What is an application support engineer (ASE)?
An application support engineer (ASE) is an IT professional who is responsible for troubleshooting the software applications a company uses and ensuring that help desk tickets are resolved in a timely fashion. In a large enterprise, an ASE might act as a subject matter expert for a specific software stack. In a small to mid-size business, an ASE will typically be responsible for supporting a limited number of client-facing software applications.
Application support engineers play an important role in companies that depend heavily on software to operate efficiently. In general, ASEs are responsible for monitoring application performance to detect and address problems before they affect users, conducting root cause analyses (RCA) to prevent recurring issues and assisting with software updates and patches.
Depending on a company's size and industry, an ASE might be tasked with managing communication between an organization's IT department and its business users or providing expert technical assistance on behalf of a software vendor. Many ASEs begin their careers as help desk technicians or IT support specialists. Over time, as an ASE gains more experience, they might choose to move into more granular support roles that focus on specific applications or software suites.
To get hired as an ASE, job candidates should have a strong mix of technical skills, soft skills and hands-on experience with application software. Familiarity with application monitoring tools, ticketing systems and IT service management (ITSM) platforms, like ServiceNow or Jira, can also be useful, as can certifications in ITIL or CompTIA and or specific cloud platforms.
Application support engineer role
As the title suggests, an ASE's main role is to provide support for the software applications that enterprise users require to do their jobs. This means ASEs must understand how specific applications are supposed to work on the client-side as well as the backend. When end users face issues that hinder the software's usability, it is the ASE's job to troubleshoot and resolve the issues as quickly as possible.
That said, the ASE's role is rarely limited to simply diagnosing configuration errors, system errors, bugs and other problems that result in a poor user experience (UX). Some ASEs, particularly in large companies, are also tasked with working with vendors and using what they learn to identify potential enhancements that can improve the product's usefulness and UX.
In some cases, ASEs might be expected to be a subject matter expert (SME) for a specific software application or suite. Vendors and large enterprises typically hire this type of ASE to provide deep technical expertise, resolve complex issues that go beyond general support, and serve as a liaison between users, software developers and other technical team members.
The day-to-day responsibilities of an application support engineer can vary significantly depending on the organization's size, industry, software environment and internal IT structure. In general, however, ASE responsibilities tend to fall into a few consistent categories:
Incident and ticket management
ASEs typically work within a help desk or IT service management system to log, prioritize and resolve tickets. Responsibilities often include the following:
- Responding to general application-related questions and IT service desk trouble tickets from users in a timely and relevant manner.
- Assessing multiple open issues and prioritizing issues that have the greatest effect on product usability and/or user productivity.
- Documenting the helpdesk event management process.
Troubleshooting and issue resolution
ASEs use debugging tools and diagnostic procedures to identify root causes and implement fixes. Responsibilities often include the following:
- Minimizing service disruptions and operational downtime.
- Performing root cause analyses to understand and address underlying issues that might be affecting application performance.
- Researching how to resolve common issues, and if possible, prevent them from recurring.
- Appling required patches and updates to improve application performance and stability.
- Following corporate best practices for change control.
User support and communication
In their support role, ASEs act as a bridge between internal technical teams and end users. Responsibilities often include the following:
- Interacting with end users to ensure software applications meet their needs.
- Gathering information about reported problems.
- Providing updates during the incident response process and helping users understand their issue's underlying cause and resolution.
Application monitoring and maintenance
ASEs often act as the "eyes and ears" for applications in a production environment. Responsibilities often include the following:
- Ensuring that applications are compatible with the organization's broader IT infrastructure.
- Monitoring application performance in real time.
- Adjusting system settings and application configurations to improve application performance.
- Analyzing data in log files to identify performance bottlenecks and early warning signs of instability.
- Applying patches and updates to improve application availability, performance and stability.
Collaboration with stakeholders
ASEs frequently act as subject matter experts for specific applications or systems and manage communication between internal and external stakeholders. Responsibilities often include the following:
- Working closely with the organization's quality assurance (QA) and IT infrastructure teams.
-
Informing product managers and business analysts about the frequency and effect of application issues on business processes.
- Gathering user feedback on desired features or improvements and communicating them to internal development teams for consideration in future releases.
Documentation and knowledge management
ASEs are expected to contribute to an organization's knowledge base, maintain service reports and write up actionable bug reports for software engineering teams. Responsibilities often include the following:
- Acquiring and aggregating relevant information about application issues from user stories, technical logs and monitoring tools.
- Documenting issue triage processes, service events and solutions.
- Creating internal user guides, FAQs and automated chatbot responses.
- Providing data on application usage and performance trends to help infrastructure teams plan for future capacity needs.

