Gemini vs. ChatGPT: What's the difference?
ChatGPT took the early lead among AI-generated chatbots before Google answered with Gemini. While ChatGPT and Gemini perform similar tasks, there are differences.
ChatGPT and Gemini are two leading AI chatbots with distinct strengths. OpenAI's ChatGPT is known for its conversational fluency, structured responses, and strong summarization and content creation performance. In contrast, Google's Gemini excels in real-time web access, complex reasoning and research-based tasks, making it a strong competitor in the AI space.
The two chatbots account for much of the considerable buzz around generative AI (GenAI), a type of artificial intelligence that uses data from machine learning models to answer questions and create images, text and videos.
OpenAI, backed by Microsoft, introduced ChatGPT in November 2022. Google made its GenAI move in March 2023 with Bard. In February 2024, Google rebranded Bard as Gemini when it debuted an improved version of the AI chatbot.
OpenAI and Google are continuously improving the large language models (LLMs) behind ChatGPT and Gemini to give them a greater ability to generate humanlike content. However, the field is still evolving, and models don't always return correct answers. Despite the occurrence of AI hallucinations -- wrong answers generated by AI -- ChatGPT and Gemini are being widely adopted by businesses and consumers seeking to automate time-consuming tasks.
This article is part of
What is GenAI? Generative AI explained
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is the AI system that made GenAI the hot technology of 2023. According to OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, ChatGPT reached 1 million users within five days of its release.
Generative Pre-trained Transformer, the model ChatGPT is based on, finds patterns within data sequences. Its AI language model produces responses to user queries and serves as the interface that lets users communicate with the language model. Popular applications for ChatGPT include content generation of emails, social media posts and blogs; text summarization; language translation; code generation; learning and education; building virtual assistants; simulation and training; research assistance; and building games and other entertainment applications.
ChatGPT is multimodal, meaning users can use images and voice to prompt the chatbot. ChatGPT's Voice mode -- available on iOS and Android phones -- lets users converse with ChatGPT, which can respond in one of five AI-generated voices.
What is Google Gemini?
Gemini is Google's GenAI model, built by the Google DeepMind AI research library. It powered Google's Bard GenAI tool, which launched in March 2023. Google rebranded Bard as Gemini in February 2024, several months after launching Gemini Advanced based on its new Ultra 1.0 LLM foundation. In May 2024, Google first offered users of Gemini Advanced access to the newer Gemini 1.5 Pro model, followed by Gemini 2.0 in December.
Gemini is designed to retrieve information as a simple answer, similar to the way smart assistants such as Alexa and Siri work. It uses LLMs to reply to prompts with information it has already learned or can retrieve from other Google services.
Google Gemini is multimodal; it understands audio, video, computer code and text. In May 2024, Google released its Veo and Imagen 3 models for improved, safer and more accurate image and video generation. Seven months later, Google released its Veo 2 and updated Imagen 3.
Gemini's capabilities are integrated into Google's search engine and available in Google Workspace apps such as Docs, Gmail, Sheets, Slides and Meet. Gemini for Google Workspace is the new name for Duet AI for Google Workspace, which was Google's answer to the Microsoft Copilot AI assistant. Google Gemini is available through an app on Android phones and in the Google app on iOS.
Gemini Nano, another part of the Google Gemini family, is used in devices such as Google's Pixel 8 Pro smartphones.
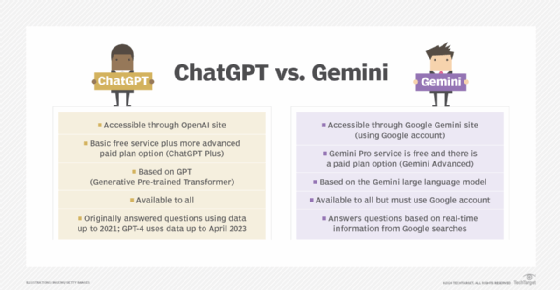
ChatGPT and Google Gemini: Paid plans
As of January 2025, GPT-4o is the default model in the free version of ChatGPT, with GPT-3.5 still available as an option. Paid subscriptions -- ChatGPT Plus, Team and Enterprise -- offer enhanced access to GPT-4o and GPT-4. While GPT-4 was once the leading GenAI model, Google's Gemini Advanced has emerged as a strong competitor.
