable to IP spoofing attacks and has largely been replaced by stateful inspection firewalls.
Stateful inspection firewalls
Stateful inspection firewalls -- also known as dynamic packet-filtering firewalls -- monitor communication packets over time and examine both incoming and outgoing packets.
This type of firewall maintains a table that keeps track of all open connections. When a new packet arrives, it compares information in the packet header to the state table -- its list of valid connections -- and determines whether the packet is part of an established connection. If it is, the packet is let through without further analysis. But, if the packet doesn't match an existing connection, it's evaluated according to the rule set for new connections.
Although stateful inspection firewalls are quite effective, they can be vulnerable to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. DoS attacks take advantage of established connections that this type of firewall generally assumes are safe.
Circuit-level gateway firewalls
When a trusted client or server sends a packet to an untrusted host and vice versa, a circuit-level gateway firewall examines the TCP handshaking between the two packets. It controls network traffic at the session level and keeps track of the OSI model's session layer. Instead of examining the content of the packets, this firewall inspects the protocol headers of the packets to determine if a session is legitimate.
Whenever a circuit-level gateway firewall receives a request from a trusted client or server to connect to an untrusted host, it starts a three-way handshake with the destination host to establish a session. It then forwards the packets between the two hosts without further inspecting the content of the packets.
This type of firewall can provide a higher level of security than packet-filtering firewalls because it can detect and prevent certain attacks, such as port scanning and DoS attacks. However, because it doesn't examine the packet content, a circuit-level gateway firewall can't offer the same level of security as an application layer firewall.
Application layer and proxy firewalls
This type of firewall is referred to as a proxy-based or reverse-proxy firewall. They provide application layer filtering and can examine the payload of a packet to distinguish valid requests from malicious code disguised as a valid request for data. As attacks against web servers became more prevalent, so did the need for firewalls to protect networks from attacks at the application layer. Packet-filtering and stateful inspection firewalls can't do this at the application layer.
Since this type of firewall examines the payload's content, it gives security engineers more granular control over network traffic. For example, it can allow or deny a specific incoming Telnet command from a particular user, whereas other types of firewalls can only control general incoming requests from a particular host.
When this type of firewall lives on a proxy server -- making it a proxy firewall -- it becomes harder for an attacker to discover where the network is and creates yet another layer of security. Both the client and the server are forced to conduct the session through an intermediary -- the proxy server that hosts an application layer firewall. Each time an external client requests a connection to an internal network server or vice versa, the client opens a connection with the proxy instead. If the connection request meets the criteria in the firewall rule base, the proxy firewall opens the connection.
The key benefit of application layer filtering is the ability to block specific content, such as known malware or certain websites, and recognize when certain applications and protocols, such as HTTP, FTP and domain name system, are being misused. Application layer firewall rules can also be used to control the execution of files or the handling of data by specific applications.
Next-generation firewalls
This type of firewall is a combination of the other types with additional security software and devices bundled in. The benefit of an NGFW is that it combines the strengths of each type of firewall to cover each type's weaknesses. An NGFW is often a bundle of technologies under one name, as opposed to a single component.
Modern network perimeters have so many entry points and different types of users that stronger access control and security at the host are required. This need for a multilayer approach led to the emergence of NGFWs.
An NGFW integrates three key assets: traditional firewall capabilities, application awareness and an IPS. Similar to the introduction of stateful inspection to first-generation firewalls, NGFWs bring additional context to the firewall's decision-making process.
NGFWs combine the capabilities of traditional enterprise firewalls, including network address translation, URL blocking and VPNs, with quality of service functionality and features not traditionally found in first-generation products. NGFWs support intent-based networking by including Secure Sockets Layer and Secure Shell inspection and reputation-based malware detection. NGFWs also use DPI to check the contents of packets and prevent malware.
When an NGFW, or any firewall, is used in conjunction with other devices, it's termed unified threat management.
Virtual firewalls
A virtual firewall runs entirely within a virtualized environment and provides the same security and inspection capabilities as a hardware firewall.
It monitors and inspects network traffic between VMs and between VMs and the outside world. The firewall is situated between the VMs and the hypervisor that provides the virtualization layer and inspects traffic at the network layer to determine whether to allow or block packets based on a set of predefined rules.
Virtual firewalls can filter traffic based on IP address, ports, protocols and other factors and provide the same security and inspection capabilities as physical firewalls. Some virtual firewalls also offer security capabilities, including application-level security, intrusion detection and intrusion prevention. SonicWall NSv Series and Juniper vSRX Virtual Firewall are examples of virtual firewalls.
Cloud-native firewalls
A cloud-native firewall is a type of virtual firewall that's specifically designed to operate within a cloud-based infrastructure. It's a network firewall security system that provides traffic filtering and monitoring for VMs and containers running in a cloud environment.
Cloud-native firewalls provide the same security and inspection capabilities as traditional virtual firewalls but are optimized for the dynamic and scalable nature of cloud-based environments. They're designed to integrate with cloud orchestration platforms, such as Kubernetes, and provide automated security policy enforcement across a large number of cloud resources.
