RISC (reduced instruction set computer)
What is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC)?
RISC (reduced instruction set computer) is a microprocessor that is designed to perform a smaller number of computer instruction types, so it can operate at a higher speed, performing more millions of instructions per second, or MIPS. Since each instruction type that a computer performs requires additional transistors and circuitry, a larger list or set of computer instructions tends to make the microprocessor more complicated and operate slower.
What are advantages of RISC technology?
The RISC concept has led to a more thoughtful microprocessor design. Among those design considerations are the following:
- How well an instruction can be mapped to the clock speed of the microprocessor -- ideally, an instruction can be performed in one clock cycle.
- How simple a computer architecture is required.
- How much work the microchip must do itself without resorting to software for help.
Besides performance improvement, other design improvements that have come out of RISC include the following:
- Speed. New high-performance microprocessors can be developed and tested faster because the design is less complicated.
- Ease. RISC systems make it easier for operating system and application programmers to use the microprocessor's instructions to develop code with a smaller instruction set.
- Simplicity. RISC's simplicity enables more freedom to choose how to use the space on a microprocessor.
- Efficiency. Higher-level language compilers produce more efficient code than formerly because they tend to use the smaller set of instructions found in RISC computers.
- Concurrency. RISC technology supports pipelining in which a number of instructions can be executed concurrently, thus increasing instruction throughput and system performance.
What's the difference between RISC and CISC systems?
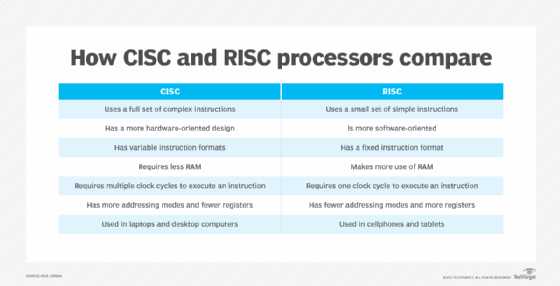
RISC and complex instruction set computer (CISC) are the main processor architecture types. They are differentiated by the data processing instruction sets their central processing units (CPUs) use.
CISC
CISC systems have more complicated instructions and microcode than RISC. The CISC architecture lets systems initiate multiple actions on a computer. The complex microcode requires more computing power to execute the commands. Laptop, desktop and other general-purpose computers use CISC processors because they can perform many different computing tasks.
RISC
RISC systems use hard-wired code with a simple instruction set that needs a less costly CPU than a CISC device. RISC processors are used in smartphones, printers, tablets and devices that do a specific set of repeatable activities. RISC CPU technology is increasingly popular in data center systems because of their performance and ease of use.
The history of RISC architecture
John Cocke of IBM Research in Yorktown, N.Y., developed the original RISC concept in 1974. He proved that about 20% of the instructions in a computer did 80% of the work, adhering to the Pareto principle. The first computer to benefit from this discovery was IBM's PC/XT in 1980. Later, IBM's RISC System/6000, or RS/6000, also made use of the idea. The term RISC is credited to David Patterson, a computer science professor at the University of California, Berkeley.
The RISC concept was used in Sun Microsystems' Scalable Processor Architecture, or SPARC, microprocessors. It also led to the founding of MIPS Technologies in 1998. After several changes of ownership, MIPS Technologies is now known simply as MIPS and continues to manufacture RISC-based processor components. Many current microchips use RISC architectures, particularly RISC-V, an open source instruction set architecture that uses RISC designs.
What you need to know to decide between RISC vs. CISC processors for edge computing.
