What is customer profiling?
Customer profiling is the detailed, systematic process of constructing a clear portrait of a company's ideal customer by gathering and analyzing information about their demographic, psychographic and behavioral attributes. It's a foundational tool for businesses to tailor their strategies and offerings, ensuring they resonate effectively with their target audience.
In today's fast-paced, increasingly digital market, understanding customer behavior is paramount. A nuanced grasp of consumer preferences, habits and needs empowers businesses to curate products, services and marketing campaigns that are appealing and deeply relevant. This targeted approach often yields higher, loyalty and, ultimately, revenue.
The role of customer profiling in digital transformation
With businesses increasingly shifting toward digital channels, customer profiling is critical for navigating this transition. Profiling helps companies adapt by providing insights into how customers behave online, which platforms they prefer and what types of digital interactions they value most.
By integrating customer profiles with digital transformation strategies, companies can ensure that their online presence aligns closely with customer expectations, leading to enhanced user experiences and streamlined online customer journeys.
Customer profiling vs. market segmentation
While customer profiling might seem intertwined with market segmentation, there's a distinct difference. Market segmentation categorizes the broader market into different groups or segments based on shared characteristics. Customer profiling dives deeper, focusing on creating a more intricate, individualized picture of potential customers, reflecting specific preferences and behaviors.
Think of market segmentation as looking at the forest, while customer profiling is about examining each unique tree. Both are vital but serve different roles in influencing go-to-market strategy.
Customer profiling components
Crafting an accurate, useful customer profile is akin to solving a jigsaw puzzle; every piece of information has its place and importance. The more detailed and nuanced the information, the clearer the picture of the ideal customer becomes.
Demographic information
Demographic information refers to the basic, often statistical data about customers, including factors such as the following:
- Age. Understanding the age range of customers can help a company tailor products or services to specific age groups.
- Gender. Gender can influence buying behaviors and preferences in many industries.
- Location. Geographical data can reveal cultural preferences, logistical considerations or even climate-based needs.
- Education and income. These factors might determine purchasing power and preferences.
The preceding factors are helpful in identifying who might be ideal customers; some additional factors to consider include marital status, occupation and family size.
The specific customer profiles that a business uses will depend on what it's selling and who its target audience is.
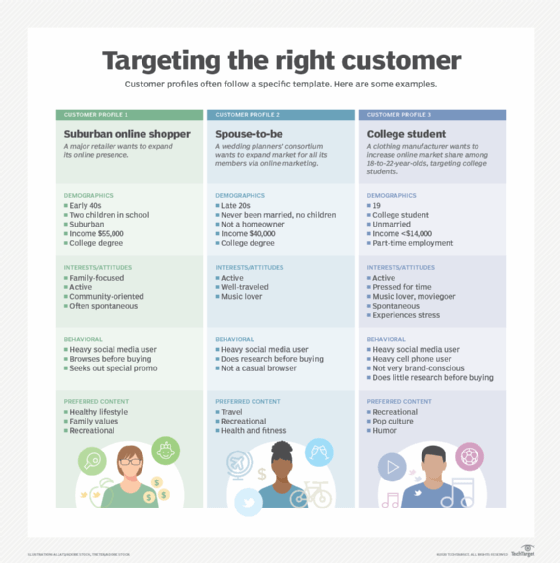
Psychographic information
Psychographic data concerns the more intangible, yet equally crucial aspects of a customer's personality and lifestyle. This includes their interests. What hobbies or activities does the customer engage in? What are their product preferences? This could include styles for an apparel brand or flavors for a food manufacturer, but it also includes how they prefer to be approached in terms of marketing. Do they watch television? Are they on social media regularly? Do they listen to podcasts?
Customer values are another important psychographic consideration. What beliefs or principles guide their choices and decisions? By understanding these, businesses can appeal to customers on a more personal, emotional level.
Behavioral data
Behavioral data is the actionable information reflecting how customers engage with a business. It includes data points such as their purchase history and volume, brand interactions (e.g., clicks, likes, shares) and level of customer loyalty. Are they repeat customers? Do they refer others?
By analyzing behavioral data, companies can identify trends, predict future behaviors, and tailor strategies to resonate with customers (based on the customers' established habits) or influence new ones.
Each of these considerations contributes to the rich tapestry of customer profiling, allowing businesses to approach their market with precision, empathy and foresight.
Data collection for customer profiling
With so much information needed for effective customer profiling, it's essential for businesses to take a thorough approach to data collection. The following methods are crucial elements in the process of profiling, each offering unique insights into customer behavior and preferences:
- Surveys and feedback forms are direct tools used to gather information from customers about their experiences, preferences and expectations. They can be designed to be broad or targeted, and the feedback obtained can provide businesses with clear action points for improvement or validation of current practices. The immediacy of responses, combined with the possibility of anonymity, often leads to candid, invaluable insights.
- Social media can provide insight built on a treasure trove of customer data. From likes, shares and comments to direct mentions of brands, tracking social media activity can give businesses a window into their customers' lives and preferences. Currently, platforms like X (formerly Twitter), Facebook, Instagram and TikTok offer analytics tools that track engagement rates, peak activity times and popular content, clarifying what resonates with audiences.