Web application firewall
A WAF is designed to protect web applications by filtering, monitoring and blocking malicious HTTP/HTTPS traffic between a web application and the internet. Unlike traditional firewalls that operate at lower layers of the OSI model, WAFs function at the application layer, enabling them to identify and mitigate threats that target specific vulnerabilities in web applications. Common threats blocked by WAFs include SQL injection, cross-site scripting, cross-site request forgery and file inclusion attacks.
WAFs inspect incoming and outgoing HTTP requests and apply a set of predefined rules or policies to determine whether the traffic is benign or malicious. These rules can be based on known attack patterns, anomaly detection, or behavioral analysis.
WAFs can be deployed in various forms, including network-based appliances, host-based software, or cloud-based services, providing flexibility to match an organization's infrastructure and security needs.
Understanding firewall vulnerabilities
Less advanced firewalls -- packet-filtering firewalls, for example -- are vulnerable to higher-level attacks because they don't use DPI to fully examine packets. NGFWs were introduced to address that vulnerability. But NGFWs still face challenges and are vulnerable to evolving threats. For this reason, organizations should pair them with other security components, such as intrusion detection systems and intrusion prevention systems. Examples of modern threats that a firewall can be vulnerable to include the following:
- Insider attacks. Organizations can use an internal firewall on top of a perimeter firewall to segment the network and provide internal protection. If an attack is suspected, organizations can audit sensitive data using NGFW features. All the audits should measure up to baseline documentation within the organization that outlines best practices for using the organization's network. Examples of behavior that might indicate an insider threat include the following:
- Transmission of sensitive data in plain text.
- Resource access outside of business hours.
- Sensitive resource access failure by the user.
- Third-party users accessing network resources.
- Distributed DoS attacks. A DDoS attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted network by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of traffic. It uses multiple compromised computer systems as sources of attack traffic. Exploited machines can include computers and other networked resources, such as internet of things (IoT) devices. A DDoS attack is similar to a traffic jam preventing regular traffic from arriving at its destination. The key concern in mitigating a DDoS attack is differentiating between the attack and normal traffic. Many times, the traffic in this attack type can come from seemingly legitimate sources and requires cross-checking and auditing from several security components.
- Malware. Malware threats are varied, complex and constantly evolving alongside security technology and the networks it protects. As networks become more complex and dynamic with the rise of IoT, it becomes more difficult for firewalls to defend them. Firewalls are also susceptible to fileless malware attacks that operate in memory and use legitimate system tools to execute malicious activities, making it difficult for traditional firewalls to detect.
- Patching and configuration. A poorly configured firewall or a missed vendor update can be detrimental to network security. IT admins should be proactive in maintaining their security components.
- Exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities. Attackers can exploit unknown vulnerabilities in firewall software before vendors release patches. For example, the ArcaneDoor campaign targeted Cisco's Adaptive Security Appliances by exploiting two zero-day vulnerabilities, enabling attackers to execute malicious code and maintain access even after reboots or updates. This campaign compromised numerous global government networks, highlighting the dangers of unpatched firewall devices.
- Supply chain attacks. Supply chain attacks represent a sophisticated cyberthreat where attackers bypass traditional firewall defenses by compromising trusted third-party vendors and their software distribution channels. Instead of directly attacking an organization's network, cybercriminals infiltrate the trusted vendors' systems and insert malicious code into legitimate software updates. The SolarWinds incident of 2020 exemplifies this approach, where attackers successfully embedded malicious code into routine software updates, which were then distributed to thousands of organizations worldwide through authorized channels.
Firewall vendors
Enterprises looking to purchase a firewall should understand their needs and network architecture. There are many different types of firewall vendors offering a range of features. According to Gartner Peer Insights and Informa TechTarget's independent research, the following NGFW vendors are recognized for their performance and market presence:
- Check Point Quantum. It delivers advanced, AI-powered threat prevention, unified policy management, and scalable performance to protect enterprise networks, data centers and remote users from sophisticated cyber threats.
- Fortinet FortiGate. It offers intrusion protection and other AI-powered services designed for smaller organizations, as well as enterprise data centers.
- Palo Alto Networks PA Series. With ML-based threat detection and intrusion, it offers options for small and medium-sized businesses, large enterprises and managed service providers.
- SonicWall Network Security appliance Series. It offers advanced threat protection, as well as URL filtering, malware detection and intrusion protection.
- HUAWEI Unified Security Gateway. USG combines advanced firewall protection, high-performance routing, and seamless integration with UniFi's centralized management system to deliver secure and efficient network operations.
Firewall best practices
The following are some common firewall best practices that most organizations should follow:
- Block all traffic by default and only permit specific traffic.
- Follow the principle of least privilege, and grant users only the minimal level of access required to complete their duties.
- Perform regular security audits to check for any vulnerabilities.
- Administer firewall change control to manage and track changes to firewall rules.
- Keep the firewall software current to ensure it can detect and block any new threats.
- Optimize firewall rules to reduce unnecessary processing and boost performance.
- Divide the network into distinct segments, such as internal, external or guest, to contain potential breaches and enforce tailored security policies for each zone.