Here is a breakdown of the free versions and various subscription plans for individuals and businesses.
ChatGPT for individuals
Free version. Available using web and mobile, with API access for developers.
ChatGPT Plus ($20 per month). Full access to GPT-4o, which is faster, more accurate and includes advanced data analysis. GPT-4o also supports image description and captioning. Unlike GPT-3.5, which is trained on data until January 2022, GPT-4o is trained up to October 2023. ChatGPT Plus users get priority access during peak times and integration with OpenAI's Dall-E 3 for text-to-image generation.
ChatGPT for businesses
ChatGPT Team ($25 per user, per month, billed annually). Includes all ChatGPT Plus features, more message capacity, GPT sharing, faster responses and an admin console.
ChatGPT Enterprise (custom pricing). Offers unlimited, high-speed GPT-4 access, advanced admin tools, better customer support, analytics and longer input windows.
Google's Gemini Advanced
Users can access the paid tier of Gemini with the Google One AI Premium plan for $19.99 per month, which includes 2 TB of storage. It features Gemini Pro 1.5 with a 2 million-token context window for large-scale data analysis.
What are the main differences between Gemini and ChatGPT?
ChatGPT and Google Gemini have become increasingly similar. Both offer a free service, a nearly identically priced subscription service, and similar interfaces and use cases. As noted, the differences are largely in their language models.
They're also used for many similar functions and work by users typing in a query to get a response. Both chatbots raise privacy concerns about how user data can be used. However, they differ in their training models, data sources, user experiences and data storage.
Training models
ChatGPT is built on OpenAI's GPT-3.5 or GPT-4. Gemini has three sizes: Gemini Pro for a wide range of tasks, Gemini Ultra for highly complex tasks and Gemini Nano for mobile devices. Gemini Pro 1.5, which powers the subscription Gemini Advanced version, is faster and more advanced than the model used for the free Gemini service.
Data sources
The main difference between ChatGPT and Gemini is the data sources used to train their LLMs. GPT-4o uses predefined data up to October 2023, while Gemini draws on data pulled from the internet in real time. It's tuned to select data from sources that fit specific topics, such as coding or the latest scientific research.
User experience
ChatGPT users can log into the free ChatGPT with any email account. ChatGPT also includes an API that developers can use to integrate OpenAI LLMs into third-party software. It lacks a Save button, but users can copy and paste answers from ChatGPT into another application. It does have an Archive button that can list previous responses in ChatGPT's left-hand pane for quick retrieval.
Because ChatGPT is text-based, it can't include images, videos, charts or links in its answers. It also lacks the ability to search the internet.
Because of OpenAI's close partnership with Microsoft, ChatGPT can be used through Windows apps such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint and Outlook. Also, Microsoft's Copilot AI assistants use the GPT-4 language model.
Gemini Pro's interface lets users like or dislike a response, modify its size or tone, share or fact-check it, or export it to Google Docs or Gmail. The "review other drafts" option shows alternate versions of its answer. Gemini also lets users upload images through Imagen 3, its highest-quality text-to-image model.
Data storage and privacy
Both ChatGPT and Google Gemini store user data.
ChatGPT stores all prompts and queries entered. Users can review previous conversations through its archive feature. Although users can delete responses and conversations, the chatbot might continue to use these responses in its LLM for training. This raises privacy concerns when users enter personal data or proprietary information. OpenAI also discloses that ChatGPT gathers geolocation data, network activity, contact details such as email addresses and phone numbers, and device information.