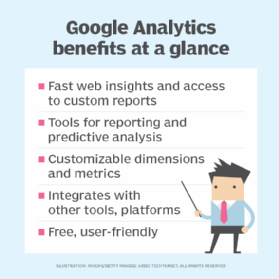
- Website analytics and user behavior can come into focus with tools like Google Analytics or other website monitoring Using them, businesses can gain insight into how users navigate their sites, which pages they spend the most time on, where they drop off and what content prompts action. When website analytics and user behavior analytics are interpreted correctly, the findings can shed light on user behavior, helping businesses optimize their web presence for enhanced customer experiences.
- Direct customer interactions, such as face-to-face conversations, remain quite powerful. Whether it's a sales call, customer support interaction or casual chat at a physical store, these direct interactions can provide unfiltered feedback. Listening to customers' tones, understanding their pain points and empathizing with their needs can yield insights not readily seen from a survey or an analytic tool.
New tools, such as heatmaps, track where customers hover on webpages and what sections draw the most attention. These tools provide even deeper insights into user behavior.
Collecting data through these methods ensures a multifaceted understanding of customers. The key lies in synthesizing this data, combining the quantitative with the qualitative, to build profiles that genuinely reflect the consumer landscape.
How to create effective customer profiles: Best practices
Building accurate customer profiles requires more than just collecting data -- it involves a thoughtful, strategic approach to data analysis and applications. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Focus on quality over quantity. Gather only the most relevant data that adds value to your understanding of the customer.
- Use diverse data sources. Incorporate both direct (e.g., surveys) and indirect (e.g., website behavior) data sources to capture a comprehensive view.
- Regularly update profiles. Customers' preferences and behaviors can change over time, so routinely refresh profiles to keep them accurate.
Following these best practices helps businesses ensure that their customer profiles remain actionable and reliable, driving consistent results.
Customer profiling benefits
While the meticulous process of collecting data paints a vivid image of the customer landscape, the true value of customer profiling shines when these insights are put into action. Harnessing the power of detailed profiles helps businesses understand their customers and can yield tangible benefits that enhance the entire spectrum of business operations. Here are some ways that companies make data come alive with better experiences for their customers:
- Enhanced personalization is key to standing out. By understanding the intricate details of customer preferences, habits and needs, businesses can tailor their offerings to meet individual demands. With advances in AI-driven personalization, businesses can deliver hyper-customized experiences, from product recommendations to personalized marketing emails. When customers feel seen and understood, they're more likely to engage and invest in a brand.
- Effective marketing strategies are typically built on data from customer profiles. With profile data in hand, marketing teams can craft campaigns that resonate deeply with the target audience. Instead of casting a wide net, businesses can channel their efforts and resources into campaigns that speak directly to the right people. As digital marketing platforms become more sophisticated, businesses can use automation tools and AI to segment their audiences and deliver personalized content on a massive scale.
- Improved product development often starts with using the rich pool of insights gathered from customer profiling. Acting on those insights, businesses can refine existing products or develop new ones that cater directly to market demands. Understanding gaps in the market, anticipating needs, or simply enhancing features based on feedback can lead to offerings that are innovative and aligned with customer needs. Agile development methodologies allow companies to iterate quickly based on real-time feedback from customer profiles.
- Increased customer loyalty and retention is the prized achievement that comes when businesses meet or exceed customer expectations and foster trust. Trust breeds loyalty. Customer profiling ensures that businesses are always a step ahead, anticipating needs and addressing concerns even before they arise. This proactive approach to customer satisfaction is a sure way to increase retention rates and cultivate a loyal customer base. Loyalty programs driven by behavioral data and preferences are becoming more personalized, offering tailored rewards that resonate with individual customers.
In summary, the focused lens of customer profiling equips businesses with the tools they need to serve their market more effectively. It yields data-driven insights that are fuel for actionable strategies that enrich customer experiences and facilitate sustained business growth.
Customer profiling challenges
While the benefits of customer profiling can be substantial, properly implementing a profiling program and basing business decisions on it is not simple. As businesses plunge deeper into the realm of customer data, they encounter challenges that demand both ethical consideration and strategic foresight.
Balancing detailed profiling with data privacy concerns
Data privacy is a central concern for consumers. While detailed customer profiles can give businesses a competitive edge, it's crucial to ensure that data collection and usage adhere to privacy regulations and respect the individual rights of customers. With the advent of regulations like GDPR and CCPA, businesses must be more transparent and careful in handling customer data, ensuring they meet compliance standards while maintaining consumer trust.
Ensuring the accuracy and relevance of collected data
Data is only as valuable as its accuracy and relevance. Redundant, outdated or trivial (ROT) data can lead to misguided strategies that could alienate customers rather than engage them. Regularly updating profiles, cross-referencing sources for validation and building an optimal system to sift through ROT are all essential practices to ensure the insights derived from profiles are accurate and actionable.
Data cleaning and validation processes are critical to ensure profiling remains relevant and useful in real-time decision-making.
While the challenges of customer profiling are undeniable, they do not overshadow its immense value. With careful navigation to avoid the potential pitfalls, businesses can use the practice to improve how they interact with their market and bridge the gap between their product offerings and real customer needs.
Additionally, advancements in AI and machine learning tools are helping businesses overcome these challenges by automating data validation and ensuring continuous updates to customer profiles.
Customer profiling is more than a tool; it should be seen as an essential part of a core philosophy, emphasizing the importance of customer-centricity in crafting successful business strategies. When done right, it delivers insights that enable businesses to connect more deeply with their customers, ensuring long-term success.
Learn all about CRM (customer relationship management) and see how to create customer profiles with examples. Check out five customer journey phases for businesses to understand and four benefits of a customer data platform.








