How to create a customer journey map -- with template
Customer journey maps help CX teams delve into the data gathered during a customer's experience. They also help businesses to understand the failures and successes of sales.
As a CX professional, a crucial part of providing a positive customer experience is the ability to place yourself in the mind of your customer. Conversely, a failure to fully understand the customer's thought process when making a purchase means that you don't know how potential sales can slip through the cracks.
You can put yourself into your customer base's shoes by developing your customer journey map. Then, you can use a customer journey template to create a customer journey map that applies to your specific business. The final step is introducing automation and AI into the customer journey map process to streamline the process and facilitate meaningful insights that translate into increased sales.
What is a customer journey?
The processes a customer takes when interacting with your business to purchase -- or not purchase -- a product or service is known as a customer journey. The user experience starts with the customer's recognition of your product or service. The customer path will then go through a series of customer interactions, thoughts and considerations about the product or service until a decision is made on whether the customer believes the product or service you are selling is worth the money you're asking.
The customer journey isn't considered complete with a successful sale. Instead, the customer will again go through the process, this time deciding whether to become a repeat customer or advocate for your business or brand.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a documented flow diagram created to visualize the journey that most of your current and potential customer base will likely follow. It's essentially a step-by-step representation of your customer's interactions as they discover, research, purchase and reflect on the value of the product or service.
Customer journey maps are like service blueprints -- both are visual tools for understanding business processes. A service blueprint, however, delves into the process an organization takes when delivering a service, while a customer journey map details the customer experience, including a customer's emotions and touchpoints. CX teams carefully track all of the inputs and insights along the customer journey. In modern implementations, data analysis ensures that customer conversion rates are at peak levels and that teams can gather insights on lost sales and use those insights to adjust customer journey processes to enhance the likelihood of a closed deal.
Why are customer journey maps important?
For many businesses, a customer's journey is becoming increasingly complicated, thanks to social media and other connected technologies used as touchpoints between potential customers and the product or service. Creating a customer journey map that includes modern touchpoints and collects the necessary data for further analysis is more important than ever. The result is a detailed shared vision across the organization so all departments can better support the process.
A customer or user journey map's purpose depends on your company's overall goal. In general, however, journey maps provide visibility into what potential customers look for at various customer touchpoints. This information can then change how you interact with customers to increase the chances of a sale.
Customer journey map template
Because each business is unique, every customer journey map will be slightly different. A customer journey template can help you create your specific map. Get started with our free customer journey template to help create your specific map.
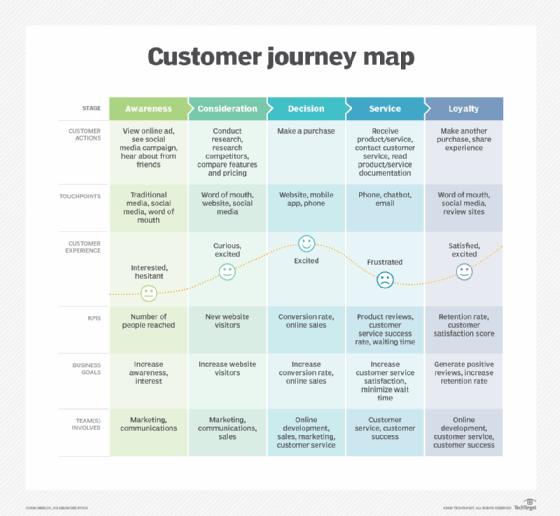
6 steps to create a custom customer journey map
When building a customer journey map for the first time, it's important to understand how to create the most accurate and useful for prospective customers and the business selling a product or service. CX teams should gather internal information that details marketing, service and sales processes. But even more so, a customer journey map should collect information directly from prospective, current, former and even lost customers. This includes information-gathering techniques such as customer surveys, service ratings and market testing. This data is likely stored and cataloged in a digital CX platform. This platform serves as a data lake where AI can automate various processes and analyze the likelihood of a successful sale.
With this type of information gathered, you can create a customer journey map in just six steps using the template provided in the previous section. Each step corresponds to a different column in the template.
1. Define your target customer
In the first step, understand who your product or service caters to most. Be sure to know how it differentiates from competitors. AI-based tools can help perform market research, conduct surveys and automatically identify emerging trends that allow businesses to quickly pivot their products or services to areas expected to grow. Based on this information, you can identify one or more customer demographics to categorize most customers into.