According to OpenAI's privacy policy, it collects any personal information a user provides. This includes account information, such as name, contact information, payment card information and transaction history. OpenAI also might disclose geolocation data to third parties, such as vendors and service providers, and to law enforcement agencies if required by law.
OpenAI said the user retains ownership rights of input data and owns the output. However, it "may use Content to provide, maintain, develop, and improve our Services, comply with applicable law, enforce our terms and policies, and keep our Services safe."
Gemini stores conversations in a user's Google account for 18 months, but users can change the retention period to three months or 36 months in their activity settings. Gemini conversations can also appear in searches, raising privacy concerns.
Google discloses that it collects conversations, location, feedback and usage information. The Google Privacy Policy claims Google uses collected data to develop, provide, maintain and improve services and to provide personal services such as content and ads. Customers can delete information from their accounts using My Google Activity or by deleting Google products or their Google accounts.
Google said it will share information with third parties with user consent and law enforcement when required.
| Main differences between ChatGPT and Gemini | ||
| Feature |
ChatGPT |
Gemini |
| Training models |
OpenAI's GPT-3.5 or GPT-4. |
Gemini Pro for a wide range of tasks, Gemini Ultra for highly complex tasks and Gemini Nano for mobile devices. |
| Data sources |
GPT-4o uses predefined data up to October 2023. |
Gemini uses data pulled from the internet in real time. |
| User experience |
Because ChatGPT is text-based, answers can't include images, videos, charts or links. It also lacks the ability to search the internet. |
Gemini Pro's interface lets users like or dislike a response, modify its size or tone, share or fact-check it, or export it to Google Docs or Gmail. |
| Data storage and privacy |
ChatGPT stores all prompts and queries, so users can review previous conversations. Users can delete responses, but the chatbot might still use them for training, raising privacy concerns. OpenAI also collects geolocation, network activity, contact details and device information. |
Gemini stores conversations in a user's Google account for 18 months, but users can change the retention period to three months or 36 months. Gemini conversations can also appear in searches, raising privacy concerns. |
Which chatbot is better?
There is a bit of a GenAI arms race going on now, with OpenAI and Google updating their models. Google has been especially aggressive, perhaps because ChatGPT came out first and Gemini must play catch-up. With each new version of LLMs, Google and OpenAI make significant gains over their previous versions.
Research
According to a July 2024 article in the Journal of Academic Ethics, Gemini delivers more accurate results for academic research, scoring 100% on all queries; ChatGPT-3.5 scored 70%, struggling with bibliographic sources, formatting and general deductive abilities. Recent research found that both models provided appropriate and comprehensive answers, but Gemini's responses were more relevant, thorough and supported by references compared to ChatGPT's.
However, ChatGPT excels at less complex, more general topics, such as top-performing blog topics in the pet industry, with more lucid content and referenced responses, according to a January 2025 Backlinko article.
Image generation
Research studies differ on the superiority of the models, with results seeming to depend on the prompts used. For example, a December 2024 article by Tom's Guide found ChatGPT superior to Gemini, as it offered more accurate results and better image interpretation across seven prompts. In contrast, Backlinko argued that Gemini's image generation produces vastly inferior quality compared to ChatGPT. Ethan Mollick, an associate professor who studies AI at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, writes a knowledgeable "One Useful Thing" Substack newsletter that tests GenAI every six months. He recently concluded that Gemini's premium Imagen 3 "leads the pack."
Creative writing, copywriting and email generation
Both models can suggest blog topics, article ideas and outlines; plan email and social media campaigns; generate video scripts; write sales copy for web and landing pages; execute email campaigns; and craft social media captions. All studies and tests have indicated that both models deliver humanlike, imaginative, high-quality responses. However, Backlinko concluded that Gemini offers more creative and original responses, while ChatGPT excels at video scripts, outlining, repurposing blog posts and transcribing text from images.
Summarization
Across studies, ChatGPT shows better summarization results, as it's more terse, concise and accurate than Gemini. Also, in contrast to ChatGPT, Gemini doesn't support document uploads, requiring users to copy and paste content into the model for results.
