5 Whys (Five Whys)
Five Whys, sometimes written as "5 Whys," is a guided team exercise for identifying the root cause of a problem. Five Whys is used in the "analyze" phase of the Six Sigma DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) methodology.
The exercise begins with a facilitator stating a problem and then asking the question "Why?" (meaning "Why did the problem occur?"). The group brainstorms answers based on direct observation. Once the group agrees upon an answer, the facilitator again asks the question, "Why?"
The purpose of this exercise is root cause analysis, frequently included as part of a risk management plan for repeat problem prevention. By brainstorming repeated answers to the same question, teams are forced to problem solve and arrive at several distinct possibilities. This exercise got its name because it generally takes five iterations of the questioning process for the group to arrive at the root cause of a problem -- but it is perfectly correct for the facilitator to ask less than five "whys" or more than five "whys" depending on the group's needs.
Example of the Five Whys exercise
Here is an example of how a Five Whys exercise might proceed:
Facilitator: Our websites were down from 2 p.m. to 2:45 p.m. on Saturday. Why?
Group: Because the external DNS server failed.
Facilitator: Why did the external DNS server fail?
Group: Because the central process unit (CPU) was peaked at 100% and couldn't handle outside requests.
Facilitator: Why did the CPU peak at 100%?
Group: Because the server kept trying to autoupdate Windows.
Facilitator: Why did the server keep trying to autoupdate Windows?
Group: Because when the administrator created the server, he forgot to uncheck the autoupdate service.
Facilitator: Why did the administrator forget to uncheck the autoupdate service when he created the server?
Group: Because he was in a hurry and got distracted by an alarm going off.
Once the team has agreed that they have identified the root cause of the problem -- in this case, the administrator getting distracted and forgetting to turn off autoupdate -- the facilitator should help the group to determine appropriate corrective action.
Facilitator: How can we make sure that each administrator unchecks autoupdate when he creates a new server, no matter how hurried or distracted he gets?
Group: Create a Vanilla server image with autoupdate turned off. Have administrators clone this image when deploying new servers.
Criticisms of the 5 Whys
Though the Five Whys can be useful for basic brainstorming, this exercise is not a comprehensive analysis tool. Teruyuki Minoura -- a former director of global purchasing of Toyota -- is a critic of this technique's efficacy. According to Minoura, the Five Whys do not ensure that the root cause analysis will be successful.
One downside of the Five Whys exercise is that brainstormers tend to mistake symptoms of the root cause for the actual root cause. When this happens, participants tend to stop investigating, thinking they found the problem -- when they should be tracing the symptoms back to lower-level root causes.
As the Five Whys relies on group brainstorming, it is limited to what is already known by participants. Therefore, if the root cause of a problem is unknown to any participants in the exercise, it will be impossible for them to find it.
Furthermore, the process does not include any support to guide participants toward the correct answer. This leads to inconsistent results, as different groups may brainstorm five different reasons than what another group might brainstorm.
How to use the 5 Whys
To use the Five Whys for root cause analysis, it is important to take certain steps:
- Assemble a cross-functional, multidisciplinary brainstorming team. When finding members to participate, organizers should try to include individuals from different positions, departments and seniority levels. A team leader or other facilitator should be brought in.
- Define the problem. A clear problem statement should be proposed and communicated to the team participating in the root cause analysis. Problem statements should be as concise and focused as possible; a broad, unfocused problem statement can be time consuming and unproductive.
- Keep discussion focused. During the actual brainstorming process, the session's facilitator or group leader should keep the discussion focused, asking questions to encourage new ideas. Ideas and points brought up while answering each "Why" should be based on objective facts or data, through a scientific approach. The session does not have to stop after the fifth "Why" -- it should be answered as many times as needed to create a productive result.
Other considerations for conducting a root cause analysis with the Five Whys technique include the following:
- Distinguish root causes from their symptoms.
- Assess the process, rather than the people; human error should not be labeled the problem.
- Encourage focused and precise answers.
- Use whiteboards, papers or other tools that might help participants visualize each point.
- Analyze causes and effects step by step, instead of jumping to premature conclusions.
- Work to create a space where participants can be sincere and feel trusted.
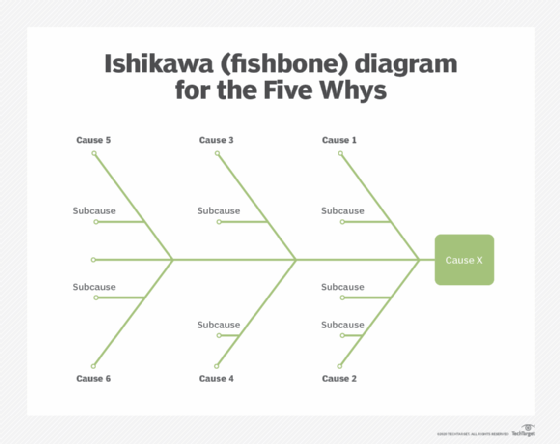
When answering each "Why," it is recommended to use a diagram to help the team keep track of relationships between different proposed symptoms, causes and root causes. This is particularly useful for complex problems. Popular diagram types for this exercise are Ishikawa diagrams and tree diagrams. Ishikawa diagrams, also called fishbone diagrams, map out branches of possible causes and sub-causes that intersect as one common problem, to be addressed in the root cause analysis. Tree diagrams show how one common problem branches out to multiple causes -- with each cause branching to their own potential root causes, and possible solutions.
