What is Six Sigma and how does it work?
Six Sigma is a business methodology for quality improvement that measures how many defects there are in a current process and seeks to systematically eliminate them.
In 1984, a Motorola engineer named Bill Smith developed the Six Sigma management system to reduce the variations in Motorola's electronic manufacturing processes that were causing product defects.
Since then, the strategies, tools and cultural norms that support the management system have been adopted by upper management and project teams in a wide variety of industries to increase operational excellence. Additionally, the meaning of the word defect has broadened to include any deficiency in business processes that prevents a company from meeting its customers' needs.
Six Sigma's methodologies have become a cornerstone in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare and IT, helping organizations achieve consistency, efficiency and customer satisfaction.
How does Six Sigma work?
In statistical analysis, the Greek letter sigma (Σ) is used to denote a standard deviation from the mean. In the 1920s, statistical process control pioneer Walter Shewhart proposed that in lean manufacturing, three sigma from the mean is the tipping point that indicates there are too many defects and that process improvement is required.
This was the accepted norm for many years until Smith proposed gathering and analyzing data at a more granular level and making six sigma the point at which a process has to be corrected.
Because it is almost impossible to achieve zero defects -- a concept known as infinity sigma -- six sigma allows for 3.4 defects per million opportunities for a defect to occur. In contrast, three sigma allows for 66,807 defects per million opportunities.
Once the necessary data has been gathered, a company that is implementing Six Sigma methodologies uses statistics to create a baseline sigma. The baseline illustrates how close -- or how far -- the company is from achieving Six Sigma and serves as a measuring stick for assessing future improvement.
Advanced Six Sigma tools, such as statistical software and AI-driven analytics, now enable organizations to streamline data collection and analysis, further enhancing accuracy and decision-making.
What is the importance of Six Sigma?
Six Sigma proponents claim that its business strategy benefits include up to 50% process cost reduction, cycle time improvement, less waste of materials, a better understanding of customer requirements, increased customer satisfaction and value stream, and more reliable products and services.
Motorola holds the federal trademark for Six Sigma, and it is generally acknowledged that Six Sigma can be costly to implement and can take several years before a company begins to see bottom-line results.
In 1995, General Electric CEO Jack Welch's public endorsement of Six Sigma helped businesses outside of manufacturing understand how Six Sigma methodologies can be used to improve customer satisfaction in any industry.
More recently, organizations have adopted Six Sigma alongside digital transformation initiatives to optimize processes, increase agility and adapt to changing market demands.
What are the key principles of Six Sigma?
The key principles are the following:
- Customer focus. Ensuring processes align with customer expectations.
- Use data. Employing statistical analysis for decision-making.
- Improve continuously. Encouraging a culture of ongoing refinement.
- Involve people. Engaging teams at all levels.
- Be thorough. Implementing detailed process analysis.
These principles form the foundation of Six Sigma's methodologies and ensure consistent, measurable outcomes.
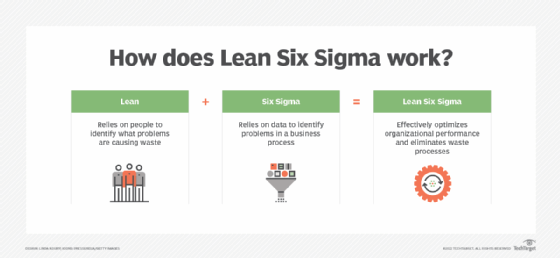
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma combines Six Sigma's focus on reducing defects with the Lean project management methodology's emphasis on eliminating waste. Together, they help organizations do the following:
- Streamline workflows by removing inefficiencies.
- Reduce costs through better resource utilization.
- Improve product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Adapt processes quickly to meet evolving demands.
This hybrid approach is particularly effective in industries such as healthcare, logistics and manufacturing.
Six Sigma methodologies
The above principles can be applied with one of two improvement methodologies: Six Sigma DMAIC and Six Sigma DMADV. Each name is derived from the major steps in its process, but each has its own use.
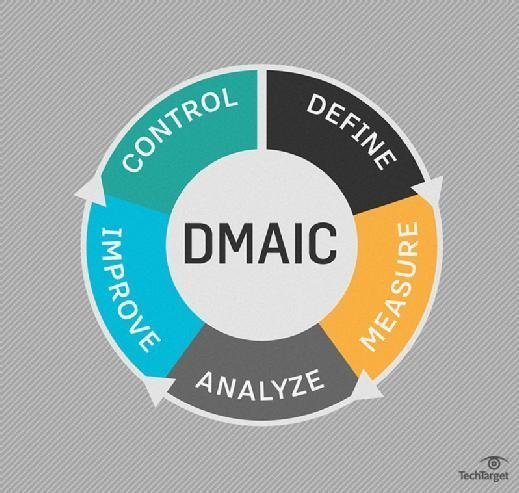
- DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) is used to correct a process that already exists.