This process can help determine the desire of the prospective customer -- and how strong that desire is for your product or service. For example, are your target customers impulse shoppers, or do they conduct plenty of research first? Is price the most important purchase factor -- or are you targeting an audience looking for a premium brand or service, regardless of price? Once you define your target customer, completing the customer journey map template will be easier, especially the rows for customer goals and emotions.
2. Identify marketing strategies (awareness)
Next, understand how your brand or product is marketed to the targeted customers you previously identified. This includes methods such as the following:
- Websites.
- Social media.
- Online or print ads.
- YouTube videos.
- Webinars.
You can record this information in the touchpoints row in the customer journey map template. Once you identify marketing strategies, you can also fill in the awareness column.
This information lets you decide whether the marketing content or methods are optimal for your target audience. For example, an in-depth product comparison guide would likely be good marketing content for customers conducting thorough research on a product or service in highly competitive markets.
3. Determine customers' preferred research method (consideration)
In this step, your goal is to walk through the various thought processes that the defined customer persona would go through, given their general demeanor, appetite for the product or service and types of marketing and informational content available to them. You can record this information in the consideration column on the customer journey map template.
Consideration is the point in the customer journey where you can begin to understand the research prospective customers do and what they consider trustworthy resources from a product research perspective.
4. Understand reasons for a sale or lack of a sale (decision)
The point where a potential customer decides if the product or service is right for them contains a wealth of information. Unfortunately, this thought process is largely hidden from the company selling the product. That's why customer satisfaction surveys and marketing feedback are so valuable. This data gets to the heart of why some sales happen while others don't. You can record this data in the decision column of the customer journey map. This information is vital for predicting the customer's attitude toward your products -- or the market.
5. Analyze customer satisfaction (service)
A customer purchase isn't the last step in the customer journey; it's also important to determine how to educate and help customers with the product or service once they've made that purchase. In this step, you should understand what determines whether a customer is satisfied or unsatisfied. Mostly, this revolves around whether the product or service met the expectations of the marketing and customer research performed. Remember that not only the specific product or direct service dictates satisfaction. It can also come down to other factors, including the following:
- How customer service representatives treated the customer.
- If the customer could get satisfactory and timely answers to post-purchase questions, either through product documentation or conversations with customer service reps.
- How long the customer needed to wait on hold for customer service, if at all.
- The user experience of the website and other digital touchpoints.
6. Build repeat customers or brand advocates (loyalty)
Businesses thrive on repeat customers, so evaluating your customer's loyalty is important. From there, you can determine how to generate brand advocates -- customers who recommend your business through word of mouth, social media or positive reviews.
Based on the level of satisfaction, determine how likely it is that customers will repurchase products or services continuously. Perhaps even more importantly, how likely are they to advocate for your brand or product to friends and family? Customers who are passionate about what you're doing should be the goal of every business. Gathering data on this step gauges how smoothly the customer journey went.
Reevaluate and update customer journey maps
Customer journey maps are fluid. As products, services and customer interactions change, so will the customer journey map. You must update maps as products and customer preferences change -- or as there are changes in the market. This can include new competitors, changes in regulations, product obsolescence, changes in economic conditions or shifts in targeted customers. Generally, you should review customer journey maps semiannually -- or when major market changes occur.
The growing use of AI within customer journey maps
The use of artificial intelligence to help optimize the customer journey process and provide automated analysis has become increasingly common. Several customer journey tool vendors have integrated advanced AI into their platforms to speed up the creation of customized journey maps, provide multiple feedback touchpoints, and collect and store data throughout a customer's decision-making and ongoing loyalty steps. The goals of AI within the customer journey include the following:
- Delivery of automated analysis with actionable items that better ensure the success of a sale.
- Provide additional customer checkpoints that deliver flexibility regarding the analysis and consideration steps.
- The dispatch of rapid-response services for customers to help streamline product or service offerings conveniently.
- Detailed insights about changes to customer attitudes, desires and market changes to help with future product or service development for future sales offerings.
Time is of the essence in highly competitive markets, and AI has been shown to be a way to deliver more customers and provide accurate insights that can help companies achieve improved sales conversion rates with fewer human resources required.








