
What is reinforcement learning?
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a machine learning training method that trains software to make certain desired actions. Reinforcement learning is based on rewarding desired behaviors and punishing undesired ones.
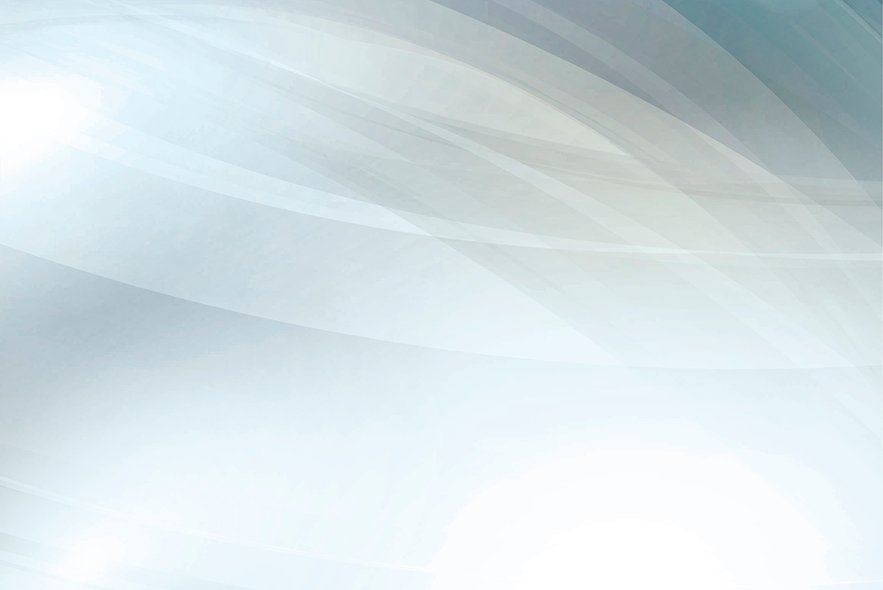
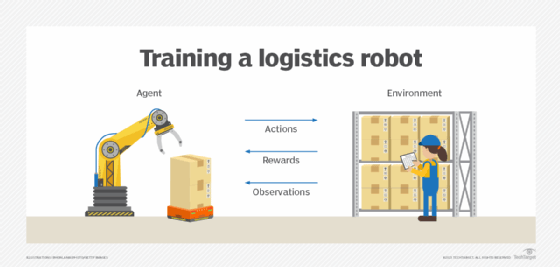
In general, a reinforcement learning agent -- the software entity being trained -- is able to perceive and interpret its environment, as well as take actions and learn through trial and error.
Reinforcement learning is one of several approaches developers use to train machine learning systems. This approach is important because it empowers an agent to learn to navigate the complexities of the environment for which it was created. For example, an agent can be taught to control a video game, or a robot in an industrial setting can be taught to perform a specific task. Over time, through a feedback system that typically includes rewards and punishments, the agent learns from its environment and optimizes its behaviors.
How does reinforcement learning work?
An action is the steps an RL agent takes to navigate its environment. For example, this could be selecting a tab to navigate to a webpage. In reinforcement learning, developers devise a method of rewarding desired actions and punishing negative behaviors. This method uses a reinforcement learning algorithm to assign positive values to the desired actions to encourage the agent to use them, while negative values are assigned to undesired behaviors to discourage them. This programs the agent to seek long-term and maximum overall rewards to achieve an optimal solution.
These long-term goals help prevent the agent from getting stuck on less important goals. Over time, the agent learns to avoid the negative and seek the positive.
The Markov decision process serves as the basis for reinforcement learning systems. In this process, an agent exists in a specific state inside an environment; it must select the best possible action from multiple potential actions it can perform in its current state. Certain actions offer rewards for motivation. When in its next state, new rewarding actions are available to it. Over time, and through a trial-and-error process, the agent begins making the optimal actions to maximize its cumulative reward, or the sum of rewards the agent receives from the actions it chooses to perform.
This learning method has been adopted in artificial intelligence (AI) as a way of directing unsupervised machine learning through rewards or positive reinforcement and penalties or negative reinforcement.
