What is data?
In computing, data is information translated into a form that is efficient for movement or processing. Relative to today's computers and transmission media, data is information converted into binary digital form. It is acceptable to use data as a singular subject or a plural subject. Raw data is a term that describes data in its most basic digital format.
The concept of data in the context of computing has its roots in the work of Claude Shannon, an American mathematician known as the father of information theory. He ushered in binary digital concepts based on applying two-value Boolean logic to electronic circuits. Binary digit formats underlie the CPUs, semiconductor memories and disk drives, as well as many of the peripheral devices common in computing today. Early computer input for control and data took the form of punch cards, followed by magnetic tape and the hard disk.
Early on, data's importance in business computing became apparent by the popularity of the terms data processing and electronic data processing, which, for a time, encompassed the full gamut of what is now known as information technology. Over the history of corporate computing, specialization occurred, and a distinct data profession emerged along with growth of corporate data processing.
How to store data
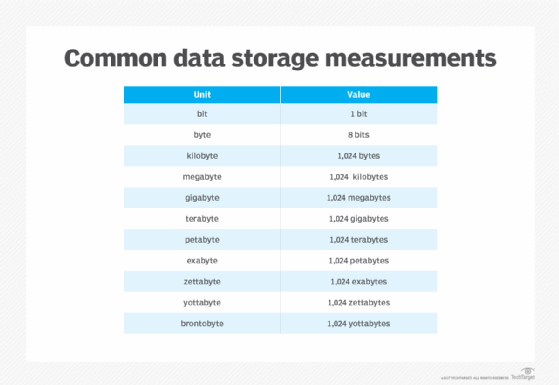
Computers represent data, including video, images, sounds and text, as binary values using patterns of two numbers: 1 and 0. A bit is the smallest unit of data and represents a single value. A byte is eight binary digits long. Storage and memory are measured in megabytes and gigabytes.
The units of data measurement increase as the amount of data collected and stored grows. For example, the term brontobyte is data storage that is equal to 10 to the 27th power of bytes.
File formats also store data, such as mainframe systems using ISAM and VSAM. Other file formats for data storage, conversion and processing include comma-separated values. These formats continued to find uses across a variety of machine types, even as more structured data-oriented approaches gained footing in corporate computing.
Greater specialization developed as database, database management system and then relational database technology arose to organize information.
Types of data
Growth of the web and smartphones over the past two decades led to a surge in digital data creation. Data now includes large amounts of unstructured data including text, audio and video information, as well as log and web activity records. Generative AI can generate synthetic data. Artificial data sets help train AI and machine learning models, software testing and predictive modeling.
The term big data describes data in the petabyte range or larger. A shorthand take depicts big data with 5Vs – value, volume, variety, veracity and velocity. As web-based e-commerce spread, big data-driven business models evolved to treat data as an asset. Such trends spawned greater preoccupation with the social uses of data and data privacy.
Data has meaning beyond its use in computing applications oriented toward data processing. For example, in electronic component interconnection and network communication, the term data is often distinguished from control information, control bits and similar terms to identify the main content of a transmission unit. In science, the term data describes a gathered body of facts. That is also the case in fields such as finance, marketing, demographics and health.
Data management and use
The proliferation of data in organizations places more emphasis on ensuring data quality by reducing duplication and guaranteeing the use of the most accurate, current records. The many steps involved with modern data management include data cleansing, and extract, transform and load processes for integrating data. Metadata complements data for processing. Metadata is sometimes referred to as "data about data." It helps administrators and users understand database and other data.
Analytics advancements can combine structured and unstructured data. They increasingly strive for real-time performance, can handle incoming data consumed at high ingestion rates and process data streams for immediate use in operations.
The idea of the database for operations and transactions extends to the database for reporting and predictive data analytics. An example is the data warehouse, which is optimized to process questions about operations for business analysts and business leaders. The increasing emphasis on finding patterns and predicting business outcomes led to the development of data mining techniques.
Data professionals
The database administrator profession is an offshoot of IT. As experts on databases, administrators design, tune and maintain the database.
The data profession took firm root as the relational database management system (RDBMS) gained wide use in corporations, beginning in the 1980s. The relational database's rise was enabled in part by the Structured Query Language (SQL). Later, non-SQL databases, known as NoSQL databases, arose as an alternative to established RDBMSes.
Companies employ data management professionals or assign workers the role of data stewardship, which involves carrying out data usage and security policies as outlined in data governance initiatives.
A distinct title -- the data scientist -- describes professionals who focus on data mining and analysis. The benefit of presenting data science in an evocative manner has even given rise to the data artist, an individual adept at graphing and visualizing data in creative ways.
Data engineers collect and prepare the data for data scientists and analysts. Engineers must know how to work with structured and unstructured data from different sources to assemble a quality data set for use. Data architects craft the framework for data management operations. They define policies, procedures and models for how to collect, organize, store and access data.