Application support engineer skills
The specific skills required of an ASE can vary depending on the organization's industry and the software that employees use. For example, an ASE in charge of a healthcare application may need to understand how electronic medical records (EMR) work and the importance of data privacy. In contrast, an ASE responsible for automating IT workflow with Ansible or moving a proprietary internal app to Microsoft Azure might need experience with systems integration applications.
These differences aside, most ASEs are expected to have skills in the following core areas:
Application performance management (APM). ASEs should be able to evaluate application performance, identify inefficiencies and implement strategies to improve reliability, speed and the user experience.
Application monitoring. ASEs must be proficient in using AI-enabled monitoring tools to track application health, identify bottlenecks and reduce downtime.
Troubleshooting and debugging. ASEs need the skills required to diagnose and resolve user-reported issues. They should be able to identify root causes and apply technical fixes without interrupting operations.
Communication. As the primary point of contact for users experiencing application issues, ASEs must be able to communicate clearly and thoughtfully across multiple channels. They should have strong active listening and time management skills and be able to work with stakeholders who have varying technical backgrounds.
Data analytics. ASEs should be able to analyze application logs and user behavior patterns to help solve user-reported issues.
SQL and database querying. Many application issues involve data access and data integrity problems, so ASEs should know how to query databases, understand schemas and troubleshoot data-related issues using SQL or similar query languages.
Scripting and automation. ASEs are often expected to write and/or use scripts that can automate recurring tasks, streamline deployments or extract log data.
Operating systems. ASEs often work across Windows, Linux or macOS environments, so they need to understand each OS's file system and be familiar with basic OS system administration tasks.
APIs and integration points. Since many enterprise applications rely on REST APIs and webhooks, ASEs should be comfortable reading API documentation, making API test calls and troubleshooting integration issues.
Security awareness. ASEs may be tasked with troubleshooting user permissions, so they need to understand basic role-based access control.
ITIL and/or IT service management. Many ASEs work within structured ticketing systems like ServiceNow or Jira. It's important for ASEs to understand how these systems work and the role they play in ITIL frameworks.
Cloud computing. Now that more applications are hosted in cloud or hybrid environments, ASEs need to be familiar with Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud and feel comfortable working with virtualization platforms.
Diagnostics tools. Many observability platforms (like Datadog, Splunk, Dynatrace or New Relic) use AI/machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies, predict failures or generate insights from application log data. ASEs should understand how these tools work and know how to interpret their outputs.
Generative AI. In large companies, senior ASEs might be tasked with helping to build and train chatbots that can provide low-level help desk support. The insight an ASE brings to the project can bridge the gap between generative AI capabilities and application-specific use cases.
Application support engineer salary
Salaries for application support engineers can vary widely depending on the job candidate's experience, the organization's industry and the job opening's location.
According to Indeed, the average annual salary for an ASE in the United States is approximately $99,054 as of May 2025. Senior ASEs in the United States can earn as much as $164,727 per year, while entry-level salaries might start at $76,415.
The size of the company that's hiring an ASE can also impact salary. Larger companies in industries like finance, healthcare or technology often have bigger IT budgets and more complex application environments. To attract and retain ASEs with skills in specific areas, they tend to offer higher salaries and provide more benefits. In contrast, smaller or mid-sized companies might offer lower base salaries but compensate by providing a more flexible work environment.
Given the variability, job seekers are encouraged to consult individual job postings to understand the specific salary range offered by a particular company.
Application support engineers in the enterprise
In most enterprises, ASEs are part of a large IT department that employs a number of support professionals with varying skill levels and areas of specialization. Depending on the company structure, ASEs might report to a senior ASE, a support team manager or a senior software engineer.
As is common in large enterprises, ASE support is often divided into tiers. Tier 1 ASEs typically assist end users and handle basic troubleshooting issues. More complex or unresolved issues are escalated to tier 2 or tier 3. ASEs in these tiers usually have advanced skills that allow them to resolve deeper technical problems.
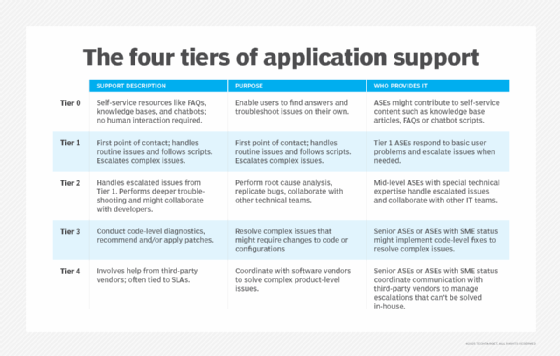
Application support engineers can help businesses stay competitive by automating helpdesk ticket routing and using chatbots to provide instant responses to common issues. Explore service desk automation examples to enhance IT support.
