Top AI recruiting tools and software of 2026
AI now reaches every corner of recruiting and talent acquisition. Here's the latest on AI tools, from chatbots to agentic AI, plus details on products from 9 top vendors.
Neither potential employers nor job searchers can avoid AI in the dance that is today's sourcing, recruiting, applying and interviewing. Yet, like all new disruptive technologies, there is a disparity in the degree to which AI is applied within applications. Likewise, there is the inevitable gap between early and late adopters, compounded by business maturity level, user readiness and training, and the perceived ability of AI to address current issues.
While vendors were busy either bolting AI features to their products or extending their AI native-built applications over the past year, two of my favorite companies were acquired: Paradox, with its leading AI conversational assistant Olivia, was acquired by Workday, and SmartRecruiters, a longtime favorite, was bought by SAP. Both bring distinctive, proven AI capabilities to these companies' product offerings.
Considerations for setting purchase criteria
What should buyers look for when seeking AI in talent acquisition products in 2026?
There are four levels of AI maturity, varying from assistive AI, which provides suggestions, recommendations, and summaries; copilots that execute tasks when prompted by a human; semi-agentic models that proactively run multi-step workflows with human oversight; and totally autonomous agents that execute end-to-end processes with minimal human intervention. Buyers should be aware of these differences when choosing products. Many vendors claim to have agents but instead deliver copilots.
The ubiquitous chatbot
Chatbots are universal, and many job candidates say they prefer chatting with a bot over talking to a human -- to a point. While early chatbots were often little more than pop-ups that gave people a menu of choices from which to access more information, today AI adds natural language processing to interpret questions and give more specific, tailored responses to people searching for information.
This article is part of
Ultimate guide to recruitment and talent acquisition
A chatbot is a reactive, conversational interface that can answer questions or complete simple tasks only when prompted by a user. Paradox's bot, Olivia, is a case in point. It can manage an entire hiring process for an hourly worker in a series of friendly text conversations, though not without the potential for security breaches and other risks. StepStone's Mya, SmartRecruiters' Winston, SAP's Joule (which will now benefit from Winston's recruiting specialty), Beamery's Ray and iCIMS' Digital Assistant, which automate self-service, qualification screening and interview scheduling, are just a few among many.
You can expect any recruiting system to include a bot that can suggest jobs to candidates, assist them in applying, update their progress through the hiring cycle, schedule and even conduct interviews, and onboard them -- whether or not the bot has a classy name.
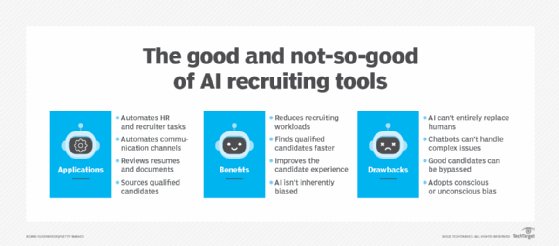
GenAI: Master content generator
Generative AI, which produces new content, such as text, images and program code, is proving a boon to recruiters. It can create personalized correspondence, engaging job descriptions, as well as offer and rejection letters.
GenAI is also useful to candidates for creating resumes -- including nefarious ones who list fake qualifications to match job requirements for which they lack the necessary skills. Just as it is a time-saver for recruiters, it enables applicants to send out many more tailored resumes and cover letters than ever before. On the downside, this often leads to swamping recruiters with mediocre candidates.
Examples of GenAI tools include ChatGPT, Gemini and Claude. While AI-generated content should always undergo human review, these are effective labor-saving tools for the talent acquisition process.
Copilots: The move to decision support
But then, what are copilots? On the one hand, copilot is specific branding used primarily by Microsoft for its suite of AI-powered assistants. Like ChatGPT and the others mentioned above, Microsoft Copilot is an example of generative AI that searches and delivers information in response to questions. However, unlike general-purpose GenAI tools like ChatGPT, copilots are designed to operate with specific work data in the vendor's ecosystem.
