sales-qualified lead (SQL)
What is a sales-qualified lead (SQL)?
A sales-qualified lead (SQL) is a prospective customer that has been researched and vetted -- first by an organization's marketing department and then by its sales team -- and is deemed ready for the next stage in the sales process.
An SQL has displayed intent to buy a company's products and has met an organization's lead qualification criteria that determine whether a buyer is a right fit. The label is applied to a prospect that has gone past the engagement stage and is ready to be pursued for conversion into a full-fledged customer.
SQL vs. MQL
What constitutes an SQL varies among and even within companies, because marketing and sales teams often don't agree on how to qualify leads. Marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) are often identified by the marketing department at the start of the process when the company wants to foster interest in its products. MQLs are typically passed on to sales teams once they have shown intent to buy, thus becoming SQLs.
The difference between MQLs and SQLs is readiness to buy. An SQL is determined by the company's lead management process, which assesses the actions a prospect takes that indicate intention to buy. To target serious buyers, companies employ a lead scoring process designed to save salespeople time and expedite quota attainment.
Ideally, sales and marketing teams will collaborate to determine which qualities and actions a prospect must take to advance to the next stage of the process. Many lead quality issues originate when marketers send the sales team leads that have no intention of buying, which slows down the sales process.
How do organizations identify SQLs?
Companies assign different priorities to various prospect actions, such as website activity or responses to marketing materials. Companies will place an importance on each action during the lead scoring process to differentiate between a customer that has a passing interest in a product and one that is serious about buying. Repeat visitors to a company's website hold more weight than first-time visitors, for example, and certain actions, such as downloading a white paper or filling out a form, could move a prospect closer to being deemed an SQL.
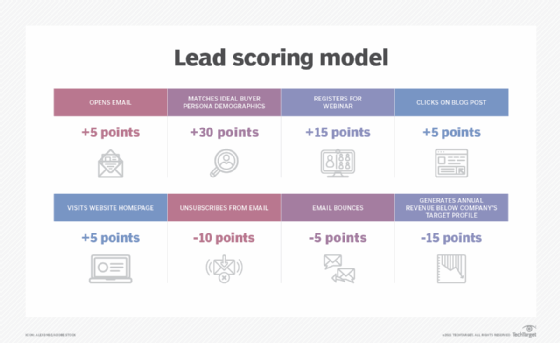
Demographics are also an important factor in the makeup of an SQL, as companies aim to use techniques such as customer profiling to determine whether a lead is ready for the sales department. Information such as a lead's industry, company size and job role are critical to determining how interested and serious leads are in purchasing a company's products. As the prospect moves closer to being labeled an SQL, information such as pain points or budget becomes relevant to the sales team before they directly contact the prospect.
Editor's note: This article was written by Tim Ehrens in 2015. TechTarget editors revised it to improve the reader experience.