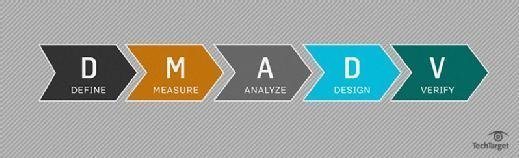
- DMADV (define, measure, analyze, design, validate) is used to create a new process.
DMAIC
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of Six Sigma DMAIC:
- Define. Identify the project goals and all customer deliverables.
- Measure. Understand current performance.
- Analyze. Determine root causes of any defects.
- Improve. Establish ways to eliminate defects and correct the process.
- Control. Manage future process performance.
DMADV
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of Six Sigma DMADV:
- Define. Identify the project scope and all customer deliverables.
- Measure. Understand current performance.
- Analyze. Determine root causes of any defects.
- Design. Create a process that meets customer needs and expectations.
- Verify. Ensure processes perform adequately and are designed to meet customer needs.
The first three steps of this methodology are identical to DMAIC. Because the two acronyms are so similar, some companies use the acronym DFSS (design for Six Sigma) in place of DMADV.
When contemplating Six Sigma DMAIC versus DMADV, it is important to understand the circumstances in which each should be used. The DMAIC methodology should be used when an existing product or service is not meeting customer needs or performing to its highest standards. The DMADV methodology should be used when an organization is developing a new product or service, or when using DMAIC for a current project or process has failed.
Six Sigma certification and resources
All Six Sigma processes are executed by the following, per the terms created by Motorola:
- Six Sigma White Belts are entry-level participants focused on basic principles.
- Six Sigma Yellow Belts are team members who understand specific projects.
- Six Sigma Green Belts are midlevel practitioners who lead projects under supervision.
- Six Sigma Black Belts are leaders of complex projects with extensive expertise.
- Six Sigma Master Black Belts are overseers of multiple projects and strategy alignment.
The International Association for Six Sigma Certification (IASSC) and other organizations provide certifications to validate expertise in Six Sigma methodologies.

At IASSC, Yellow, Green and Black Belt exams are designed to measure a person's knowledge of topics contained within IASSC's Lean Six Sigma Body of Knowledge.
Another Six Sigma training organization offering certification is 6Sigma.us.
How to implement Six Sigma
To implement Six Sigma within an organization, the first step is to properly make the case for statistical tools like Six Sigma and its potential benefits to get stakeholder buy-in. Additionally, it's important to set the expectation that being entirely defect-free is not realistic. However, there are some best practices that can help to ensure as much improvement as possible.
Once management understands the potential behind the methodology, the following eight steps can help to implement a Six Sigma project and ensure a clean rollout:
- Step 1. Motivate stakeholders by highlighting quality losses.
- Step 2. Implement project management and obtain the necessary resources.
- Step 3. Educate team members on the Six Sigma management method.
- Step 4. Create a quality control chart and identify priorities.
- Step 5. Assign ownership for all team members involved.
- Step 6. Ensure measurement of the right metrics and indicators.
- Step 7. Perform a root cause analysis to understand the defect.
- Step 8. Govern the program to ensure proper implementation and continuous improvement.
Please note that these steps can vary depending on whether you are using Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma.
Real-world applications of Six Sigma
Six Sigma is widely used in various industries to solve unique challenges, such as the following:
- Healthcare. Reducing patient wait times and improving care delivery.
- Manufacturing. Enhancing product quality and reducing defects.
- Retail. Optimizing inventory management and streamlining supply chains.
- IT and software development. Identifying and resolving system inefficiencies.
By tailoring Six Sigma tools to their specific needs, organizations can achieve significant improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What is the difference between Six Sigma vs. Lean Six Sigma?
The purposes of Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma are different. The Six Sigma method is focused on limiting fluctuation within business processes and quality management of process output by implementing problem-solving statistical methods.
Conversely, the primary focus of Lean Six Sigma is to eliminate waste and improve existing processes.
Learn about the Five Whys, which is used in the Analyze phase of the Six Sigma DMAIC methodology; SIPOC, which is often used during the Define phase; and fishbone diagrams, which are one of the basic quality tools used in the Analyze phase. Also, check out top digital transformation trends.