For example, iCIMS Copilot is talent acquisition-specific: It generates interview questions for open requisitions for specific roles based on defined criteria, including proficiencies, level of experience, skills, industry and more. Beyond just generating content, iCIMS Copilot can recommend changes in real time as it dynamically marks up users' work. For example, if you ask the tool to make a senior-level job description more junior, it will suggest changes that cater to less experienced candidates.
Other AI products branded as copilots include the following:
- Findem Copilot focuses on automating and personalizing candidate sourcing and pipeline building.
- Paychex Recruiting Copilot, developed in partnership with Findem, uses AI to analyze candidate data and help hiring teams find and match talent faster.
- Talentech AI Copilot assists recruiters and HR teams with job ad creation, screening, generating questions for structured interviews, campaign design, talent pool analysis, HR-related FAQs and more.
- Recruit Copilot is standalone software that focuses on automating resume screening and candidate ranking to accelerate hiring.
Similar functionality is available from many vendors, but these tools might not be called copilots. AI-based assistants by Eightfold, SeekOut and others serve similar purposes, in that they help recruiters write job ads, screen candidates, create interview questions, summarize candidate data, etc. And they are getting smarter: PageUp recently announced Paige, which uses generative and agentic AI to support recruiters, from candidate sourcing to automating routine steps. Like other GenAI tools, it provides on-demand answers to queries, skills matching, resume summarization and content suggestions, but it also -- through agentic AI -- automates repetitive duties (e.g., filling fields, job creation workflows) and suggests next-best actions to speed up hiring.
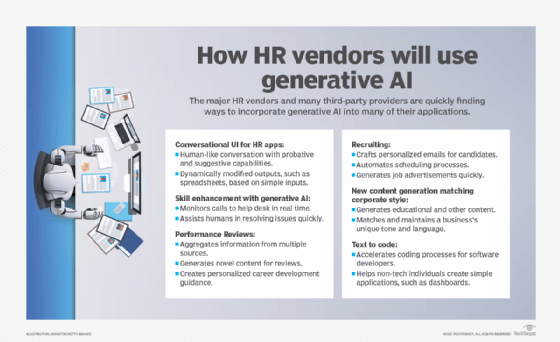
The rise of agentics
An AI agent is software that can understand goals, make decisions and take actions autonomously -- often across multiple steps and tools -- to achieve a desired outcome on the user's behalf. It interacts with its environment, collects data and uses the data to perform self-determined tasks to meet predetermined goals.
AI agents are action-oriented and interact with other agents. They analyze the collected data to predict the best outcomes that support the goals and then use the results to formulate the next action they should take.
The shift from assistive AI (e.g., suggesting templates or matching candidates) to agentic AI adds the following capabilities:
- Agents can interact directly with candidates.
- They can perform multi-step tasks without explicit human control at every step.
- They can integrate deeply with CRM, applicant tracking systems (ATSes) and other HR systems to orchestrate workflows from end to end.
Some AI agents learn over time; some don't. Learning is a design choice, not a requirement. In general, there are three types: static agents that follow rules but don't update themselves, agents that learn from explicit or implicit feedback, and agents that learn continuously. It's imperative to understand agent behavior in the products you buy.
In addition to vendors discussed below, companies with an increasingly strong agentic agenda include SpiderX AI, which focuses on multimodal, autonomous recruiting agents; Cielo, with agents tied to talent acquisition workflows; and Torre.ai, with agentic recruiting from sourcing to placement.
Top contenders for 2026
There are many ways to evaluate products and vendors, including breadth or depth of functionality, technology, price, global availability, the software's sophistication and complexity, the degrees of support and training provided and the vendor's reputation for integrity or eco-consciousness, among others. Key for any buyer is that the product -- with or without AI -- addresses all of the talent acquisition pain points that the organization faces.
Below is a review of products that merit consideration in 2026, chosen because they are from established vendors, they are comprehensive, or, in my judgment, they represent the best of today's leading edge. These products all tend to address the needs of at least three distinct user groups: candidates, recruiters and hiring managers, and already-hired employees.
Here is what you can expect from any competitive suite: support for sourcing, job posting, data parsing, candidate shortlisting or ranking, multichannel communications, career site and mobile device chatbots, and intuitive UIs geared to the respective needs of the candidate, hiring manager and recruiter. All deliver analytics relevant to their product scope. Expect AI-supported scheduling of interviews and follow-up conversations, along with immediate and totally automatic conducting of interviews without recruiter intervention. Many have extended their capabilities to current employees to meet the growing demand for career growth and mobility.