SEO
According to Backlinko, ChatGPT is the better option for SEO, delivering superior results with more relevant keyword suggestions, engaging title and headline options, and more effective sales emails.
Coding
Some researchers find both models equally proficient at writing code, although Mollick suggested ChatGPT is superior to Gemini at this task. Regarding data analysis, a January 2025 ClickUp blog post concluded that ChatGPT provides more thorough explanations for technical queries. Mollick noted that while ChatGPT's Code Interpreter excels at statistical analyses, Gemini outperforms with graphing.
Reasoning and decision-making
In general, the longer the model processes the query, the better the outcome. While ChatGPT provides virtually instant responses, Gemini asks users to wait several seconds as it generates its response. According to Mollick, future ChatGPT spinoffs might yet triumph over Gemini in reasoning, particularly with newer models from the o1 family: o1-mini, o1, o1-Pro and the expected o3.
| Google Gemini vs ChatGPT: Key features | ||
| Feature |
ChatGPT |
Gemini |
| Research |
Better for general research on less complex topics. |
Better for academic, complex and scientific research. |
| Image generation |
Produces excellent results, depending on prompts. |
Gemini's premium Imagen 3 seems to produce superior image generation. |
| SEO/copywriting/ |
Has more relevant suggestions for keyword ideas, more engaging options for titles and headlines and more effective email copy. |
While both models produce high-quality content, Gemini is noted for its imaginative responses. |
| Summarization |
ChatGPT is more terse, concise and accurate in its summaries than Gemini. The model also enables uploads. |
Gemini doesn't support file uploads. |
| Creative content |
ChatGPT provides longer blogs and is also better at video scripts, outlining, repurposing blog posts and transcribing text from images. |
Arguably, Gemini provides more creative, original responses. |
| Coding |
ChatGPT's Code Interpreter excels at executing code and provides detailed explanations for technical queries. |
Gemini outperforms at explaining graphs. |
| Reasoning and decision-making |
New ChatGPT derivatives (the o1 family) might gain the reasoning edge in the future. |
Gemini seems to be more advanced at reasoning since it takes longer to process its responses. |
Summary
OpenAI's ChatGPT and Google's Gemini each have distinct strengths. ChatGPT is better for general research, SEO, copywriting, advertising and summarization, offering more concise, engaging and humanlike responses to its users. It also excels at writing code and produces longer blogs and better video scripts.
In contrast, Gemini is stronger in academic and complex research, advanced reasoning and creative originality. It might outperform ChatGPT in image generation and graphing. Overall, Gemini is more cerebral, analyzing vast databases with up-to-date results, while ChatGPT provides more natural, humanlike responses, making it ideal for customer support. Users can try free versions to see which chatbot fits their needs.
There have been several in-depth reviews about the chatbots worth noting:
- Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and BerriAI benchmarked Gemini Pro against GPT-3 and GPT-4 on 10 diverse language tasks with the goal of providing an impartial, in-depth analysis. They found Gemini's strengths included performance on long, complex reasoning chains and translating into non-English languages. On the downside, it struggled with mathematical reasoning -- especially with large numbers -- and showed bias on multiple-choice questions, while its aggressive content filtering blocked many responses. In summary, the researchers concluded Gemini Pro did not match GPT-3 and GPT-4 but "exhibits strengths in handling complexity and reasoning depth."
- Ethan Mollick performed what he called "tasting notes" of Gemini Advanced vs. GPT-4. Mollick concluded that Gemini Advanced is the first advanced AI model that can compete with GPT-4. He said each has its strengths and weaknesses; for example, GPT-4 uses code in a more sophisticated way and is better at hard verbal tasks, while Gemini is better at explanations and search functions. But both "are weird and inconsistent and hallucinate more than you would like."
