7 must-have skills for customer experience professionals
CX professionals must seek to understand customer problems and perspectives, so they need skills in communication, data collection, relationship building and empathy.
The experience potential customers have when interacting with a brand doesn't just determine if they will make a purchase. It also determines whether they will become lifelong fans and tell everyone they know to shop there -- or leave negative reviews and shop the competition.
Given the importance that customers place on CX, decision-makers are on the lookout for individuals who have the right skill set to positively affect customer loyalty and satisfaction.
To land a job as a CX professional, candidates need a blend of communication and project management skills.
What is customer experience and why is it important?
Customer experience is the perception customers have of a brand before, during and after they purchase a product or service. CX can include the following:
- How quickly a customer service representative was able to solve a problem.
- How fast a website or mobile app loaded.
- How well a customer could find what they were looking for.
CX drives customer loyalty, according to a 2022 report from Forrester. Customers tend to remember their interactions with brands for months following their most recent experience, which can influence their loyalty.

Brands can do the following to offer great CX:
- Publish content in a timely manner.
- Solve problems quickly and accurately.
- Consistently offer high-quality products or services.
- Put the customer at the center of all interactions to keep them coming back.
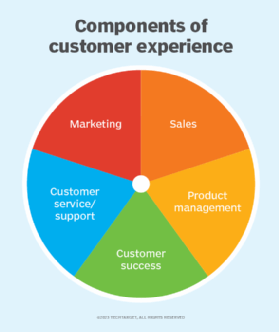
CX isn't just limited to customer service but involves the entire organization, starting in the C-suite and extending to marketing, sales, engineering and IT. That means there are jobs for CX professionals across several different areas, including customer success, sales and product management.
Top skills for customer experience professionals
Regardless of the exact career path a CX professional takes, the following skills can help them make the cut.
1. Strategic outlook
Anything a CX professional does should align with the overall objectives of the organization. Every CX initiative should meet a specific goal, depending on where the company is and where it wants to head in the future.
CX professionals must identify ways to improve CX and build loyalty and trust among customers. If the organization is new, then gaining new customers may be the top priority. An established brand, on the other hand, may focus more on customer retention, depending on what else is happening within the business. Ultimately, identifying those targets and then developing a plan to meet those goals is a critical skill to have.
2. Data-driven mindset
CX professionals must know the areas where their organizations already do well and where they need to improve. However, these professionals can't improve what they can't measure, and that's why a data-driven mindset is essential in a CX role.
Organizations can measure customer satisfaction with surveys and other data collection methods. There are many surveys and metrics available to determine customer satisfaction, but two of the most popular metrics include net promoter score and customer satisfaction score.
While quantitative, measurable data is necessary, it's also important to collect qualitative data to understand why a customer provides an organization with a given rating. CX professionals can stand out from their peers if they know how to blend objective metrics with subjective feedback.
3. Communication and storytelling
CX professionals must be able to analyze business data and determine the best course of action for an organization. But more importantly, they need to be able to communicate that course of action to those around them.
Communication skills are necessary at all levels of CX. For instance, sales and customer service professionals need to be able to speak with customers, understand their problems and help solve them. Meanwhile, CX leaders must be able to encourage their team members and explain their vision.
CX professionals can use storytelling to communicate more effectively. A good story helps get a message across to internal stakeholders and shows them how collected data affects the organization. Storytelling can also highlight how a particular product or service can benefit customers.
4. Relationship building
CX involves more than just one department -- from pre-purchase to post-purchase. These departments include marketing, sales, customer success, customer service and customer support. Therefore, CX professionals need to be able to build relationships.
Relationship building means identifying and getting support from critical internal stakeholders and collaborating with them to enhance CX. A CX professional's work will never be siloed, even when they work independently, so cultivating relationships should be at the top of their agendas.
5. Project management and process simplification
Project management skills can also set professionals apart in the CX industry. CX professionals should be able to break down complex problems into manageable pieces and identify others around them who can help complete various tasks.
With numerous digital channels and new competition popping up on a regular basis, most organizations work on multiple initiatives simultaneously. This means that CX professionals need to juggle multiple items at once, prioritize key initiatives and lead others to stand out.
6. Empathy and listening skills
While organizations should aim to solve customer issues as quickly as possible, it's equally important to show empathy when solving those problems. Empathy is key to retaining loyal customers and driving business success.
No two customers are the same, so CX professionals should be adept at addressing a variety of customer emotions -- including delight, frustration and anger. Customer-facing employees should acknowledge customer feelings, which can be done through active listening, making statements and asking questions related to what the customer has said.
Some common empathy statements CX professionals can use to show they are listening include the following:
- I apologize for your experience.
- I understand how frustrating this must be.
- What can I do to remedy the situation?
- You're right.
The most effective CX professionals can listen to their customers and find ways to solve their problems.
7. Adaptability
CX is a fast-changing industry. Technology and customer preferences are constantly changing, so CX professionals must be adaptable and flexible. These professionals must be able to adapt in the following ways:
- Work in a team or independently as the situation requires.
- Pivot to new channels and initiatives.
- Pick up new skills.
- Work with emerging technologies.
No matter what, CX professionals must adjust as necessary to continue finding ways to improve CX.
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of CX. Customers are the lifeblood of any organization, and without them, every company would cease to exist. Therefore, it's up to CX professionals to develop the skills necessary to better themselves and improve the experience of their customers.
Editor's note: This article was updated to improve the reader experience.