Look for agent-managed workflows and review the vendor's agentic AI roadmap for how it might meet your requirements. The goal here is not to cover every feature or function, but to differentiate products based on points of uniqueness or specific strengths and to present vendors in alphabetical order, not ranked.
Beamery
The Beamery suite covers talent acquisition, internal mobility and redeployment, skills analytics and workforce planning, and predictive talent pipelines. Last summer, Beamery launched its Workforce Intelligence Suite, which includes a Task Intelligence module that breaks down roles into tasks. According to Beamery, layering this capability with skills and market data enables HR leaders to build a digital organizational twin of their workforce, modeling how best to apply AI alongside people, as well as reskill and redeploy workers with precision to build a more adaptive organization.
For organizations transitioning to a skills-first approach, Task Intelligence provides the following capabilities:
- Role-to-task mapping. This function analyzes internal human capital management (HCM) systems, job descriptions and planning inputs to break complex roles into core tasks and the skills required to perform them.
- Enriched task-level intelligence. Combining internal data with real-time labor market signals enables companies to evaluate each task's demand, effort, skill requirements and automation potential.
- Automation opportunity analysis. This function identifies high-effort, high-frequency tasks that are strong candidates for automation or augmentation and estimates time as well as cost savings.
- Reskilling and redeployment pathways. This capability pinpoints business-critical tasks and matches them to available talent with the relevant skills.
- Scenario modeling with a digital organizational twin. Merging task-level data with Beamery's Skills Intelligence and Talent Market Insights modules enables leaders to simulate the impact of workforce changes before they act.
Beamery also uses AI to reveal skills gaps and critical role vulnerability, but the ability to combine real-time external labor market insights with internal HR data to forecast skill availability makes Beamery's latest offering stand out.
Last summer's announcement also included Ray, an AI assistant that provides contextual recommendations across sourcing, hiring, workforce planning and upskilling.
Eightfold AI Talent Intelligence Platform
Eightfold markets a talent intelligence platform that enables "holistic" talent strategies. Through its proprietary global data set of more than 1.5 billion talent profiles and skills, Eightfold's AI-native technology generates recommendations to help employers decide how and when to build, buy or borrow talent. It employs a skills-based framework that matches people to opportunities, including full-time, part-time, project and gig work. Eightfold uses that data to understand the availability, maturity, relevance, learnability and evolution of skills in specific organizations and throughout the global market.
Eightfold's Talent Design uses a skills-based approach to drive decision-making for upskilling, reskilling, hiring, staffing of contractors and attaining diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) goals. Additionally, Talent Design examines skill adjacency and context to determine what capabilities will be needed in the future as an organization grows. The platform also enables self-learning, data-driven updates that help to ensure consistent, unbiased evaluations of individual capabilities and the ability to learn against globally standardized job descriptions and requirements.
The Eightfold AI talent intelligence platform and accompanying suite of applications is available in 155 countries and 24 languages. One of the signature applications, Talent Management, enables employees to find reskilling and upskilling opportunities across courses, mentors and projects based on current skills and career aspirations. The goal of people developing their own skills and assuming responsibility for their career growth is addressed through curated opportunities for continuous learning. In addition, Talent Management includes capabilities for succession planning, helping organizations to better understand the potential of their workforce on a global scale and to guide individual employees toward further learning, skill development and career opportunities.
The other main module of the talent intelligence suite, Talent Acquisition, represents the original functionality that Eightfold AI focused on when it was founded in 2016. Eightfold Talent Acquisition provides functions for sourcing, CRM, applicant tracking -- e.g., requisition management, job distribution, offer management, etc. -- interview scheduling and more. Eightfold AI also introduced copilots that use GenAI to improve productivity and the user experience for candidates, employees and recruiters.
All in all, Eightfold's semi-agentic intelligence layer acts more as a brain for strong decision-making than an autonomous executor of action. As a bonus, the platform integrates with Workday, SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting, Oracle Taleo, Oracle Fusion Cloud Recruiting, Greenhouse and others.
