What is machine code (machine language)?
Machine code, also known as machine language or native code, is the elemental language of computers. It is read by the computer's central processing unit (CPU), is composed of digital binary numbers and looks like a very long sequence of zeros and ones. Binary code is the only language that computer hardware can understand.
Each CPU is associated with a specific instruction set architecture (ISA) that defines the set of operations the CPU can understand and perform. The ISA is built into the processor's microarchitecture, acting as an interface between the hardware and software. The ISA specifies which instructions can be submitted to the CPU and how those instructions must be formatted.
The processor reads the instructions and performs the tasks that they define. Each instruction is made up of a specific number of bits and includes one opcode and one or more operands. The opcode tells the computer what to do, and the operands tell the computer what data to use.
Depending upon the processor, the ISA might require that all instructions be the same length, or it might permit instructions of varying lengths. The processor's architecture determines the instruction's length and how each one is patterned. Instruction execution is controlled by firmware or the CPU's internal wiring.
An example using the MIPS instruction set
An ISA that has been widely implemented is Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined Stages (MIPS), which is based on the reduced instruction set computer (RISC) architecture. All MIPS instructions are 32 bits long, with the operand specified in the first six bits. MIPS supports three types of instructions:
- Register (R-type or R format). All operand data values within the instruction are in registers.
- Immediate (I-type or I format). One operand data value is specified within the instruction, and the other specified data values, either one or two, are in registers.
- Jump (J-type or J format). The instruction is used to jump to the location specified within the instruction.
Each instruction type is formatted a little differently from the other because they contain a different number of elements, although they all still have a 32-bit length. For example, an R-type instruction includes six elements, the most of any of the three, as shown in the following syntax:
op rs rt rd shamt func
Each syntax element occupies a specific number of bits within the entire 32-bit instruction. The syntax elements must also be provided in the specified order. The following table describes each element and lists its number of bits.

Suppose an R-type instruction is used to add two values together. The first value is in register 17, and the second one is in register 18. The sum of the two values will be stored in register 16. The R-type opcode is 0, as noted above, and the R-type addition function is 32, as defined by MIPS. The following table shows the value for each element within the instruction. The first row (after the header) is in plain text, and the second row provides the binary equivalent for each value.

When the binary values in the bottom row are concatenated, they produce the entire 32-bit instruction that is submitted to the CPU.
The following binary value shows the instruction in its entirety, divided into four octets:
00000010 00110010 10000000 00100000
Each MIPS instruction must be submitted to the CPU in the proper 32-bit format. The operand indicates the operation and type of instruction. If the operand is 000000, it is an R-type, in which case, the instruction's purpose is indicated by the final six bits (func).
Moving from source code to machine code
Most software is developed in a human-readable programming language, such as C++, C#, Java, PHP, Python or Swift, which are all considered high-level languages. The source code is saved as text files that are ultimately translated to machine code by a compiler, assembler or interpreter. The exact approach depends on the programming language and the target platform.
One common approach is to use a compiler to translate the source code into assembly code. The assembly code is then submitted to an assembler, which generates the machine code. Next, the machine code is fed to a linker. The linker combines the machine code files into an executable package that can be fed to a processor. The following figure illustrates this process.
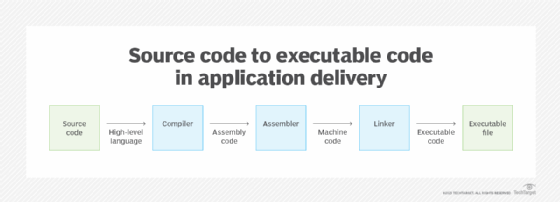
Languages such as Java and C# take a different approach to moving from source code to machine code. The code still runs through a compiler, but the compiler does not generate assembly code. Rather, it produces bytecode or another type of intermediary language. The intermediary code is then submitted to an interpreter for each target platform. The interpreter generates the machine code for that platform.
In some cases, developers will write software directly in assembly code, eliminating the need for a compiler. Assembly language is considered a low-level language like machine code, except that assembly language is written in plain text and is human-readable. Assembly code is submitted directly to an assembler, which converts the assembly language to machine code.
Assembly code corresponds more directly to machine code than a high-level programming language. Assembly code uses descriptive words, known as mnemonics, that correspond to the ISA's operands. For example, the MIPS example above adds two values together. The operand in this case is 32, or 100000 in binary. The assembly code mnemonic for this operation is add.
Human programmers rarely, if ever, deal directly with machine code anymore. If developers are debugging a program at a low level, they might use a printout that shows the program in its machine code form. The printout, which is called a dump, can be very difficult to work with. Some dump utilities display the data as hexadecimal values because they are easier to read.
Learn about a modern approach to enterprise software development and the differences between functional vs. object-oriented programming. Explore the pros and cons of using low-code platforms in the enterprise and the differences between interpreted vs. compiled languages and scripting vs. programming languages.
