How to create a data security policy, with template
When it comes to data security, the devil is in the details. One critical detail organizations shouldn't overlook is a succinct yet detailed data security policy.
Data security policies are often confused with information security policies. The latter typically focus on all aspects of information security, including equipment, applications, employees, vendors, and other internal and external resources, in addition to data. By contrast, data security policies focus specifically on protecting data, databases and related data content.
General security policies also often encompass data security. Still, many organizations need a separate data security policy that outlines specific data security processes, such as data inventorying and data classification, as well as data security measures and controls, including encryption, backups and access control.
Creating and implementing an enterprise data security policy are critical, as is updating it regularly and when needed. Also key is knowing which elements to include in such a policy.
What is a data security policy?
A data security policy is a formal document that outlines how an organization secures its data. It provides guidelines about the secure use, management and monitoring of data within an organization.
This article is part of
What is data security? The ultimate guide
The ultimate goal of a data security policy is to protect sensitive data by ensuring authorized access, transmission and storage of data, while also meeting compliance requirements with government and industry regulations.
Why are data security policies important?
Data security policies are important for the following reasons:
- They specify how an organization intends to manage the security of its data and information.
- They formally document all data security controls and procedures.
- They help prevent unauthorized access to an organization's data.
- They help security teams identify and remediate vulnerabilities, misconfigurations and other security issues.
- They describe employees' responsibilities for accessing and protecting company data.
- They help demonstrate compliance with local and global data privacy and security standards and regulations, such as ISO 27001, ISO 27002, NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-53, PCI DSS, GDPR and Federal Information Security Modernization Act.
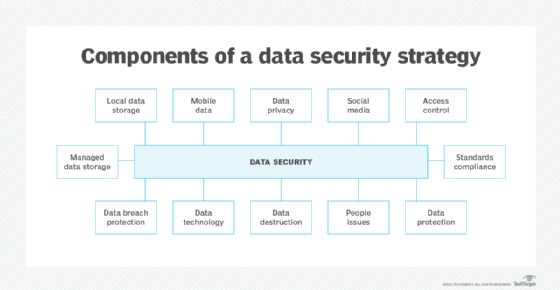
Key elements of a data security policy
While data security policies might vary from company to company, they generally include the following elements:
- Purpose. Introduces the policy, why it exists and what it aims to achieve.
- Scope. Provides information on the data, people and systems the policies apply to.
- Roles and responsibilities. Lists who manages, upgrades and maintains data, as well as the elements and components of the policy, and their responsibilities.
- Objectives. Explains why this policy is needed.
- Strategy and focus. Lays out the primary strategy to achieve the objectives, as well as any IT security frameworks and standards the policy aligns to, such as the ISO 27000 series, NIST SP 800 series, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Center for Internet Security Controls, etc.
- Policy. Outlines the policy and any related processes, as well as how policy violations and updates will be addressed. Includes tools and technologies used to ensure data security.
- Additional and related policies. Lists other policies adjacent to the data security policy, as well as how they might apply. This could include the following:
- A data classification policy that defines categories and criteria for classifying data.
- A data retention policy that outlines how long to keep data and how to dispose of it.
- An email security policy that has guidelines for protecting email communications.
- An incident response plan with instructions on how to respond to and limit the effects of security incidents.
- A data backup policy that defines steps for backing up and storing data.
- A password policy that outlines rules for creating and using passwords.
- A remote access policy with guidelines for securely accessing data and systems from remote locations.
- An acceptable use policy with rules on how an organization's systems, data and services can be used. Also, consider an AI acceptable use policy to govern AI and generative AI use in the organization.
- Enforcement. Lists who enforces the policy, as well as policy violation penalties.
- Management and audit review. Details the schedule and cadence of policy updates and reviews.
- Version history. Lists updates made, including by whom, when and what changed.
Data security policy template
Click here to access our editable data security policy template. Use it as a starting point for content and structure.
How to create a data security policy
Organizations with formal cybersecurity or information security policies typically already have the main elements needed for a data security policy.
Best practices for creating a data security policy include the following:
- Create a team. Develop the policy with a team of individuals who can address operational, legal, compliance, and other processes and controls associated with data security.
- Determine policy ownership. Establish who owns the policy, who reviews and updates it, and who is responsible for auditing the policy.
- Conduct a data inventory. Catalog all the data in the organization, including who owns, manages and maintains the data, as well as where it is located and who can read, edit and delete it. Speak with internal departments and data owners about access controls and other requirements.
- Classify data and determine security requirements. Organize data into categories and classifications -- for example, public, confidential, sensitive, personal, etc. Perform a risk assessment to identify threats that categories of data face and to prioritize security measures.
- Identify controls, processes and technologies for protecting data. Establish procedures and the tools needed to protect sensitive information from data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other malware and cyberattacks, as well as data loss and errant use. Consider the following categories:
- Access controls. Define authentication and authorization guidelines, including who has access to what data and how that access is provided. Use the principle of least privilege, role-based access control, password security and MFA.
- Encryption. Set protections for data in use, in motion and at rest. Consider encryption algorithms, key management and certificate management.
- Network security. Outline network security controls to protect infrastructure and access. This could include firewalls; event logging; extended detection and response; security orchestration, automation and response; patch management; and VPNs.
- Endpoint security. Define processes to protect endpoints, including desktops, laptops, mobile devices, IoT devices, printers and point-of-sale systems. Use endpoint detection and response (EDR), encryption, antivirus and antimalware, and logging.
- Mobile security. Similar to endpoint security, define processes to protect mobile devices, such as tablets and smartphones. Consider encryption, application security, EDR, mobile backups, and network and wireless access.
- Data storage. Securely and properly store data. Consider data retention policies, backups, encryption, and data destruction and deletion.
- Backups and recovery. Define methods for backing up data, as well as recovery processes in the event of a breach, data loss or system failure.
- Logging and monitoring. Conduct security log management to gain visibility into activity such as data accessed, changes in user privileges and data downloads.
- Incident response. Cover when and how to deploy an incident response plan for data loss or damage.
- Physical controls. Consider physical access controls, secure workstations, and physical data storage and disposal.
- User responsibilities. Outline specific end-user requirements, such as instructing employees to lock their screens, defining which data can and cannot be shared, keeping passwords secure and other cyber hygiene best practices.
- Prepare and circulate a draft of the policy. Write the policy in language employees, management and other stakeholders without security expertise will understand. Ask senior management, legal, compliance, risk management, IT, HR and other relevant departments to review the policy.
- Document noncompliance penalties. List noncompliance penalties for employees, visitors, contractors and others governed by the policy.
- Create a review cycle. Determine a review schedule to ensure the policy, over time, accurately reflects the organization's current data and security posture, as well as the current threat landscape. Establish procedures to test and validate that data security protocols and controls perform properly.
- Announce the policy.
- Train users. Conduct security awareness training to ensure employees understand the policy and their responsibilities. Coordinate with HR to ensure uniform compliance.
- Integrate the data security policy with other data protection activities.
- Regularly review and update the policy.
- Periodically audit the policy.
Using AI for data security
Many of today's data security tools contain AI features to improve the data infrastructure's overall security posture.
AI can analyze incoming data traffic, as well as outgoing traffic, and identify and flag code violations and the presence of malware. It can also automate various daily operational activities, such as analysis and remediation of suspicious or abnormal activity, while supporting the company's security operations center. Even more important is AI's ability to perform threat hunting and find suspicious activities before they become disruptive.
Paul Kirvan, FBCI, CISA, is an independent consultant and technical writer with more than 35 years of experience in business continuity, disaster recovery, resilience, cybersecurity, GRC, telecom and technical writing.