Employ
Employ was created to consolidate the following recruiting products across different market segments, small business through enterprise:
- JazzHR typically focuses on the ATS needs of SMBs. It uses basic AI to streamline workflows like resume parsing, knockout questions and simple candidate profile summaries, and it provides automated candidate evaluations tied to job descriptions.
- Lever targets midmarket and growth companies focused on candidate engagement. Its differentiator is blending ATS with CRM automation. AI supports that two-way recruiting cadence.
- Jobvite is positioned as an end-to-end, enterprise-grade recruiting platform. It embeds AI across the entire hiring lifecycle, including sourcing, engagement, screening and interview processes.
These brands operate independently, with separate product lines and customer bases, but they share some core AI capabilities:
- Candidate fit scoring. All three can employ the Talent Fit feature to compare resumes to job descriptions using large language models and produce a fit score and guidance, purportedly without human bias.
- AI-driven screening and automation. Employ is rolling out "AI companions" for screening, interviewing and other functions, which can surface top talent and provide candidate feedback across platforms, starting with Lever and expanding to the others.
- Responsible AI governance. Employ's AI suite uses tools like IBM watsonx.governance for transparency and bias monitoring.
hireEZ
HCM software vendor hireEZ unveiled EZ Agent, a semi-autonomous agentic recruiting application built into its AI-first talent acquisition platform, to automate sourcing, screening, outreach, scheduling, analytics and other recruiting tasks while keeping human recruiters in control of strategic decisions. In addition to sourcing, search refinement and pipeline rebuilding, the agent can proactively make recommendations and execute workflow while keeping the recruiter in the approval loop for outreach and actions.
EZ Agent improves with each interaction, refining parameters and understanding recruiter preferences to enhance outcomes. Operating with contextual understanding enables it to make decisions and execute multi-step hiring processes without constant human input. For instance, it adjusts strategies in real time based on candidate engagement and recruiter feedback, and it actively manages workflows such as sourcing candidates, launching campaigns and screening applicants. Its ResumeSense feature flags inconsistencies in resumes and highlights key qualifications for recruiter review, maintaining both precision and transparency.
Other highlights of the hireEZ platform include the following:
- Generative AI for job descriptions. This function creates engaging, inclusive job descriptions tailored to attract diverse talent.
- Integration enhancements. Seamless synchronization with ATS platforms provides two-way data updates, eliminating the need to switch systems during recruiting.
- Text campaigns. hireEZ's texting feature, described as the "dating-app swipe" of recruiting, offers direct, high-stakes communication to stand out in competitive markets.
iCIMS
iCIMS offers an enterprise-grade recruiting platform with embedded, end-to-end AI designed to help organizations hire more efficiently while maintaining transparency, control and compliance. iCIMS AI is built to support human decision-making, with a strong emphasis on responsible, explainable AI use across the hiring lifecycle.
Key capabilities include the following:
- AI-driven candidate matching and ranking. iCIMS AI analyzes candidate profiles across applicants, internal talent and past candidates to surface strong-fit matches while providing recruiters visibility into how recommendations are generated. AI outputs are designed to inform decisions, not replace them.
- Agentic AI sourcing with recruiter oversight. The platform can automatically search internal databases to rediscover qualified candidates while ensuring recruiters retain control over outreach and selection decisions.
- Generative AI to support recruiter workflows. Recruiters can use natural-language prompts to generate job descriptions, interview questions, candidate communications and search queries, helping teams reduce manual work without sacrificing quality or consistency.
- AI-enabled career site optimization. The platform can automatically generate SEO-friendly job content and translate career-site experiences into multiple languages, expanding reach while maintaining consistency across regions.
- Built-in responsible AI framework. iCIMS applies formal responsible AI principles focused on transparency, bias mitigation, auditability and human-in-the-loop decision-making, helping organizations adopt AI in recruiting while meeting ethical and regulatory expectations.
iCIMS is designed for large and complex organizations that require a scalable recruiting platform where AI improves speed and efficiency without compromising trust, compliance or human judgment. It was ranked No. 1 in ATS market share by Apps Run the World.