- Bernard Marr, a futurist and author of Generative AI in Practice, pointed out in a Forbes article that ChatGPT is designed to be more conversational, while Gemini processes information and automates tasks more efficiently. Marr's conclusion after using ChatGPT and Gemini is that ChatGPT-4 is the more powerful chat interface, but "Gemini is closing the gap."
Neither ChatGPT nor Gemini are perfect, and their developers admit that. Both generate hallucinations and even warn users of that in their responses. Both chatbots include a disclaimer on the bottom of their prompt screens. Gemini's reads: "Gemini may display inaccurate info, including about people, so double-check its responses." ChatGPT advises: "ChatGPT can make mistakes. Consider checking important information."
The Gemini FAQ on Google's website offers this valuable advice that can apply to all AI tools:
- Gemini can't replace important people in your life, like family, friends, teachers or doctors.
- Gemini can't do your work for you.
- Gemini can't make important life decisions for you.
Generative AI alternatives
While Gemini and ChatGPT lead the charge in generative AI, new GenAI alternative models are constantly emerging. These include AI21 Labs' Wordtune, Anthropic's Claude, Jasper, Open Assistant and Writesonic's Chatsonic. China's Baidu search engine uses AI with an application called Ernie Bot. A trio of models cater to specialized users: xAI's Grok is particularly valuable for dedicated X users; Microsoft's Copilot integrates ChatGPT-like functionality directly into Windows; and DeepSeek, a highly capable and free Chinese model, is gaining recognition.
The following alternatives offer unique strengths and cater to specific needs:
- Canva Leonardo.Ai and OpenAI Dall-E 3. Users can create stunning art from text or images.
- Character.AI. For those seeking more creative and humanlike text generation, Character.AI lets users interact with AI characters with distinct personalities.
- GitHub Copilot. Powered by OpenAI's Codex, the tool excels at generating code in various programming languages.
- Perplexity AI. The Perplexity AI search engine focuses on providing answers with verifiable sources, making it a strong choice for research.
- Poe. This platform offers access to multiple LLMs, enabling users to compare and choose the one that best suits their needs.
Comparison of ChatGPT vs. Gemini responses
We asked ChatGPT-4o and Google Gemini 2.0 Flash the same requests and prompts to see how their responses would compare. The results are as follows.
Idea generation
Prompt. What are the five hottest IT trends an IT professional should know about?
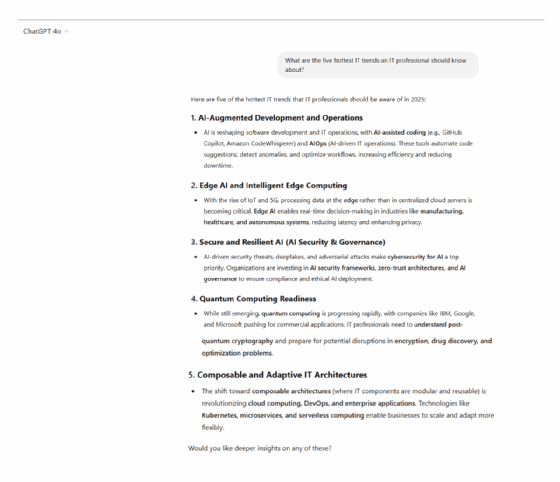
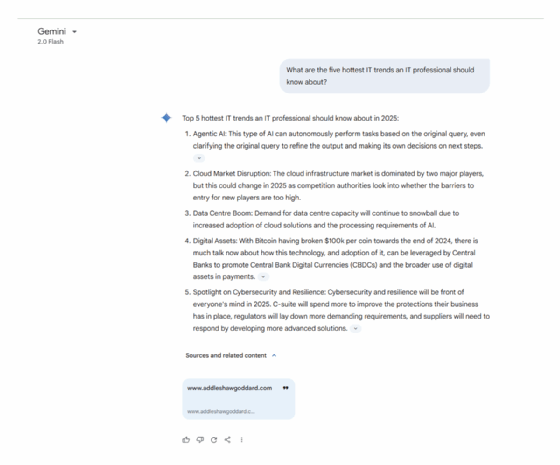
Analysis. Regarding idea generation, ChatGPT's response is structured and highly detailed, breaking each trend into why it matters, its effect and the key skills IT professionals need. This makes it particularly useful for users seeking informative responses. In contrast, Gemini takes a broader, more narrative-driven approach, emphasizing overarching themes such as agentic AI, cloud computing and cybersecurity.