Types of reinforcement learning algorithms
There are a several different reinforcement learning algorithms available that are typically grouped into the following two categories:
- Model-based RL enables an agent to create an internal model of an environment. This lets the agent predict the reward of an action. The agent's algorithm is also based on maximizing award points. Model-based RL is ideal for static environments where the outcome of each action is well-defined.
- Model-free RL uses a trial-and-error approach in an environment. The agent performs different actions multiple times to learn the outcomes. As it performs these actions, it creates a strategy -- called a policy -- that optimizes its reward points. Model-free RL is ideal for unknown, changing, large or complex environments.
Applications and examples of reinforcement learning
While reinforcement learning has been a topic of interest in the field of AI, its widespread, real-world adoption and application remain limited. Noting this, however, research papers abound on theoretical applications, and there have been some successful use cases.
Current uses include, but aren't limited to, the following:
- Gaming.
- Resource management.
- Personalized recommendations.
- Robotics.
- Machine learning.
- Military use.
Gaming is likely the most common use for reinforcement learning, as it can achieve superhuman performance in numerous games. An example of this involves the game Pac-Man.
A learning algorithm playing Pac-Man might be able to move in one of four possible directions -- up, down, left and right -- barring obstruction. From pixel data, an agent might be given a numeric reward for the result of a unit of travel: 0 for empty spaces, 1 for pellets, 2 for fruit, 3 for power pellets, 4 for ghost post-power pellets, 5 for collecting all pellets to complete a level, and a 5-point deduction for collision with a ghost. The agent starts from randomized play and moves to more sophisticated play, learning the goal of getting all the pellets to complete the level. Given time, an agent might even learn tactics such as conserving power pellets until needed for self-defense.
Reinforcement learning can operate in a situation if a clear reward can be applied. In enterprise resource management, reinforcement algorithms allocate limited resources to different tasks as long as there's an overall goal it's trying to achieve. A goal in this circumstance would be to save time or conserve resources.
In robotics, reinforcement learning has found its way into limited tests. This type of machine learning can provide robots with the ability to learn tasks a human teacher can't demonstrate, to adapt a learned skill to a new task and to achieve optimization even when analytic formulation isn't available.
Reinforcement learning is also used in operations research, information theory, game theory, control theory, simulation-based optimization, multi-agent systems, swarm intelligence, statistics, genetic algorithms and ongoing industrial automation efforts.
The military uses reinforcement learning to prepare autonomous ground vehicles for real-life situations. It has also been used for digital war games that simulate combat scenarios.
Benefits of reinforcement learning
Advantages of using reinforcement learning include the following:
- Operates in complex environments. RL algorithms are usable in both static and dynamic environments.
- Doesn't require much attention. RL algorithms can learn without human supervision.
- Is optimized for long-term goals. RL algorithms are focused on optimizing processes to gain maximum cumulative rewards.
Challenges of applying reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning, while high in potential, comes with the following tradeoffs:
- Limited applicability. It can be difficult to deploy and remains limited in its application. One of the barriers for deployment of this type of machine learning is its reliance on exploration of the environment. For example, if a robot that was reliant on reinforcement learning was deployed to navigate a complex physical environment, it would seek new states and take different actions as it moves. With this type of reinforcement learning problem, however, it's difficult to consistently take the best actions in a real-world environment because of how frequently the environment changes.
- Time-intensive. The time required to ensure the learning is done properly through this method can limit its usefulness and be intensive on computing resources. As the training environment grows more complex, so do the demands on time and compute resources.
- Hard to interpret. Complex RL algorithms will have a reason behind why they make a specific set of actions, but it might become difficult for human observers to determine the logic behind them.
- Resource-intensive. Reinforcement learning requires a lot of data and computation. Supervised learning, by comparison, can deliver faster, more efficient results to companies if the proper amount of data is available. Supervised learning can be employed with fewer resources.
Common reinforcement learning algorithms
Rather than referring to a specific algorithm, the field of reinforcement learning is made up of several algorithms that take somewhat different approaches. The differences are mainly due to the different strategies they use to explore their environments:
- State-action-reward-state-action. This reinforcement learning algorithm starts by giving the agent what's known as a policy. Determining the optimal policy-based approach requires looking at the probability of certain actions resulting in rewards, or beneficial states, to guide its decision-making.