Oracle
Oracle is very likely the leader in overall enterprise-wide agentic AI at this writing. The agent roster includes job discovery, job fit advisor and interview management agents for internal mobility and recruiting; team sync advisor, team goals assistant, learning tutor and talent advisor agents in skilling and career development; and employee lifecycle policy analyst, succession planning advisor and payroll run analyst agents.
As an example, Oracle Career Coach is an AI-powered capability in Oracle Fusion Cloud Recruiting designed to deliver a more personalized, intelligent candidate experience using agentic AI that works across the Oracle Fusion Cloud HCM suite to analyze candidates' skills, experience and interests -- in both internal and external talent pools -- to surface stronger job matches. This technology is expected to help organizations improve applicant quality, increase candidate engagement and give hiring teams deeper, data-driven talent insights.
Oracle introduced the following new agents in the past year:
- Job applicant screening, which lets users ask questions about an applicant's profile, including feedback responses and scores, lifecycle information, prior actions taken, authenticity detection, assessment and background check information.
- Interview management, which automates interview scheduling by coordinating interviewer availability, managing calendar invitations, resolving conflicts and sending reminders to candidates and interviewers.
- Job requisition analyst, which supports hiring managers by answering general and role-specific questions as well as providing guidance during job requisition creation.
The agents all run on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and are integrated into Oracle Fusion Cloud HCM workflows at no additional cost. Oracle was named the highest-ranked vendor for the extended AI innovations use case in Gartner's 2025 "Critical Capabilities for Talent Acquisition (Recruiting) Suites" report.
Phenom Applied AI
Phenom delivers an AI infrastructure built specifically for HR, covering talent acquisition, talent management and workforce intelligence. The company's approach centers on AI that adapts to each organization's industry context, regulatory requirements and the distinct needs of knowledge workers and frontline teams. It was named a top AI company of 2025 by Software Magazine.
Rather than repurposing generic enterprise technology for HR, Phenom has developed its own AI-native infrastructure over the past decade. This foundation powers a unified experience from hire to retire, with proprietary ontologies that account for industry-specific nuances -- recognizing, for instance, that hiring nurses requires fundamentally different approaches than developing engineers or retaining retail associates.
The vendor's deeply refined skills ontology helps HR teams identify and fill skills gaps, aids managers in designating successors and driving career progression, and assists employees in discovering personalized advancement opportunities. This intelligence extends into talent acquisition and across the full talent lifecycle: sourcing, screening, onboarding, development, internal mobility and retention.
The platform integrates with recruiting workflows, enabling talent teams to match candidates to open roles internally or externally. By automating tasks like candidate sourcing, screening and scheduling, the system can potentially accelerate hiring while improving candidate experiences. Process mining capabilities surface optimization opportunities to improve conversion rates and hiring quality.
Phenom X+ Agents represent the company's approach to more intelligent automation. Rather than simply analyzing data or completing tasks, these agents are specialists designed to work alongside HR teams and actively execute detailed workflows across the talent lifecycle. They handle complex processes autonomously while still under human supervision, sourcing passive candidates, conducting initial screenings through conversational AI, managing interview scheduling with real-time calendar coordination and providing recruiters with AI-generated interview guides that help reduce potential biases. After the interview, agents deliver summaries that flag relevant details based on job requirements and can detect inconsistent candidate responses.
For high-volume frontline hiring, agents enable end-to-end automation where candidates search for jobs, apply, complete assessments built by Phenom's industrial-organizational psychologists, submit videos and schedule interviews -- all via chatbot or SMS, freeing recruiters to focus on evaluation and final hiring decisions. For knowledge worker roles requiring more customized engagement, agents adapt to provide tailored candidate experiences while giving recruiters AI-driven analysis during evaluation.
New capabilities announced in late 2025 demonstrate how Phenom seeks to connect business strategy to talent execution. Enterprise Talent Optimization & Work Redesign uses AI-driven task intelligence to analyze roles at the task level, revealing automation opportunities while connecting employee development to company objectives. Frontline Workforce Lifecycle & Shift Scheduling moves beyond traditional app-based experiences into an agentic, conversational model that handles shift scheduling with built-in compliance, dynamic optimization and internal mobility integration.