- Protect the firewall with strong passwords, multifactor authentication and role-based access control, and limit who can make changes to the firewall configuration.
- Bring security awareness to the users by educating them about phishing, social engineering and other threats that might try to bypass the firewall.
Controversial uses of firewalls
While firewalls are primarily seen as security tools, their capabilities can be used in ways that raise ethical, political or social concerns. Here are some controversial uses of firewalls:
- Government censorship and control. By restricting access to particular websites or content based on political or ideological goals, as in the case of government censorship, firewalls can be used for control or other unethical ends. The Great Firewall of China is an example of how firewalls can be used for ethically questionable purposes. The Chinese government uses the Great Firewall to block access to specific websites and restrict access to content deemed politically or socially sensitive. The Great Firewall also monitors online activity and collects personal information, leading to concerns about privacy and individual freedoms.
- Corporate surveillance and employee monitoring. Some companies have also come under scrutiny for using firewalls to restrict access to lawful websites for employees or to keep tabs on their online activities. Typically, DPI features of firewalls can be used to monitor online activity and collect personal information to infringe on the privacy and personal freedom of internet users.
- Geo-blocking and market segmentation. Geo-blocking is the practice of using firewalls to control geographic access. While organizations employ it for digital rights management and regional licensing compliance, this practice raises significant concerns about digital equality and fair access. By creating digital borders, geo-blocking restricts users in specific locations from content and services available elsewhere. This disparity affects user experience and fuels worry about digital discrimination and location-based price variations.
- Weaponization in cyber warfare. Nation-states or malicious actors could potentially manipulate firewall configurations as part of a cyberattack. This could involve creating backdoors, disrupting legitimate traffic, or using the firewall as a point of control within a compromised network.
- Restricting political dissent. Authoritarian regimes often use firewalls to block activist websites and protest platforms, silencing opposition and limiting political dissent. While justified by claims of national security, these measures are criticized for undermining democratic freedoms.
Future of network security
In the early days of the internet, when AT&T's Steven M. Bellovin first used the firewall metaphor, network traffic primarily flowed north-south. This simply means that most of the traffic in a data center flowed from client to server and server to client. In the past few years, however, virtualization and trends such as converged infrastructure have created more east-west traffic, which means that, sometimes, the largest volume of traffic in a data center is moving from server to server.
To deal with this change, some enterprises have migrated from the traditional three-layer data center architecture to various forms of leaf-spine architecture. This change in architecture has caused some security experts to warn that, while firewalls still have an important role to play in keeping a network secure, they risk becoming less effective. Some experts even predict a departure from the client-server model altogether.
The following are some emerging trends in network security worth exploring:
- Software-defined perimeter. The use of an SDP is more aptly suited to virtual and cloud-based architectures because it has less latency than a firewall. It also works better within increasingly identity-centric security models because it focuses on securing user access rather than IP address-based access. An SDP is based on a zero-trust framework.
- Secure Access Service Edge. SASE is becoming increasingly important for protecting networks against new and evolving threats.
- Firewall as a service. FwaaS resides in the cloud and continues to gain popularity, as it examines traffic for remote employees and servers, while using standard cloud service advantages, such as ready scalability and flexibility.
- Zero-trust policy. The zero-rust policy assumes that all access requests are potentially malicious and that access is only granted on an as-needed basis. The zero-trust approach is critical to network security going forward.
- AI and automation. AI and automation are likely to play a greater role in network security, both in terms of threat detection and response.
- Post-quantum cryptography. With the advent of quantum computing, traditional encryption methods are at risk of becoming obsolete. Post-quantum cryptography focuses on developing encryption algorithms that are resistant to quantum attacks. Many organizations are already integrating post-quantum cryptographic protocols into their services to future-proof data security. The National Institute of Standards and Technology is leading efforts to standardize these algorithms, with a transition target set for 2030.
- Fifth-generation network security. The arrival of 5G networks will drive a stronger focus on their security. The increased speeds and reduced latency of 5G present new security hurdles, especially concerning connected IoT devices and the integrity of critical infrastructure.
- Extended detection and response. XDR platforms offer a centralized method for detecting and responding to threats by consolidating data from diverse security layers such as networks, endpoints, and the cloud. This comprehensive visibility empowers organizations to identify and neutralize threats more efficiently, leading to faster response times and a stronger overall security stance.
- Hybrid mesh firewalls. Organizations are increasingly interested in hybrid mesh firewalls, a new category of unified security platforms that can be deployed as appliances, virtual instances, cloud-native solutions, or as FWaaS. This growing demand is driven by the continued expansion of hybrid environments, where businesses require network firewalls that operate seamlessly across various locations, including cloud infrastructures. According to Gartner's Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls, this trend is notable, with projections indicating that more than 60% of organizations will have diverse firewall deployments by 2026.
As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, organizations need to stay proactive in adopting innovative services for mitigating threats and ensuring network security.
Given the wide variety of firewalls available on the market, it can be overwhelming to differentiate between them. Explore the distinctions and similarities between the basic categories of firewalls.