Key takeaways. ChatGPT delivers well-organized, practical takeaways for the general user, while Gemini provides a more exploratory, high-level, up-to-date overview for professionals.
Creating content
Prompt. Write a two-paragraph summary explaining cyber-resiliency challenges.
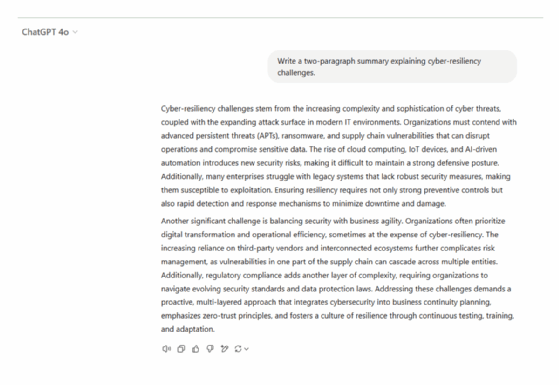
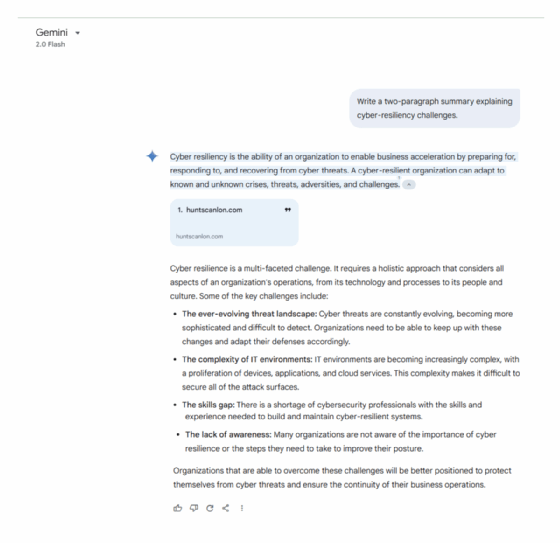
Analysis. ChatGPT's response is highly structured and technical, breaking cyber-resiliency challenges into clear categories such as attack vectors, operational continuity and regulatory compliance. It emphasizes the complexity of modern threats, the difficulties in integrating security technologies and the real-world consequences of inadequate protection. In contrast, Gemini takes a broader, more narrative-driven approach, defining cyber resilience and highlighting both technical and human factors, such as employee vulnerabilities and the cybersecurity skills gap.
Key takeaways. While ChatGPT delivers a more in-depth, analytical breakdown, ideal for users seeking detailed insights, Gemini provides a more accessible and high-level discussion, making it better suited for general audiences looking for an overview.
Planning
Prompt. What are the best cloud computing conferences to attend?