Its Unified Orchestration Engine introduces adaptive intelligence that handles exceptions in real time, combining decision engines with simulations and human-in-the-loop governance. When automation encounters exceptions -- such as a manager not showing up for an interview, resume-parsing failures or compliance rules needing enforcement -- the agents identify bottlenecks, create alternative pathways and maintain workflow momentum while preserving policy compliance and explainability.
This approach reflects Phenom's focus on building an infrastructure that learns each organization's specific patterns and applies that understanding throughout the talent lifecycle. The goal is shifting HR teams from operational tasks to strategic decisions, with AI handling administrative work while recruiters and managers bring their expertise to candidate evaluation and hiring choices.
SeekOut
SeekOut provides an AI-powered talent search engine to help recruiters quickly find and hire the most qualified passive candidates. Recruiters can use natural- language prompts instead of writing complex Boolean logic -- e.g., "find senior Python engineers in Austin with AWS experience." This makes sourcing more intuitive, and the AI creates precise search criteria from job descriptions or descriptions of ideal candidates and matches them to relevant profiles.
In addition to the generative AI common in today's applications, SeekOut Spot uses agentic AI combined with human expertise to automate candidate research, outreach, screening and engagement at scale, delivering qualified candidates faster than manual sourcing alone. AI-guided workflows help teams go from job description to search, shortlist and engagement, with intelligent recommendations at each step.
SeekOut's AI supports talent mobility by uncovering internal candidates and recommending career pathways. AI insights and workflows tie directly into existing applicant tracking and HR systems.
SeekOut's ability to locate and screen tech talent should be a draw for organizations that need technologists. With SeekOut's GitHub search, the app can provide and review code to better evaluate a potential applicant's technical prowess.
Workday
All the major contenders in the HCM market have integrated their own AI capabilities while considering build-or-buy decisions. Workday's decision to acquire Paradox, AI-native HiredScore, and document intelligence platform Evisort enabled it to augment its recruiting, expenses, succession and Workday optimize agents.
The recruiting agent, for example, uses HiredScore AI to identify the most qualified candidates from both new applications and past talent pools. Since the Paradox acquisition closed on October 1, 2025, Workday has added two applications to its growing suite of AI offerings: Workday Paradox candidate experience agent and Paradox conversational ATS, both available through Workday for new and existing customers.
Bringing HiredScore and Paradox into the Workday ecosystem connects the different stages of hiring into one coordinated process. HiredScore helps recruiters identify and prioritize the best-qualified candidates for a role. Paradox provides a conversational candidate experience to streamline hiring tasks such as answering candidate questions and scheduling interviews. These capabilities then feed directly into the Workday Recruiting module, which manages the final hiring and onboarding. This approach removes the need for disconnected tools and helps organizations manage everyone from frontline hourly workers to corporate professionals in a single system.
Another tool, Workday Assistant, offers AI-powered, role-specific support to employees. It provides quick answers to HR questions and is accessible from any device. It also helps employees take faster action, offering company-specific guidance to complete complex tasks.
Remember that AI is just another tool
Today's AI-grounded tools cover every aspect of talent acquisition, including recruitment marketing, sourcing, job description management, candidate assessment and pre-screening. They also recommend positions within an organization to qualified applicants, generate offer and rejection letters, perform skills assessments, and provide career and learning assistance and direction -- all with far more sophisticated analytics than was available in the past.
As a tool in today's recruiting and hiring products, AI is inescapable, but its forms vary within every chatbot, GenAI, copilot and agentic AI product on the market. And with compliance, bias, privacy and security risks increasing with each new advance in the technology, remember that the best product for you is not necessarily the one that ticks the most AI boxes.
Finally, remember you are not buying a risk-free AI product; it is solely an underlying technology to help address the primary recruiting issues the organization faces. Buyers are responsible for the AI recruiting tool's transparent and ethical use.
Katherine Jones is an independent market analyst and consultant. She was an analyst at the Aberdeen Group and Bersin by Deloitte and partner at Mercer following a career in high-tech companies and higher education.







