What is crypto-agility?
Crypto-agility, or cryptographic agility, is the ability of an organization to efficiently and rapidly change cryptographic algorithms, protocols or primitives in response to emerging threats, vulnerabilities or regulatory requirements. Crypto-agility is increasingly relevant as organizations face evolving cybersecurity risks and must prepare for advances in quantum computing that could compromise current encryption standards.
In a crypto-agile environment, systems are designed with modular cryptographic components that can be swapped out or upgraded without major architectural changes. This design allows for the swift implementation of new encryption algorithms or protocols when older ones become insecure or deprecated. Crypto-agility can help enterprises ensure long-term data protection and maintain compliance with shifting security frameworks.
Typically, crypto-agility is used when the encryption algorithm of a system is discovered to be vulnerable. Other use cases include when an algorithm breaks suddenly or when there's a security compromise. If one of these cases arises, an organization needs to be able to switch to using a different encryption method quickly to minimize damage. This process includes switching out cryptographic algorithms, security keys, certificates and other cryptographic technologies.
Organizations will use cryptography broadly in their environments, such as in Transport Layer Security and Secure Socket Shells. Typically, mission-critical communication systems will also make use of crypto-agility. Without crypto-agility, if an organization's cryptographic systems are compromised, they could be open to attack, leading to loss of business.
Why is crypto-agility important?
Crypto-agility is vital because cryptographic protocols that are currently secure are likely to become vulnerable in the future due to breakthroughs in cryptanalysis or the emergence of quantum computing. Without crypto-agility, organizations risk falling behind as encryption methods evolve, leaving sensitive data exposed and systems unprotected.
This is especially true in industries governed by strict regulatory requirements around cybersecurity and risk assessment. Organizations that fail to implement crypto-agile strategies might face challenges updating legacy systems, leading to inefficiencies or security gaps. Being crypto-agile can enable faster adaptation to threats and evolving regulatory standards, decreasing costly compliance risks. It also supports continuity in digital trust, even when widespread encryption protocols are required.
Benefits of crypto-agility
There are many benefits to crypto-agility. The most important include the following:
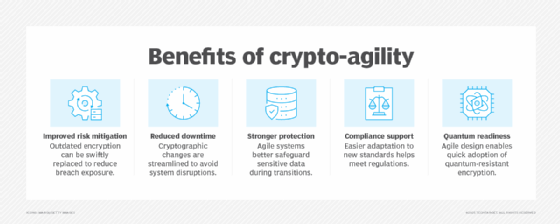
- Improved risk mitigation. Crypto-agility can ensure that outdated or broken encryption methods can be quickly replaced, minimizing exposure to security and data breaches.
- Reduced operational downtime. By streamlining cryptographic changes, organizations avoid lengthy system overhauls and business interruptions.
- Stronger data protection. Agile cryptographic systems provide enhanced safeguards for sensitive information, especially during transitional phases such as post-quantum migration.
- Regulatory compliance support. Crypto-agility simplifies compliance with government and industry frameworks by enabling proactive adaptation to new encryption requirements.
- Preparedness for quantum threats. Organizations can implement quantum-resistant algorithms efficiently when cryptographic agility is built into system design.
How to achieve crypto-agility
To set up and achieve crypto-agility, an organization must first assess existing cryptographic assets, protocols and dependencies across its infrastructure. This includes conducting a thorough inventory and identifying where cryptographic controls are in use, from data at rest to communications protocols.
Once visibility is established, organizations should develop a transition plan that outlines how to replace vulnerable algorithms with secure alternatives.
Implementing crypto-agility also requires establishing an architecture that separates cryptographic logic from application logic. This modular design enables cryptographic primitives to be updated without disrupting core systems. Automation and strong policy enforcement also support agility by standardizing implementation and reducing the margin of human error.
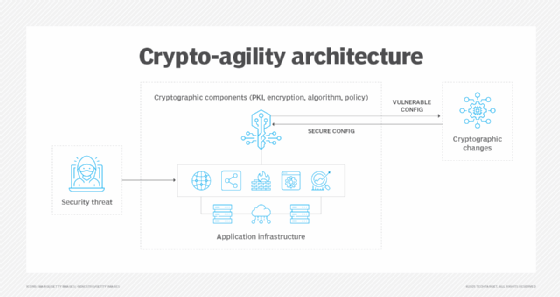
On the hardware side, crypto-agility is achieved by adopting new frameworks for incident response and application development. In addition, a layer of software is required for cryptographic application programming interfaces and secure update mechanisms.
Crypto-agility best practices
Best practices surrounding crypto-agility include the following:
- Implement automation tools. Automate key rotation, certificate renewal and cryptographic updates to minimize delays and errors.
- Establish governance and policy control. Set up clear governance structures and policies that define roles, responsibilities and oversight for crypto-agile operations.
- Deploy public key infrastructure (PKI). A well-managed PKI supports flexibility in certificate management and cryptographic algorithm updates.
- Use modular cryptographic libraries. Rely on pluggable cryptographic frameworks that enable quick substitution of algorithms.
- Enforce role-based access control. Limit who can modify cryptographic settings through access policies and segmented privileges.
- Maintain algorithm flexibility. Avoid hardcoding algorithms into systems to simplify updates and algorithm migration.
How to improve crypto-agility
To improve crypto-agility practices, organizations can do the following:
- Conduct regular risk assessments of cryptographic assets.
- Eliminate hardcoded cryptographic functions in software.
- Train IT and security teams on crypto-agility principles.
- Invest in tools that support agile key and certificate lifecycle management.
- Establish metrics and key performance indicators to track agility readiness.
Future of crypto-agility
The future of crypto-agility is closely tied to the growing urgency around quantum-safe encryption. As quantum computing becomes more viable, organizations will need to transition away from vulnerable encryption algorithms, such as Rivest-Shamir-Adleman and elliptical curve cryptography. Crypto-agility will serve as the foundational capability that enables this transition without disrupting operations.
Advancements in cryptographic design, standards development and automation tools will further embed crypto-agility into enterprise architecture. Organizations that prioritize agility will be best positioned to implement next-generation solutions.
Gartner warns that by 2029, traditional cryptography will be made obsolete by advancements in quantum computing, making crypto-agility adoption more critical.
Crypto-agility is an emerging security posture for modern enterprises. Learn why now is the right time to adopt crypto-agility.