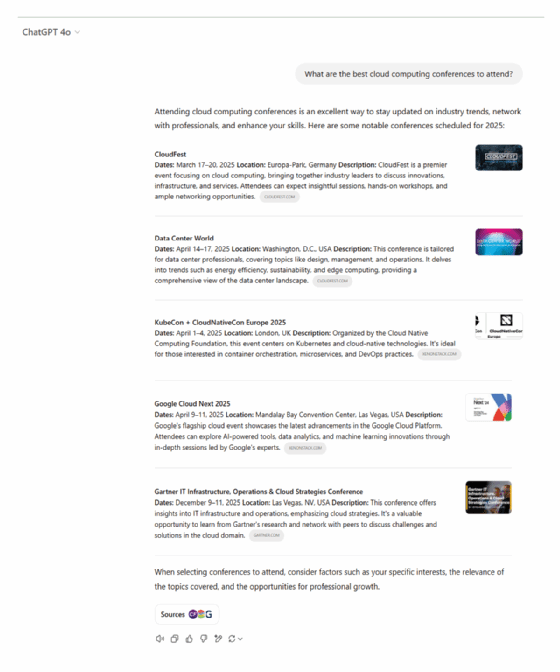

Analysis. ChatGPT provides a highly structured and comprehensive list of cloud computing conferences, detailing event dates, locations and specific reasons for attendance. Its response is fact-driven, making it ideal for users looking for a straightforward, well-organized reference. In contrast, Gemini uses a thematic approach, categorizing cloud computing conferences into major cloud provider conferences and key cloud-native and infrastructure conferences. It also includes practical tips for choosing the right conference. While ChatGPT excels at delivering exhaustive, hugely detailed information, Gemini takes a more strategic approach, focusing on decision-making considerations rather than just listing events
Key takeaways. ChatGPT is better suited for users seeking quick, concrete recommendations, while Gemini provides broader planning guidance.
Developer assistance
Prompt. List 10 frequently used SQL queries for querying a PostgreSQL database.
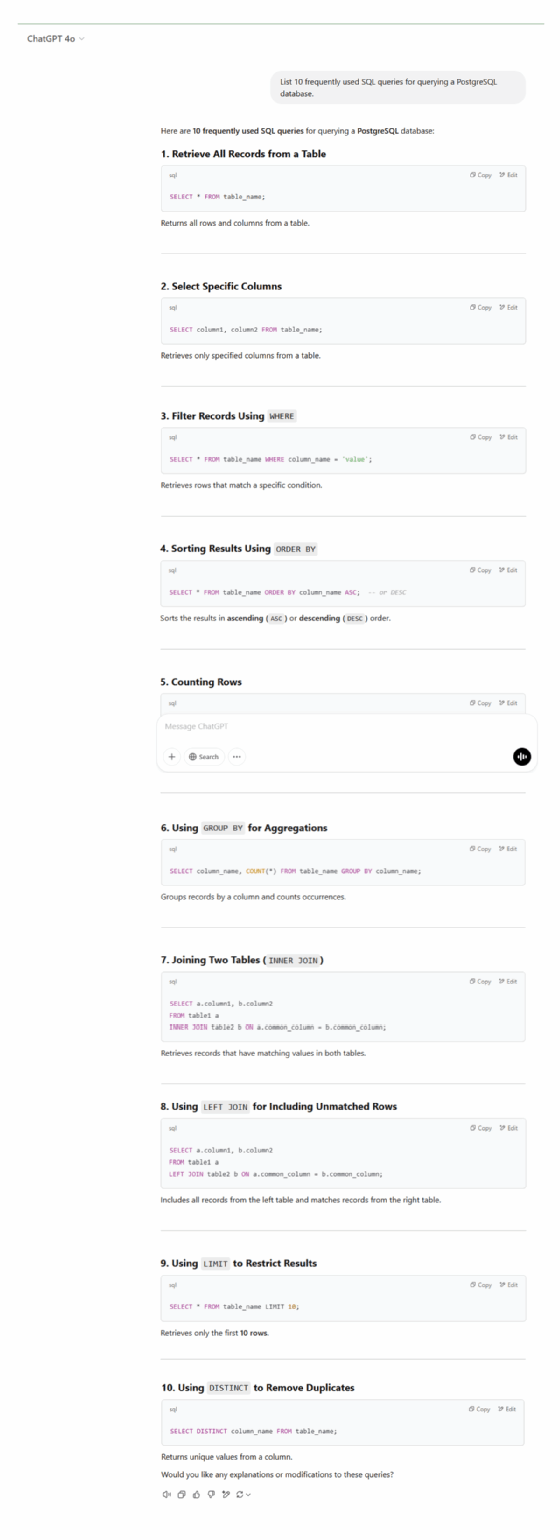
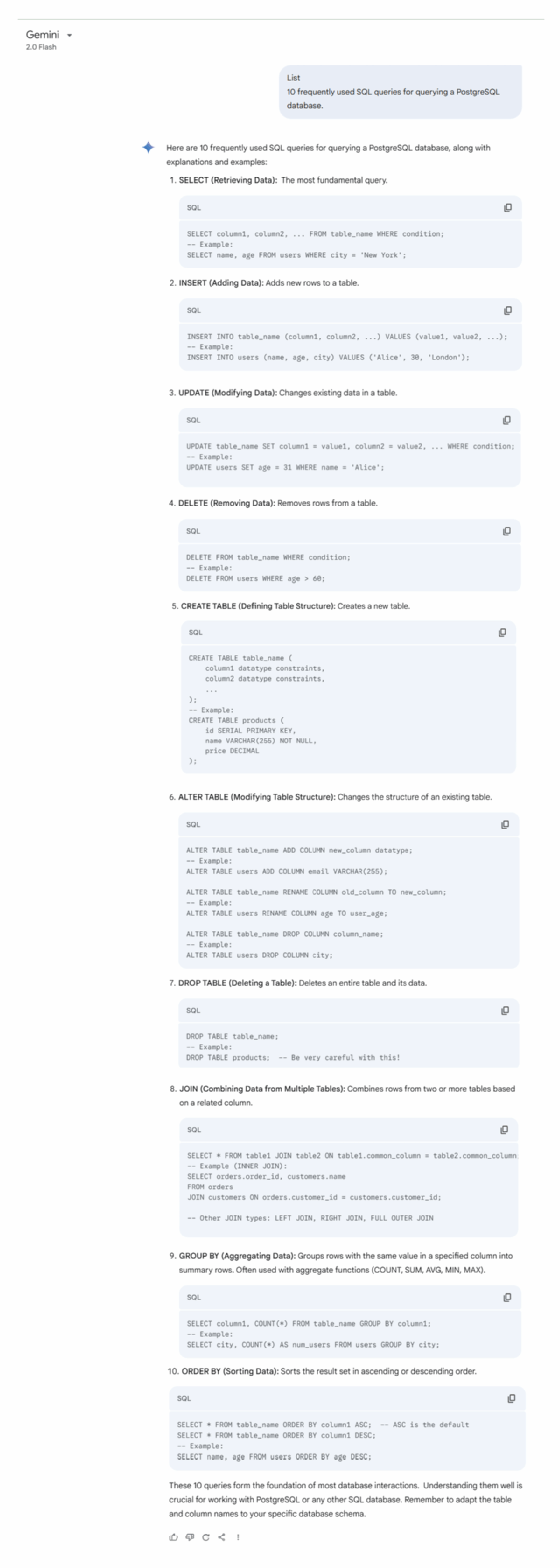
Analysis. ChatGPT's response is highly structured, categorizing commands such as data retrieval, aggregation and modifications, making it ideal for users seeking quick, actionable SQL references. In contrast, Gemini takes a more instructional approach, offering explanations alongside code examples and highlighting best practices, such as avoiding SELECT * for performance reasons.
Key takeaways. While ChatGPT's streamlined referencing makes it useful for experienced developers, Gemini's beginner-friendly responses help users new to coding.
Leah Zitter, Ph.D., is a seasoned writer and researcher on generative AI, drawing on over a decade of experience in emerging technologies to deliver insights on innovation, applications and industry trends.
Dave Raffo is MSP news editor, Channel Futures, at Informa Tech. He previously worked as an independent IT analyst and journalist, and as a senior analyst at The Futurum Group and Evaluator Group, covering integrated systems, software-defined storage, container storage, public cloud storage and as-a-service offerings. He previously worked at TechTarget from 2007 to 2021 as executive news director and editorial director for its storage coverage, and he was a technology journalist for 30 years.







