
How important is authentication in email marketing?
Marketers who have email strategies must understand the importance of authentication protocols to ensure campaigns are successful and bad actors don't reach customers.
Email marketing is crucial for digital marketing strategies, as it drives engagement, conversions and brand awareness. However, security issues -- including phishing, spoofing and email fraud -- threaten its effectiveness.
To combat these challenges, email authentication has become a critical process for marketers. Yet, the complexities of authentication and security often go unnoticed, which can lead to vulnerabilities that can undermine a marketing campaign's success. Marketers must understand these processes to deliver high-quality emails that reach their intended recipients and enhance brand reputation and trust.
Given the technical nature of email authentication, many marketers may find it overwhelming to navigate the various protocols and best practices required to secure their communications. However, this knowledge gap presents a significant opportunity. If marketers invest time to master email authentication, they can create more secure, reliable email campaigns. This expertise helps mitigate security risks and plays a crucial role in building and maintaining customer trust -- an invaluable asset in modern competitive digital marketplaces.
As more consumers become aware of the importance of email security, they are likely to gravitate toward brands that commit to protecting their information, which reinforces the importance of strong email authentication practices.
Why is email authentication important for marketing?
Email authentication refers to the set of techniques used to verify the legitimacy of an email message and confirm it originates from the domain it claims to represent. This verification process ensures that bad actors haven't forged emails, protecting both the sender's reputation and the recipient's inbox.
In the context of email marketing, authentication serves multiple purposes. It protects a brand's reputation, as it prevents unauthorized parties from sending emails that appear to come from the brand's domain. This, in turn, helps ensure legitimate marketing emails reach the intended recipients, rather than being marked as spam or rejected by email service providers.
Authentication also enhances deliverability rates. Properly authenticated emails are more likely to bypass spam filters and reach the inboxes of potential customers. This increases the chances of email opens, clicks and conversions, ultimately leading to more effective marketing campaigns.
Additionally, high-volume email senders, such as Google and Yahoo, have adopted more authentication protocols, which requires marketers to better understand and implement them. Without these protocols, campaigns are vulnerable to phishing attacks, where malicious actors impersonate the brand to deceive recipients. Such incidents can damage the brand's reputation and customer trust.
Furthermore, a lack of proper authentication can result in emails being flagged as spam, which can reduce deliverability rates and the overall effect of email marketing efforts.
Email authentication protocols to note
The following protocols make the authentication process in email marketing easier for marketers to understand and implement.
1. DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
DKIM is an email authentication protocol that enables an organization to attach a digital signature to its email messages. The recipient's mail server then validates this signature to confirm the message wasn't altered during transit and that it originates from the claimed domain. With DKIM, marketers can ensure the integrity of their emails, which helps maintain trust with recipients and improves deliverability.
2. Sender Policy Framework (SPF)
SPF enables domain owners to authorize which IP addresses can send emails on their behalf. Recipient servers check the SPF record of an incoming email and verify an authorized source sent the email. SPF helps prevent spoofing -- a tactic where attackers send emails that appear to come from a legitimate domain -- and enhances the security of email marketing campaigns.
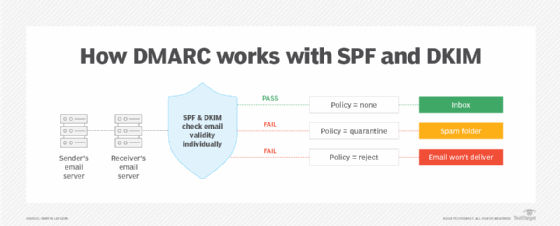
3. Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC)
DMARC builds on both DKIM and SPF, as it offers a way for domain owners to specify how to handle emails that fail DKIM or SPF checks. DMARC lets marketers instruct recipient servers to reject, quarantine or take no action on such emails, depending on the level of enforcement set.
Additionally, DMARC generates reports that provide insight into who sends emails on behalf of the domain, which helps identify potential threats and improve email security.
Best practices for email authentication in marketing
Marketers should adopt the following best practices to ensure their authentication strategies benefit both their teams and their customers.
1. Properly maintain email contact lists
Marketers must maintain an up-to-date and accurate email contact list to ensure emails reach legitimate recipients. This can involve regularly cleaning email lists to remove invalid or inactive addresses, which can reduce bounce rates and minimize the chance of emails being marked as spam. This practice also improves the sender's reputation to ensure successful email deliverability.
2. Create a unique, consistent email address
A consistent email address for all marketing communications helps build recognition and trust with recipients. Marketers should avoid frequently changing the sending address, as this can trigger spam filters and negatively affect deliverability. A unique and consistent email address, aligned with the brand's domain, reinforces authenticity and improves the likelihood of emails reaching the inbox.
3. Implement DMARC with a monitoring policy
When deploying DMARC, marketers should start with a None policy, which monitors how recipient servers handle their emails without affecting deliverability. When marketers analyze the reports generated, they can identify any issues with the DKIM and SPF configurations and make necessary adjustments. Once the authentication setup functions correctly, teams can gradually enforce stricter DMARC policies to enhance security.
4. Use third-party tools for authentication checks
Third-party tools offer additional layers of verification and monitoring for the email authentication setup. These tools can automate the process of checking the DKIM, SPF and DMARC records to ensure they are correctly configured and identify potential vulnerabilities. Regular use of these tools helps maintain the integrity of the email marketing efforts and safeguards against evolving threats.
5. Educate the team
Email authentication is a complex topic that requires ongoing attention and expertise. Organizations must ensure all members of the marketing and IT teams are well-versed in authentication protocols and best practices. Regular training sessions and updates on the latest threats and technologies can help teams stay informed and proactive in maintaining email security.
If marketers embrace these best practices, they can navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, secure their email communications and foster trust and loyalty among their audience. As the importance of the authentication process in email marketing continues to grow, staying informed and proactive can ultimately lead to more successful campaigns and a healthier bottom line.
Overall, marketers who want to protect their brand's reputation, improve deliverability and foster long-term relationships with customers must understand and implement email authentication. Make sure to prioritize email authentication within marketing strategies and keep up with the latest best practices to stay ahead of potential threats.
Griffin LaFleur is a MarketingOps and RevOps professional working for Swing Education. Throughout his career, LaFleur has also worked at agencies and independently as a B2B sales and marketing consultant.