- Q-learning. This approach to reinforcement learning takes the opposite approach. The agent receives no policy and learns about an action's value based on exploration of its environment. This approach isn't model-based but instead is more self-directed. Real-world implementations of Q-learning are often written using Python programming.
- Deep Q-networks. Combined with deep Q-learning, these algorithms use neural networks in addition to reinforcement learning techniques. They're also referred to as deep reinforcement learning and use reinforcement learning's self-directed environment exploration approach. As part of the learning process, these networks base future actions on a random sample of past beneficial actions.
- Monte Carlo tree search. This model-based reinforcement learning approach uses simulations to build a search tree, and it bases its decisions on the outcomes. The method benefits from combining the generality provided by the simulation with the precision provided by the tree search.
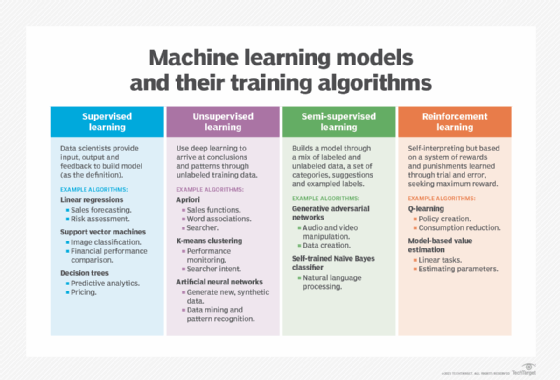
Comparing reinforced, supervised and unsupervised machine learning
Reinforcement learning is considered its own branch of machine learning. However, it does have some similarities to other types of machine learning, which break down into the following four domains:
- Supervised learning. Algorithms train on a body of labeled data. Supervised learning algorithms can only learn attributes that are specified in the data set. A common application of supervised learning is image recognition models. These models receive a set of labeled images and learn to distinguish common attributes of predefined forms.
- Unsupervised learning. In unsupervised learning, developers turn algorithms loose on fully unlabeled data. The algorithms learn by cataloging their own observations about data features without being told what to look for.
- Semi-supervised learning. This method takes a middle-ground approach. Developers enter a relatively small set of labeled training data as well as a larger corpus of unlabeled data. The semi-supervised learning algorithm is then instructed to extrapolate what it learns from the labeled data to the unlabeled data and draw conclusions from the set as a whole.
- Reinforcement learning. This takes a different approach. It situates an agent in an environment with clear parameters defining beneficial activity and nonbeneficial activity and an overarching endgame to reach.
Reinforcement learning is like supervised learning in that developers must give algorithms specified goals and define reward functions and punishment functions. This means the level of explicit programming required is greater than in unsupervised learning. But, once these parameters are set, the algorithm operates on its own -- making it more self-directed than supervised learning algorithms. For this reason, people sometimes refer to reinforcement learning as a branch of semi-supervised learning; in truth, though, it's most often acknowledged as its own type of machine learning.
A defining difference between the two is that unsupervised learning doesn't have a specified output, while reinforcement learning has a predetermined end goal of optimizing a system or completing a video game, for example.
The future of reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning is projected to play a bigger role in the future of AI. Other approaches to training machine learning algorithms require large amounts of preexisting training data. Reinforcement learning agents, on the other hand, require time to gradually learn how to operate via interactions with their environments. Despite the challenges, various industries are expected to continue exploring reinforcement learning's potential.
Reinforcement learning has already demonstrated promise in various areas. For example, marketing and advertising firms are using algorithms trained this way for recommendation engines. Manufacturers are using reinforcement learning to train their next-generation robotic systems.
Reinforcement learning also continues to improve in terms of efficiency. Transfer learning techniques integrated into the process improve efficiency by enabling agents to use past-learned skills on different problems. This decreases the time it takes to train a system.
Likewise, deep learning reinforcement learning continues to improve, with these systems becoming more independent and flexible.
Technologies such as reinforcement learning are emerging as a way to enhance AI-based digital customer experiences. Other technologies in this area include AI simulation, generative AI and federated machine learning.
Machine learning algorithms use one or more training approaches, including reinforcement learning. Read about different types of machine learning algorithms.






