What is PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act)?
PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act, sometimes seen as Plan, Do, Check, Adjust) is a repetitive four-stage model for continuous improvement in business process management. The PDCA model is also known as the Deming circle, cycle or wheel; Shewhart cycle; control circle or cycle; or PDSA (Plan, Do, Study, Act).
This iterative model is foundational to quality management and widely used across various industries to improve processes systematically. Specifically, organizations implement the model to improve the quality and effectiveness of processes within product lifecycle management, project management, human resource management, supply chain management and many other areas of business.
By using PDCA, organizations can identify inefficiencies, test potential improvements and implement changes in a controlled manner, thus aligning closely with Lean manufacturing principles.
Who created PDCA?
PDCA was popularized by W. Edwards Deming, an American engineer, statistician and management consultant. Deming is often considered the father of modern quality control. His work laid the groundwork for the Total Quality Management (TQM) and ISO 9001 quality standards, both of which emphasize the importance of continuous improvement.
However, though Deming popularized PDCA, he credited Walter A. Shewhart, an American physicist, engineer and statistician, as the original creator of the cycle. Shewhart's contributions to statistical quality control are considered foundational in the field of process improvement.
TQM processes often integrate the PDCA model to ensure improvements are systematically implemented and sustained. This approach divides improvement efforts into four sequential categories: Plan, Do, Check and Act.
The PDCA cycle
Here's an example of how PDCA is broken down in TQM:
- Plan. Define the problem to be addressed, collect relevant data and ascertain the problem's root cause. This stage involves thorough planning to ensure all potential factors are considered before moving forward.
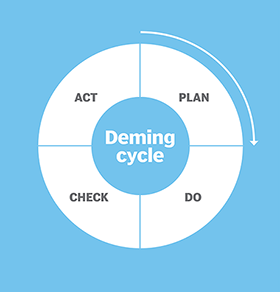
- Do. Develop and implement a solution, then decide on a measurement to gauge its effectiveness. During this stage, the planned solution is executed, and data is collected to assess its impact.
- Check. Confirm the results through before-and-after data comparison. This step involves analyzing the data collected during the Do phase to determine if the solution has successfully addressed the problem.
- Act. Document the results, inform others about process changes and make recommendations for the problem to be addressed in the next PDCA cycle. If the solution is successful, it becomes the new standard; if not, the cycle begins again with new insights.
The PDCA model is particularly valuable because it fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling organizations to adapt to changes and continuously refine their processes.
PDCA's connection to Lean manufacturing and quality management
The PDCA cycle is deeply integrated into Lean manufacturing and quality management practices. In these environments, PDCA is used to reduce waste, enhance process efficiency and continually improve product quality. Lean methodologies rely on PDCA as a foundational tool to achieve operational excellence by fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Emphasis on data-driven decision-making
PDCA is a data-driven methodology that emphasizes the collection and analysis of data at each stage of the cycle.
During the Plan phase, data helps identify root causes and set objectives. In the Check phase, data analysis is critical for verifying the effectiveness of the implemented solutions.
This approach ensures decisions are based on evidence, leading to more reliable and effective improvements.
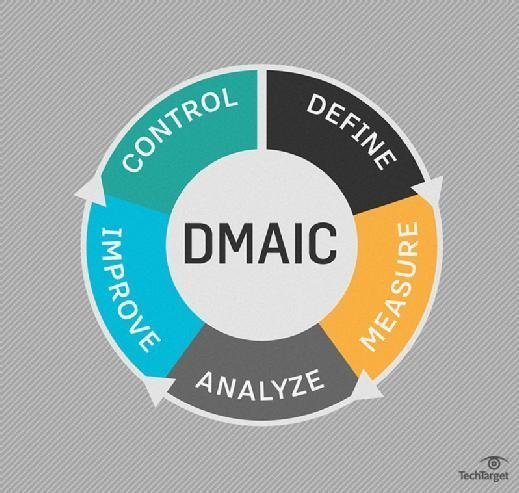
Comparing PDCA with DMAIC
PDCA and DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) are both continuous improvement tools, but they serve different purposes.
PDCA is generally used for simpler, ongoing process improvements, while DMAIC -- part of the Six Sigma methodology -- is applied to more complex, data-intensive problems. While PDCA emphasizes iterative improvements, DMAIC focuses on in-depth problem-solving with advanced statistical analysis.
Reducing complication when implementing PDCA
For successful PDCA implementation, it's essential to encourage teamwork during the planning phase and use tools like fishbone diagrams for root cause analysis. Clear communication and thorough documentation are crucial in the Act phase to ensure successful strategies are shared and standardized across the organization.
Get to know the Kaizen approach to continuous improvement, which emphasizes how small, ongoing positive changes can realize substantial benefits. Also, a business process management approach to transformation enables companies to continuously improve and reinvent their business processes, injecting innovation as they go. Check out business process management best practices to ensure success.
